




An Overview of Class 12 Biology Identification Disease Causing Organisms Symptoms Diseases Experiment
Not all organisms around the globe are beneficial for humans. Some are essentially harmful as they possess a grave threat to the optimal functioning of the human body including being potentially fatal too. These microbes that have the capacity to cause diseases are known as pathogens. Some common disease-causing organisms like Ascaris, Entamoeba, Plasmodium, and Ringworm exhibit some distinct features which help in their identification. The diseases caused by these organisms have particular symptoms as well.
Table of Contents
Aim of the experiment
Apparatus required
Theory
Procedure
Observations
i) Characteristic features
ii) Systematic position
iii) Symptoms
Results
Precautions
Lab manual questions
Viva questions
Practical based questions
Summary
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Aim
To observe and study permanent slides to identify the disease-causing organisms like Ascaris, Entamoeba, Plasmodium, and Ringworm and the symptoms of the disease.
Apparatus required
i) Permanent slides, Preserved specimens, or Photographs of Ascaris, Entamoeba, Plasmodium, and Ringworm
ii) Compound Microscope
Theory
The number of parasitic and pathogenic organisms (i.e. disease-causing) in humans is quite high. The human body is severely harmed by these organisms, bringing illnesses that often lead to diseases. These diseases may even be life-threatening. The external morphology of these organisms demonstrates distinct characteristics. The diseases they induce have particular symptoms as well.
Procedure
Carefully observe the features visible in a preserved specimen of Ascaris as it is of sufficient size to be visible to the naked eye. Note down the findings.
Observe the permanent slides of Entamoeba, Plasmodium, and Ringworm under the compound microscope as they are not easily visible to the naked eye. Initially, observe under low power magnification and then shift to high power magnification view. Write down the features visible.
Draw neat and clean diagrams of the pathogens and label them correctly.
Observations
Ascaris
i) Characteristic Features:
It has an unsegmented, long, and cylindrical body.
Sexes are separate and distinct. Females are longer than males in size.
The mouth is visible on the anterior end and it is encircled by three lips-like structures. These lips are not visible clearly to the naked eye and are viewed using a magnifying glass. One of the lips is located mid dorsally and the other two lips are present ventrolateral.
Both the posterior and anterior ends are pointed. The posterior tip in males is curved slightly.
Along the length of the body, there are single longitudinal lines on the dorsal, ventral, and two lateral sides. In comparison to the other lines, the lateral lines are somewhat more defined and distinct.
There is an excretory pore on the ventral surface, just behind the anterior end.
The male worm possesses a pair of penial spicules right next to the cloacal aperture.
A female genital aperture can be seen in the female specimen mid-ventrally at about one-third of the distance from the anterior end.
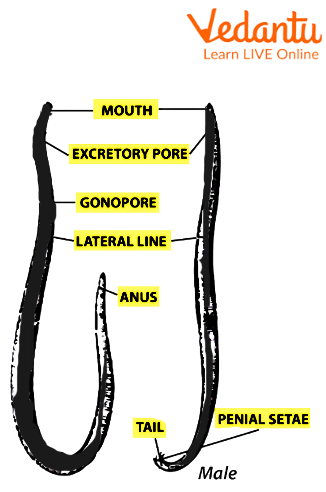
Structure of a male ascaris
ii) Systematic Position:
Phylum- Aschelminthes
Class- Nematoda
Type- <i>Ascaris lumbricoides</i>
Disease caused by Ascaris lumbricoides or roundworms- Ascariasis
iii) Symptoms:
Abdominal discomfort and pain
Swelling in the abdominal region
Nausea and vomiting
Fatigue
Entamoeba
i)Characteristic Features:
It is unicellular with protruding finger-like structures called pseudopodia which is responsible for its irregular shape.
It consists of a single nucleus which is eccentrically positioned inside the cell.
*A peripheral ring of nucleoprotein granules and a central karyosome can be seen in the nucleus. The remaining area of the nucleus appears to be empty.
In the cytoplasm, a few food vacuoles could be seen.
*There might be mature quadrinucleate cysts.
There are no contractile vacuoles.
*Distinctive feature of the pathogen
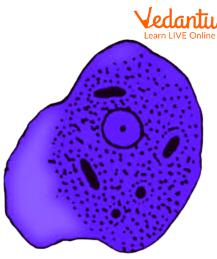
Structure of Entamoeba
ii) Systematic Position:
Phylum- Protozoa
Class- Rhizopoda
Type- Entamoeba histolytica
This is an intestinal parasite (a pathogen that resides in the intestines of humans).
