Maths Notes for Chapter 6 The Triangle and Its Properties Class 7 - FREE PDF Download
In Cbse Class 7 Maths Notes Chapter 6, you’ll get to know all about triangles, their types, and their unique properties. This chapter makes tricky parts, like angle sums and different triangle sides, much easier to understand—so you don’t have to feel confused. To make your preparation stronger, check the Class 7 Maths Syllabus to know what’s important this year.
Many students find triangles a bit puzzling, especially with rules like the sum of angles or the difference in side lengths. Vedantu’s simple notes break down these concepts so you can revise quickly—perfect for last-minute studying!
Learning this chapter is much smoother with our Class 7 Maths Revision Notes, covering all key points for CBSE exams. Use these notes to get confident about triangles and score better.
Access Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 6 - The Triangle and its Properties Notes
Class 7 Maths The Triangle and Its Properties - Important Topics
The important topics that are covered in CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 6 The Triangle and Its Properties are mentioned below:
Triangles and their basic elements.
Types of triangles based on their sides (Equilateral, Isosceles and Scalene)
Types of triangles based on their angle measurement (Right-angled, obtuse-angled and acute-angled).
Properties of a triangle.
Triangles:
Triangles are three line segments that form a closed plane figure.
In above figure, $\vartriangle \text{ABC}$ is a triangle.
The three angles and three sides of a triangle make up the triangle's six constituents.
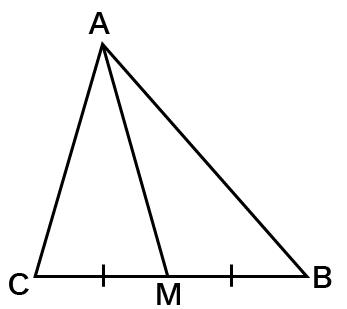
The line segment connecting a triangle's vertex to the opposite side's midpoint is known as the triangle's median.
In above figure, $\text{AM}$ is the median of triangle $\text{ABC}$.
There are three medians in a triangle.
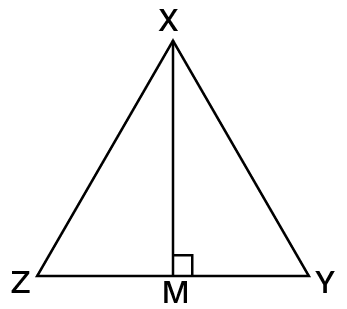
The perpendicular line segment connecting a triangle's vertex to its opposite side is known as the triangle's height or altitude of a triangle.
In above figure, $\text{XM}$ is the altitude (height) of triangle $\text{XYZ}$.
There are three elevations in a triangle.
Type of Triangle Based on Sides:
Equilateral Triangle:
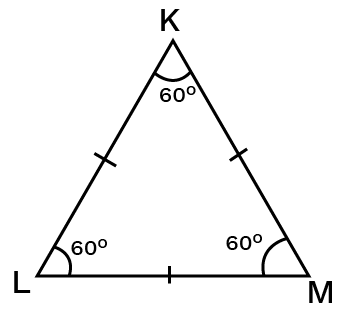
If each of a triangle's sides is the same length, then the triangle is said to be equilateral.
Each angle in an equilateral triangle is $60$ degrees.
Isosceles Triangle:
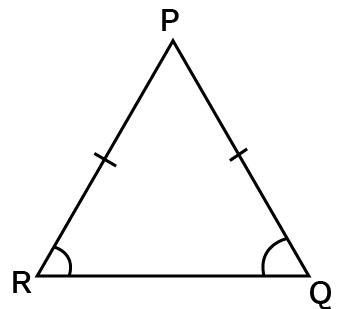
If at least two of the triangle's sides are the same length, then it is said to be isosceles.
An isosceles triangle's base is its non-equal side.
The base angles of an isosceles triangle have equal measures.
Scalene Triangle:
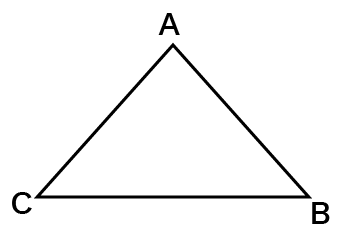
All of the sides of a triangle are different lengths.
There are no two angles that are the same.
Property of the Lengths of Sides of a Triangle:
Any two sides of a triangle have a length that is more than the length of the third side.
The length difference between any two sides is smaller than the length difference between the third and fourth sides.
This feature is important for determining whether or not a triangle may be drawn when the lengths of the three sides are known.
Types of Triangle-based on Angles:
Right Angled Triangle:
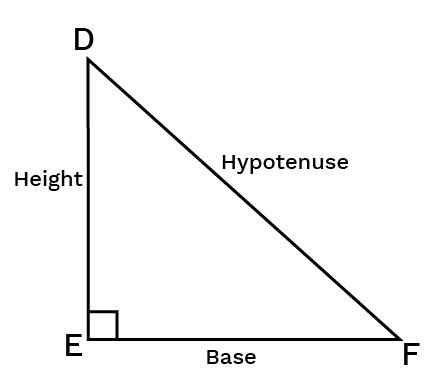
A triangle in which one of the angles is measured in ${{90}^{0}}$.
