JEE Main Updated Syllabus 2025: Download The Subject-wise PDF












FAQs on JEE Main Syllabus 2025 (Released)
1. Does the JEE Main 2025 Syllabus Include Topics Beyond the NCERT Curriculum?
Yes, the JEE Main syllabus may include topics beyond the NCERT curriculum. It is advisable to refer to additional resources to cover these topics effectively.
2. How Can I Access the Detailed JEE Main2025 Syllabus?
The detailed JEE Main syllabus can be accessed through official websites or Vedantu's sources. Regularly referring to the syllabus will help you stay on track during your preparation.
3. Is the JEE Main 2025 Syllabus the Same for Both Paper 1 and Paper 2?
Paper 1 is for students who want to pursue a career in engineering, while Paper 2 is for students who want to pursue a career in architecture or planning. The Mathematics syllabus for both papers is almost the same, but there are a few minor differences. The Aptitude Test and Drawing sections are only for Paper 2.
4. What are the important topics in the JEE Main Syllabus 2025?
The important topics in the JEE Main Syllabus 2025 vary depending on the subject. However, some of the most important topics include
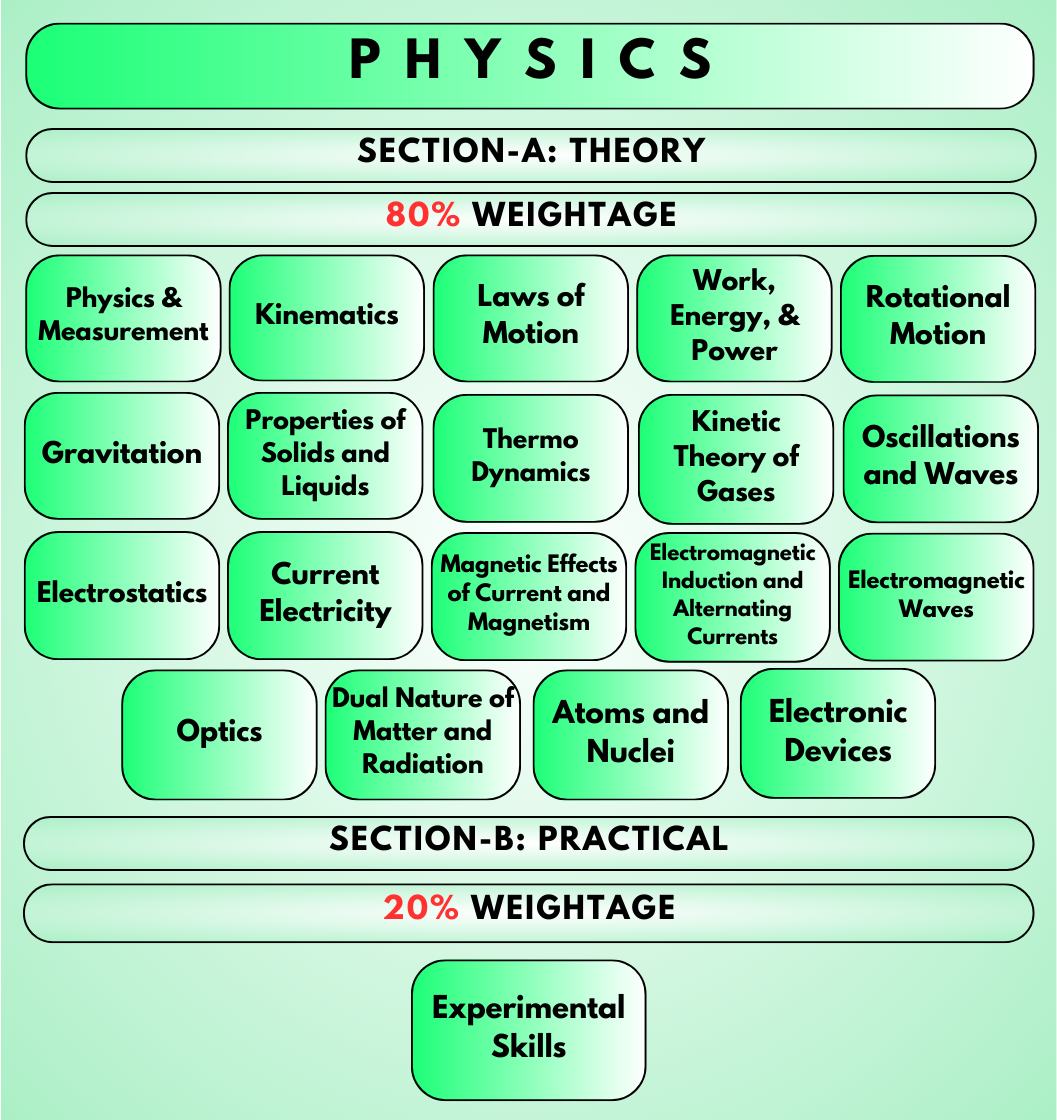
Physics: Energy and Power, 2D Motion, Logic Gates, Physical quantities in kinematics, Newton's 2nd and 3rd Laws of Motion, Properties of solids, Electromagnetic Waves and their properties, Wave nature of matter, Communication Systems.