Disease caused by Entamoeba histolytica- Amoebic dysentery
iii) Symptoms:
Diarrhoea (Frequent, loose, mucous-filled watery stools)
Pain in the abdominal region
Spasms
Nausea and vomiting
Plasmodium
i) Characteristic Features:
It is a unicellular endoparasite and can be seen in the red blood cells of an infected person.
The signet ring stage of the parasite in the erythrocyte, where it manifests as a rounded body, is the most diagnostic.
The cell contains a sizable vacuole within and the nucleus is present where the cytoplasm is concentrated.
The parasite appears as a ring due to the aforementioned features.
ii) Systematic Position:
Phylum- Protozoa
Class- Sporozoa
Type- Plasmodium vivax
Disease caused by Plasmodium vivax- Malaria
Note:
When a healthy individual gets bitten by the female anopheles mosquito, they develop a risk of infection to malaria. At that moment, the infected stage of the pathogen Plasmodium vivax, sporozoites, gets released into the peripheral blood vessels of the person and starts flowing through the bloodstream. The infective stage multiples repeatedly in the liver and erythrocytes.
iii) Symptoms:
Chills and a high temperature that periodically returns
Periods of excessive perspiration follow the chills
Headache and muscle ache
Fatigue
Nausea and vomiting
Ringworm
i) Characteristic Features:
It is a fungus that feeds on the keratin on the human skin.
Hyphae have a waxy, smooth, or cotton-like texture.
Unstained hyphae have distinct colours such as white, reddish-brown, or yellowish-brown.
ii) Systematic Position:
Kingdom- Fungi
Class- Deuteromycetes
Type- Trichophyton rubrum
Ringworm causes a fungal infection and it is communicable.
iii) Symptoms:
Skin is itchy and scaly (having sharp edges).
Red and raised patches are present in the infected areas of the skin.
The patches form a ring structure as they are redder in the periphery than in the centre.
Results
We can conclude that all disease-causing organisms have their distinctive external features. The symptoms of the diseases they cause are also specific.
Precautions
Handle the specimens and slides with care to avoid breakage.
Make sure the slides are placed in the correct position for observation under the microscope.
To prevent contamination of the slides, always hold them by the sides and not in the middle.
Always make sure to observe under low magnification at first and then move on to high magnification if it is not visible.
Lab Manual Questions
1. How long does Ascaris spend incubating outside of the human body?
Ans: The duration of incubation in Ascaris outside the human body is 6.
2. What is the genus of Plasmodium?
Ans: The genus of Plasmodium is Protozoans.
3. What is the kingdom of Ringworm?
Ans: The kingdom of Ringworm is Fungi.
Viva Questions
1. What is the infectious stage of plasmodium in the human host?
Ans: The infectious stage of plasmodium in the human host is sporozoites.
2. What is a pathogen?
Ans: Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms.
3. Are all microorganisms pathogenic?
Ans: No. Some microorganisms are helpful in our day-to-day life.
4. What is the location where Entamoeba histolytica stays in the human body?
Ans: They are located in the walls of large intestines.
5. What is the difference between a parasite and a pathogen?
Ans: A parasite is an organism that lives on or in another organism of a different species. An organism that lives on or in another organism of a different species is known as a parasite.
6. What is the common name of Ascaris lumbricoides?
Ans: The common name of Ascaris lumbricoides is roundworm.
7. What is the pathogen and carrier of malaria?
Ans: Plasmodium is the pathogen and the vector Anopheles stephensi (female) is the carrier of malaria.
8. What is the name of the disease caused by Entamoeba histolytica?
Ans: The disease caused by Entamoeba histolytica is Amoebic dysentery.
Practical-Based Questions
1. What is the correct method to hold prepared or permanent slides to avoid contamination?
Right in the middle
By the sides
Inverted
It does not matter which method is used to hold the slides.
Answer- B. By the sides
2. In the case of which of the following organisms, is there no need for a microscope to observe its features?
Ascaris
Entamoeba
Plasmodium
Ringworm
Answer- A. Ascaris
3. What does the body of Ascaris lumbricoides look like?
Long
Cylindrical
Unsegmented
All of the above
Answer- D. All of the above
4. Which sex among the Ascaris has the larger size?
Male
Female
Both have almost the same size
There are no different sexes
Answer- B. Female
5. What is the number of nuclei present in the cysts of Entamoeba?
Five
Three
Four
Two
Answer- C. Four
6. Which of the following best describes the appearance of a plasmodium parasite?
Ring
Flattened sac like
Cylindrical
String like
Answer- A. Ring
7. Which of the following gives a better description of the microbe nature of Ringworm?
Amoeba
Bacteria
Virus
Fungi
Answer- D. Fungi
8. In which of the following places Plasmodium is not found?
Latin America
Europe.
