




How to Draw and Interpret the PBr3 Lewis Structure
In PBr3, phosphorus has five valence electrons in its valence shell, out of these five electrons, three form sigma bonds with three bromine atoms and two electrons remain on the phosphorus atom as a lone pair of electrons. Hence, the hybridization of PBr3 is sp3 and the geometry will be trigonal pyramidal due to the presence of a lone pair of electrons on the central atom. Since the geometry is asymmetrical, the molecule will be polar. PBr3 has 26 valence electrons of which bromine atoms can consume eight each in bonding pairs and two electrons in lone pairs on phosphorus. In the Lewis structure of PBr3, the formal charge on the terminal bromine atom is zero.
Lewis Structure of PBr3
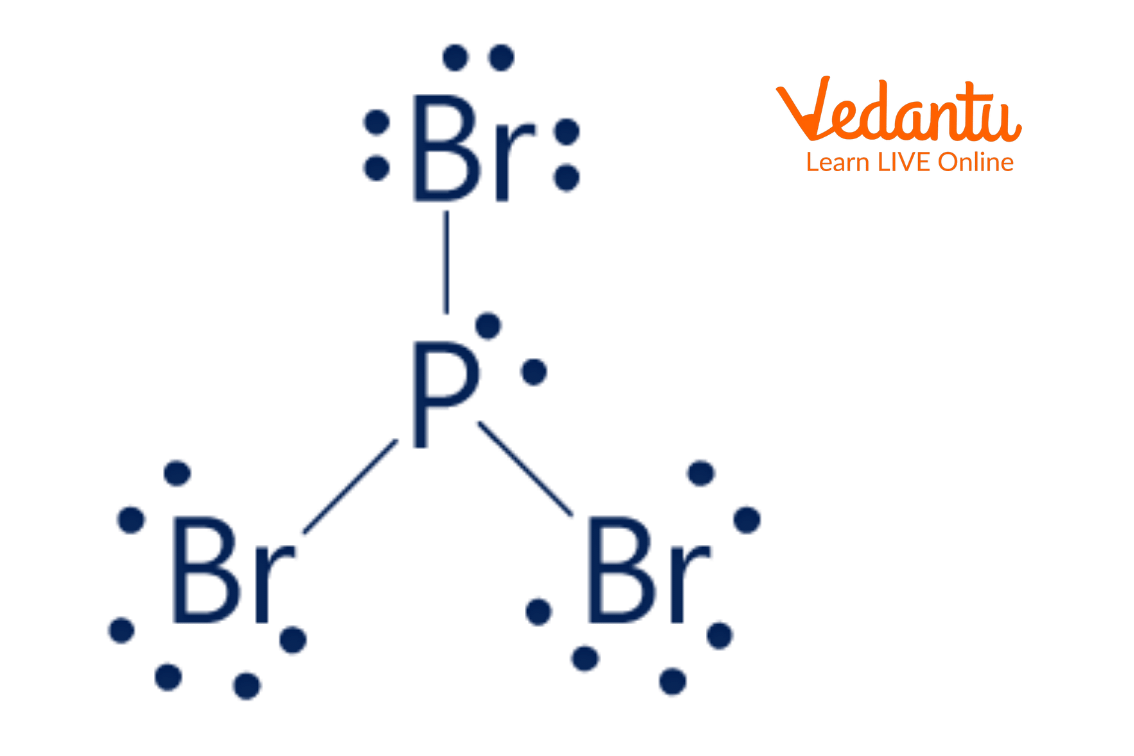
The Lewis structure of PBr3 contains three sigma bonds between phosphorus and three bromine atoms. The phosphorus is at the centre and it is surrounded by bromine atoms. The phosphorus has one lone pair of electrons and bromine atoms have three lone pairs of electrons. The hybridization of PBr3 is sp3. Hence, the electron geometry will be tetrahedral because the phosphorus atom has one lone pair and three bonded pairs with bromine atoms. So, there are four regions of electron density around the central atom. But it has a trigonal pyramidal shape or geometry due to the presence of lone pairs on the central atom. The Lewis structure of this molecule is given below.