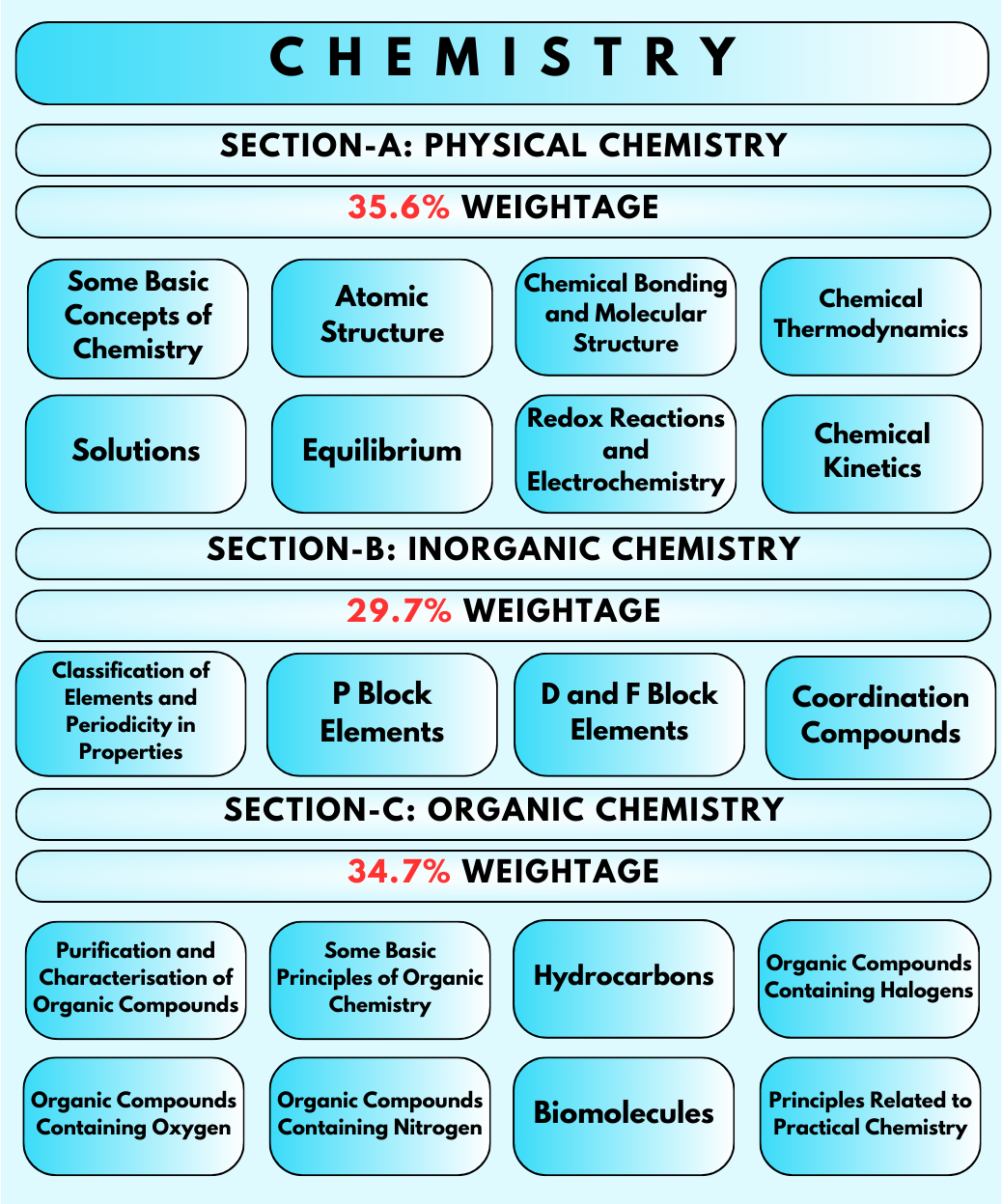
Chemistry: The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory, Chemical reactions of aldehydes and ketones, Properties of amines, Bonding in coordination compounds, Proteins, Nernst Equation, Some important compounds of calcium, General properties of the transition elements, Systematics Qualitative Analysis, Solutions.