The hypotenuse is the side opposite the right angle of a right-angled triangle, whereas the legs are the other two sides.
Obtuse Angled Triangle:
A triangle in which one of the angles is larger than ${{90}^{0}}$.
Acute Angled Triangle:
A triangle in which each of the angles is smaller than ${{90}^{0}}$.
Pythagoras Property:
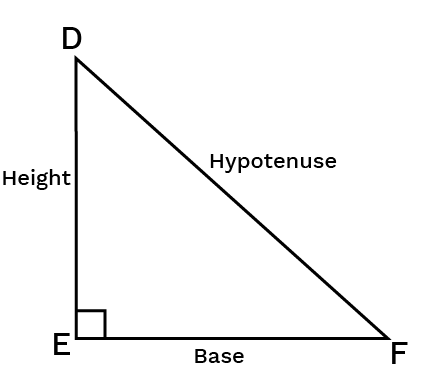
In right-angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares on the legs of a right-angled triangle.
Triangle $\text{DEF}$ is a right angled triangle. According to Pythagoras Theorem,
\[{{\left( Hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}\text{ }=\text{ S}um\text{ }of\text{ }the\text{ }squares\text{ }on\text{ }the\text{ }legs.\]
Therefore,
${{\left( \text{DF} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{DE} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{EF} \right)}^{2}}$
This property does not hold true if a triangle is not right-angled.
This feature can be used to determine whether or not a triangle is right-angled.
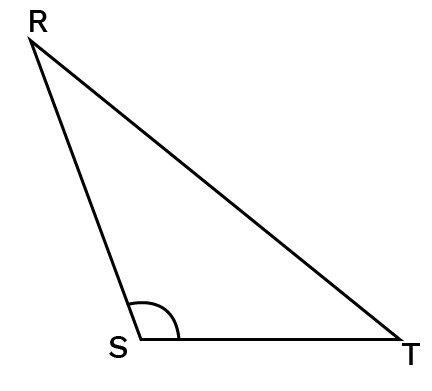
Exterior Angle:
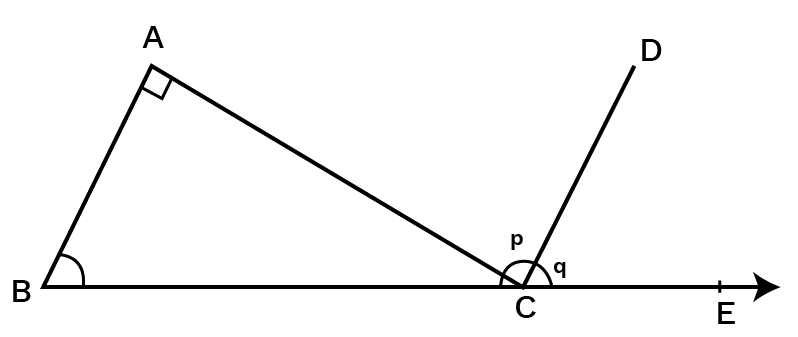
The sum of a triangle's internal opposite angles equals its outer angle that is known as the Exterior angle of a triangle.
In above figure, $\angle \text{ACE}$ is an Exterior angle.
\[\angle \text{ACE = }\angle \text{A}+\angle \text{B}\]
When a side of a triangle is made, an external angle of a triangle is formed.
There are two ways to generate an external angle at each vertex.
A Property of Exterior Angles:
The sum of the measures of a triangle's internal opposite angles equals the measure of any of its outer angles.
The Angle Sum Property of a Triangle:
The total measure of a triangle's three angles is ${{180}^{0}}$.
Property of the Lengths of Sides of a Triangle:
The lengths of any two sides of a triangle are always bigger than the third side's length.
The length difference between any two triangle sides is always less than the length of the third side.
Benefits of CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 6 Revision Notes
Here are a few points that tell us the benefits of CBSE Class 7 Maths Revision Notes:
These notes are your one-stop solution for last-minute exam preparation.
The topic-wise key points included in these revision notes will help you to revise all the chapters easily and also to brush up on the concepts.
Class 7 Maths Chapter 6 Revision Notes are made by the subject experts at Vedantu, so you can rely on these answers completely.
Referring to the CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 6 Revision Notes will help students improve their understanding of all the topics which are provided here in a detailed manner.
These notes can be downloaded for free in PDF format and can be accessed from anywhere.
Conclusion
Vedantu's free PDF notes on CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 6, "The Triangle and Its Properties," are a valuable educational resource. These notes serve as a comprehensive guide, covering essential topics related to triangles, including properties, theorems, and practical applications. They cater to the needs of CBSE Class 7 students, ensuring that they have access to high-quality study materials.
Vedantu's commitment to providing free, accessible educational content is commendable, as it empowers students to excel in their mathematical studies. These notes facilitate a deeper understanding of geometric concepts, helping students build a strong foundation in mathematics. By utilising these resources, students can enhance their problem-solving skills, geometry proficiency, and overall academic performance, making them an indispensable asset for students and educators alike.