Lewis Structure of PBr3
The above image shows the Lewis structure of PBr3. Phosphorus is attached to three bromine atoms by sigma bonds and one lone pair can be seen on the phosphorus atom.
Phosphorus Lewis Structure
The atomic number of the phosphorus atom is 15 and the electronic configuration is as follows: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
It is clear from the electronic configuration that phosphorus has five valence electrons. Hence, the Lewis dot structure of phosphorus can be drawn by showing electrons on phosphorus atoms as dots. The Lewis dot structure of phosphorus is as follows:
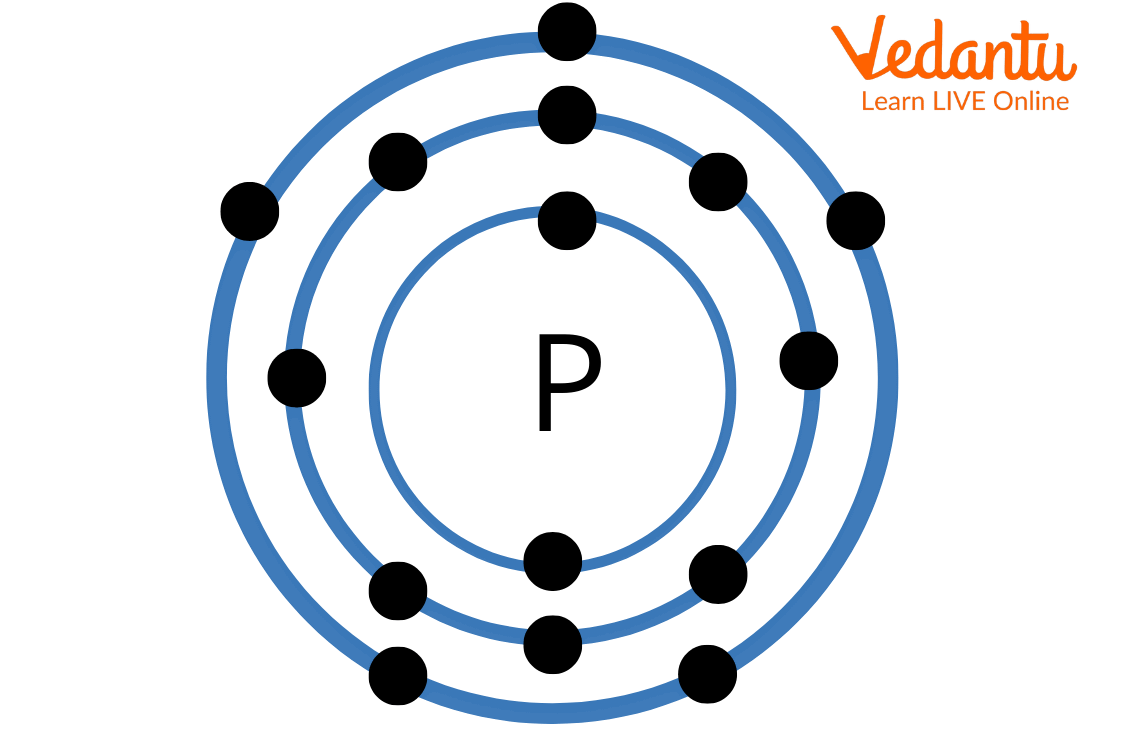
Lewis Structure of Phosphorus
Above image is the Lewis structure of phosphorus. It can be seen that there are five electrons on the Phosphorus atom.
Bond Angle of PBr3
The bond pair-bond pair repulsion increases more than the lone pair-bond pair repulsion when going down a group. So, due to bond pair-bond pair repulsion, the bromine bond angle is more than chlorine.