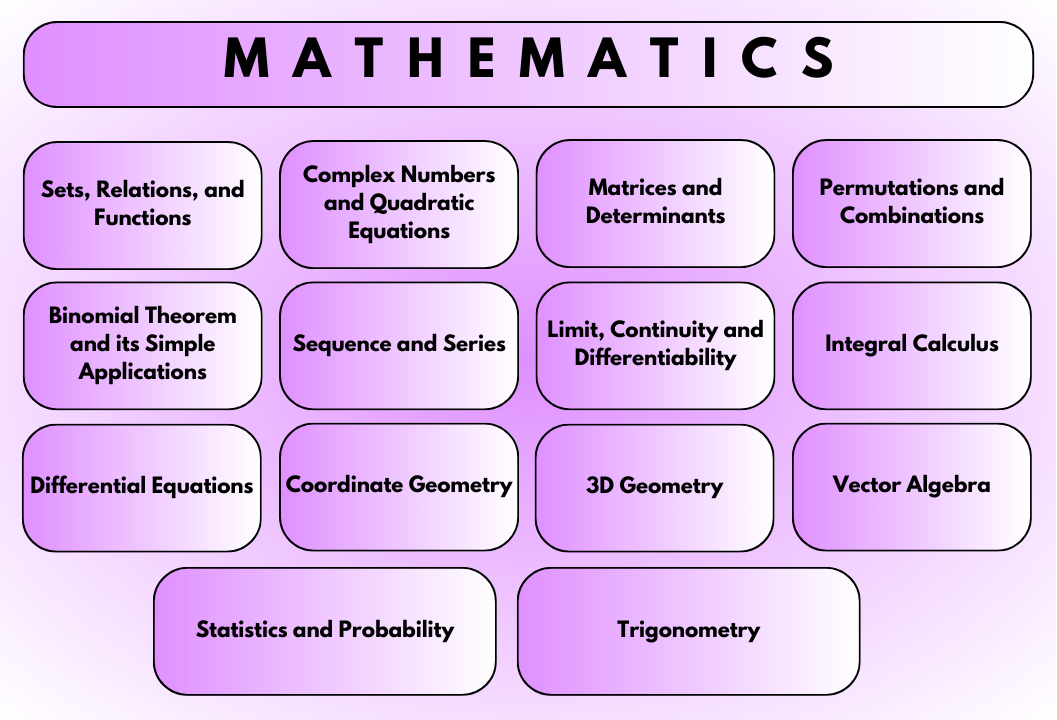
Mathematics: System of Simultaneous Linear Equations, Definite Integral, Differential equations, Analysis of Coefficients of Binomial Expansion, Summation By Sigma Operator, Area, Statistics, Scalar and Vector Product of Vector Algebra, Line.
In addition to the topics already covered, the following topics are also important for the JEE Main April 2025 Paper 1 (Session 2).
5. What are the changes in the JEE Main Syllabus 2025?
The JEE Main Syllabus 2025 has been revised to include some new topics and to remove some outdated topics. The revised syllabus is more in line with the syllabus of the IIT JEE Advanced exam. Refer to Vedantu’s JEE Main Syllabus 2025 to get updates regarding the syllabus.
6. What are the best books for the JEE Main Syllabus 2025?
Some of the best books for the JEE Main Syllabus 2025 are:
NCERT textbooks for Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics.
Cengage Physics by G. T. Iyengar.
Physical Chemistry by O. P. Tandon.
Organic Chemistry by Morrison and Boyd.
Calculus by Thomas and Finney.
8. Are there any changes made to the JEE Main 2025 syllabus?
Yes, NTA did change the JEE Main 2025 syllabus. You can find the JEE Main 2025 syllabus PDF along with the weightage of each chapter for FREE on Vedantu's official website.
9. Is JEE Main 2025 syllabus reduced?
Yes, the JEE Main 2025 syllabus is reduced, with about 25% of the syllabus removed. This is especially true for the Mathematics and Physics syllabus. The Chemistry syllabus has been reduced to a lesser extent.