Asia
Some parts of Africa.
Answer- D. Some parts of Africa.
Summary
Several organisms are pathogenic (i.e., able to inflict sickness on people) and parasitic. These organisms seriously harm the human body and frequently cause diseases by infecting people with illnesses. These illnesses might be fatal. These species' outward morphology reveals various traits. They also cause illnesses that have specific symptoms.
FAQs on Class 12 Biology Identification Disease Causing Organisms Symptoms Diseases Experiment
1. What are some important identifying features of Ascaris lumbricoides that are expected to be mentioned in the Class 12 Biology practical exam?
For the 2025-26 CBSE practical exam, you should identify Ascaris by its long, cylindrical, unsegmented body. Key features to mention include:
- Sexual dimorphism: The female is longer than the male.
- Posterior end: The male has a curved posterior end, while the female's is straight.
- Mouth: A terminal mouth surrounded by three lips is present at the anterior end.
2. How can one differentiate between a male and a female Ascaris specimen during spotting?
The primary difference is size, with the female being distinctly longer than the male. Additionally, the posterior end of the male Ascaris is curved ventrally, and it possesses a pair of penial spicules near the cloacal aperture, which are absent in the straight posterior end of the female.
3. For the practical exam, what is the causative agent of Amoebic dysentery and where is it located in the human body?
The causative agent is the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. It primarily resides in the wall and lumen of the large intestine of humans. A key identifying feature under the microscope is its irregular shape with pseudopodia and a single nucleus.
4. What is the "signet ring stage" and which pathogen is it a diagnostic feature of?
The signet ring stage is a key identifying feature of the malarial parasite, Plasmodium vivax, seen inside an infected human's Red Blood Cell (RBC). In this stage, the parasite's cytoplasm is pushed to the periphery by a large vacuole, and the nucleus is situated at one pole, making it resemble a ring. This is a crucial observation for spotting in the board practical.
5. What are two common symptoms of Ringworm infection and what type of organism causes it?
Ringworm is caused by a fungus (e.g., Trichophyton), not a worm. Two important symptoms to note are:
- The appearance of dry, scaly, and itchy lesions on the skin, nails, or scalp.
- These lesions are often raised and form reddish patches that are clearer in the centre, creating a ring-like appearance.
6. Why is the absence of a contractile vacuole an important identifying feature for a parasitic protozoan like Entamoeba histolytica?
Entamoeba histolytica lives in the human large intestine, which is an isotonic environment relative to the parasite's cytoplasm. A contractile vacuole's function is osmoregulation – to actively pump out excess water that enters the cell in hypotonic (freshwater) environments. Since there is no significant net influx of water into the parasite in the intestine, a contractile vacuole is unnecessary and therefore absent. This is a key biological adaptation to a parasitic lifestyle.
7. How do the modes of transmission for Ascariasis and Malaria differ, and why is this an important concept for the board exam?
This is a frequently asked concept to test understanding of disease prevention.
- Ascariasis: Transmitted through the faecal-oral route, by ingesting food or water contaminated with the eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides. This is a disease linked to poor sanitation.
- Malaria: Transmitted through a biological vector. The female Anopheles mosquito injects sporozoites (the infective stage of Plasmodium) into the human bloodstream when it bites.
8. What are some common questions asked in the viva voce for the Class 12 Biology practical on identifying disease-causing organisms?
For the 2025-26 board practicals, be prepared for questions that test both observation and underlying concepts. Common viva questions include:
- What is the infective stage of Plasmodium for humans? (Answer: Sporozoites).
- Name the disease caused by Ascaris lumbricoides. (Answer: Ascariasis).
- Why is a mosquito bite necessary for Malaria transmission but not for Amoebiasis? (Tests understanding of life cycles).
- State two observable differences between the male and female roundworm. (Tests spotting skills).
9. Why must permanent slides be handled with care by their edges and observed first under low power magnification?
These are critical procedural precautions. Handling slides by the edges prevents fingerprint smudges on the cover slip, which can obscure the specimen and lead to incorrect identification. Starting with low power magnification provides a wider field of view, making it easier to locate the specimen on the slide before switching to high power for detailed observation. This systematic approach saves time and ensures accuracy during the exam.
