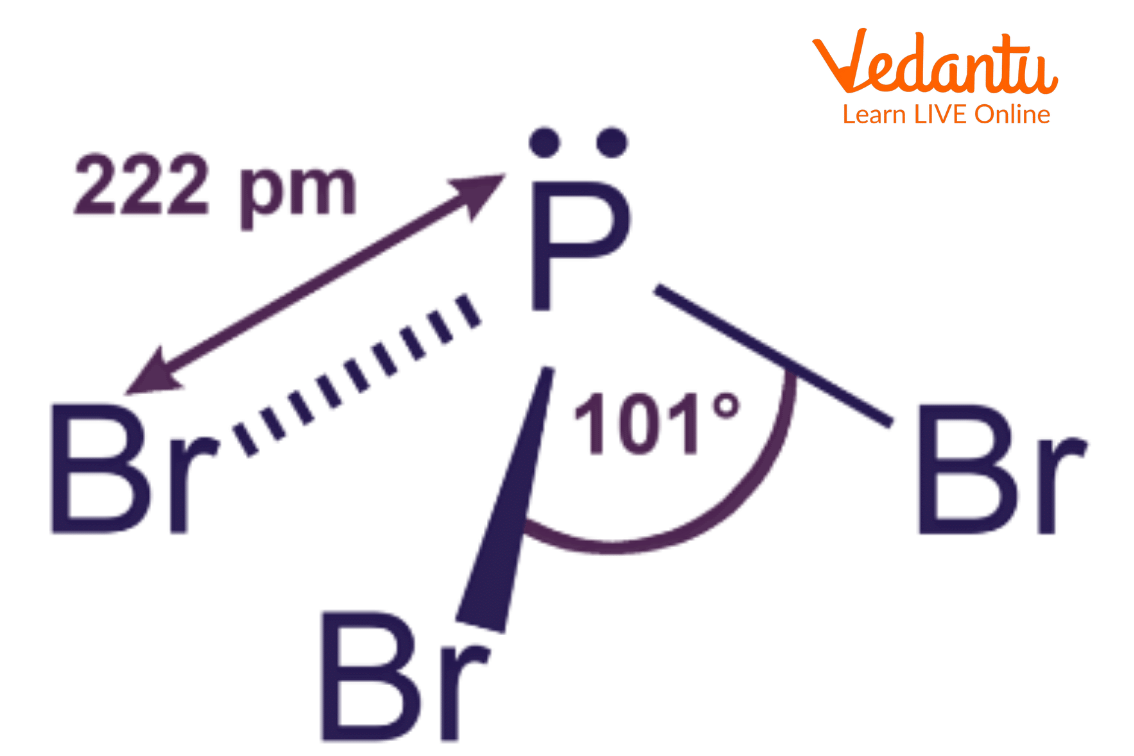
Since PBr3 is formed by a trigonal pyramidal geometry. The bond angle between Phosphorus and each bromine atom will be 101 degrees.

Bond Angle in PBr3
The above image shows the bond angle between phosphorus and bromine atoms which is 101 degrees in phosphorus and each bromine atom.
PBr3 Name
The name of PBr3 is phosphorus tribromide or tribromo phosphine.
PBr3 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry
For PBr3, the central atom is phosphorus, three bromine atoms form bonds with it and it has one modified shape to trigonal pyramidal geometry. The molecular geometry of lone pairs of electrons give rise to an sp3 hybridization and form tetrahedral geometry.
Trigonal pyramidal geometry is also shown by molecules which have four atoms or ligands. The central atom will be the apex and three other atoms or ligands will be at one base, where they are in the three corners of the triangle. There is one lone pair of electrons on the central atom.
Lewis Dot Structure of PBr3
In the Lewis dot structure of PBr3, the phosphorus atom has a total of eight electrons. Six electrons are shared between phosphorus and each bromine atom and the remaining two electrons are present on phosphorus atoms as lone pairs of electrons. Each bromine atom has three lone pairs of electrons and two shared electrons between phosphorus and bromine.
Lewis Dot Structure of PBr3
The above image is the Lewis structure of PBr3. In the structure, the phosphorus atom is bonded with three bromine atoms and has a lone pair.
Key Features of Lewis Structure of PBr3
Lewis structures extend the concept of the electron dot structure by adding lines between atoms to represent shared pairs in a chemical bond.
