
Which one the following has the smallest dipole moment?
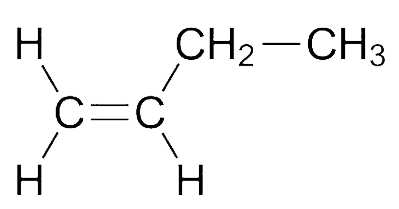
A. $1 - $Butene
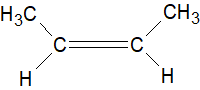
B. Cis$ - 2 - $Butene
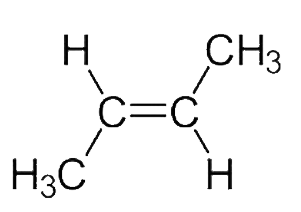
C. Trans$ - 2 - $Butene
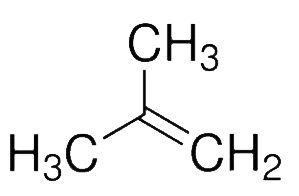
D. $2 - $methyl-propene
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In compounds where there is visible charge separation, a dipole moment can be demonstrated. Therefore, we can assert that ionic and covalent bonding both produce the dipole moment. Dipole moments are also influenced by the different electronegativity of the two atoms that are chemically connected.
Complete Step-by-Step Explanation:
The polarity of a chemical bond formed between two atoms in a molecule is often measured by a bond dipole moment. It provides us with the idea of an electric dipole moment, which is typically used to measure the separation of the positive and negative charges in a system. Dipole moments have both a magnitude and a direction, making them vector quantities. Due to the ability of a vector quantity, it can also have the value zero since two bond dipoles with opposing charges can cancel one another out.
Dipole moment is also influenced by a compound's structural characteristics or more specifically that is by the bond angle. Bond angle is zero for symmetrical structures and has some value for asymmetrical structures.
In the given options, we notice that trans\[ - 2 - \]Butene molecule shows zero dipole moment because as there is just one ethyl group connected which is increasing the \[{e^ - }\]density on the \[C = C\], the dipole moment in \[1\] will be the smallest.
Since there are \[2C{H_3}\] groups present \[II\], being cis, has a greater dipole moment.
Due to the arrangement of the $C{H_3}$groups, the dipole moment in the option$C$, Trans$ - 2 - $Butene is $O$and to the presence of $2C{H_3}$groups on one carbon of $c = c$,
And in the option$D$, $2 - $methyl-propene exhibits the highest dipole moment.
Thus, the correct option is (C) Trans\[ - 2 - \]Butene
Note: It should be noted that the product of the charge's magnitude and the separation between the positive and negative charge centers yields the dipole moment. The Greek letter \[\mu \] is used to signify it. In mathematics, it is written as: \[\mu = Q \times r\].
Complete Step-by-Step Explanation:
The polarity of a chemical bond formed between two atoms in a molecule is often measured by a bond dipole moment. It provides us with the idea of an electric dipole moment, which is typically used to measure the separation of the positive and negative charges in a system. Dipole moments have both a magnitude and a direction, making them vector quantities. Due to the ability of a vector quantity, it can also have the value zero since two bond dipoles with opposing charges can cancel one another out.
Dipole moment is also influenced by a compound's structural characteristics or more specifically that is by the bond angle. Bond angle is zero for symmetrical structures and has some value for asymmetrical structures.
In the given options, we notice that trans\[ - 2 - \]Butene molecule shows zero dipole moment because as there is just one ethyl group connected which is increasing the \[{e^ - }\]density on the \[C = C\], the dipole moment in \[1\] will be the smallest.

Since there are \[2C{H_3}\] groups present \[II\], being cis, has a greater dipole moment.

Due to the arrangement of the $C{H_3}$groups, the dipole moment in the option$C$, Trans$ - 2 - $Butene is $O$and to the presence of $2C{H_3}$groups on one carbon of $c = c$,

And in the option$D$, $2 - $methyl-propene exhibits the highest dipole moment.

Thus, the correct option is (C) Trans\[ - 2 - \]Butene
Note: It should be noted that the product of the charge's magnitude and the separation between the positive and negative charge centers yields the dipole moment. The Greek letter \[\mu \] is used to signify it. In mathematics, it is written as: \[\mu = Q \times r\].
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