Trigonal pyramidal geometry results from tetrahedral electron pair geometry when a lone pair is present on the central atom.
The Lewis structure PBr3 has trigonal pyramidal shape according to its molecular geometry and tetrahedral shape according to its electron geometry.
The trigonal pyramidal molecule is symmetrical about the central atom.
For trigonal pyramidal geometry, the bond angle is slightly less than 109.5 degrees.
FAQs on Lewis Structure of PBr3 Explained
1. What is the Lewis structure for Phosphorus Tribromide (PBr3)?
The Lewis structure of Phosphorus Tribromide (PBr3) features a central Phosphorus (P) atom connected by single covalent bonds to three Bromine (Br) atoms. The central P atom also has one lone pair of electrons. Each of the three peripheral Bromine atoms is shown with three lone pairs of electrons, which completes the octet for all atoms in the molecule.
2. How many total valence electrons are there in PBr3 for drawing its Lewis structure?
To calculate the total number of valence electrons for PBr3, you sum the contributions from each atom:
- Phosphorus (P), being in Group 15, contributes 5 valence electrons.
- Bromine (Br), being in Group 17, contributes 7 valence electrons.
- Since there are three Bromine atoms, their total contribution is 3 × 7 = 21 valence electrons.
3. What is the hybridization of the central Phosphorus atom in PBr3?
The central Phosphorus atom in PBr3 undergoes sp³ hybridization. This is determined by counting the electron domains around it: three sigma bonds with Bromine atoms and one lone pair of electrons. The total of four electron domains (3 bonding pairs + 1 lone pair) requires four hybrid orbitals, which corresponds to an sp³ hybridization scheme.
4. Why is the PBr3 molecule considered polar?
PBr3 is a polar molecule because of two key factors: 1) The P-Br bonds are polar due to the electronegativity difference between Phosphorus (2.19) and Bromine (2.96). 2) The molecule has an asymmetrical trigonal pyramidal shape. This asymmetry, caused by the lone pair on the phosphorus atom, prevents the individual bond dipoles from cancelling each other out, leading to a net molecular dipole moment.
5. What is the important difference between the electron geometry and molecular geometry of PBr3?
The primary difference is the treatment of lone pairs:
- Electron Geometry describes the arrangement of all electron domains (both bonds and lone pairs). For PBr3, with four domains (3 bonds, 1 lone pair), the electron geometry is tetrahedral.
- Molecular Geometry describes the arrangement of only the atoms. Since the lone pair is not 'seen' in the final shape, the arrangement of the P and Br atoms results in a trigonal pyramidal shape.
6. Why is the Br-P-Br bond angle in PBr3 smaller than the ideal tetrahedral angle of 109.5°?
The bond angle in PBr3 is approximately 101°, which is less than the 109.5° of a perfect tetrahedron. According to VSEPR theory, the repulsion from the single lone pair on the central phosphorus atom is stronger than the repulsion from the bonding pairs. This increased lone pair-bond pair repulsion pushes the three P-Br bonds closer together, compressing the angle between them.
7. Does the PBr3 molecule follow the octet rule?
Yes, the Lewis structure of PBr3 fully satisfies the octet rule for all its constituent atoms. The central Phosphorus atom achieves a full octet with three bonding pairs (6 electrons) and one lone pair (2 electrons). Each of the three Bromine atoms also achieves a stable octet with one bonding pair (2 electrons) and three lone pairs (6 electrons).
8. How does VSEPR theory explain the final shape of the PBr3 molecule?
The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory explains the shape of PBr3 by minimizing electron repulsion. Its application involves:
- Identifying that the central P atom has 4 electron domains (3 bonding pairs, 1 lone pair).
- This gives PBr3 a VSEPR notation of AX₃E₁.
- The four domains arrange themselves in a tetrahedral electron geometry to be as far apart as possible.
- However, since one domain is a non-bonding lone pair, the resulting shape defined by the atoms (the molecular geometry) is trigonal pyramidal.
























