
Which is most reactive of the following [ J & K $2005$]
A.Ethyl acetate
B.Acetic anhydride
C.Acetamide
D.Acetyl chloride
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: To find the most reactive compounds among the given four carboxylic acid derivatives, first we have to understand the reactivity order of attached substituents such as amide ($-N{{H}_{2}}$), a hydroxyl group ($-OH$), halogen ($-X$), etc. The higher reactivity of the attached substituents higher will be the rate of nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
Complete answer:Carboxylic acid derivatives such as ester, acid anhydride, amide, etc. undergoes a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction in which the acyl group ($R-C=O$) is a more reactive one. The reactivity of the acyl group depends on the substitution attached to it. If the attached substituent is an electron-donating group, then the electrophilicity of the acyl group is decreased or the acyl group is less reactive.
If the attached substitution is an electron-withdrawing group then the reactivity is increased as the electrophilicity of the acyl group increases.
Here we have four compounds Ethyl acetate with chemical formula$C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$, acetic anhydride with chemical formula ${{(C{{H}_{3}}O)}_{2}}O$, acetamide has a chemical formula$C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}$, and acetyl chloride with a chemical formula $C{{H}_{3}}COCl$.
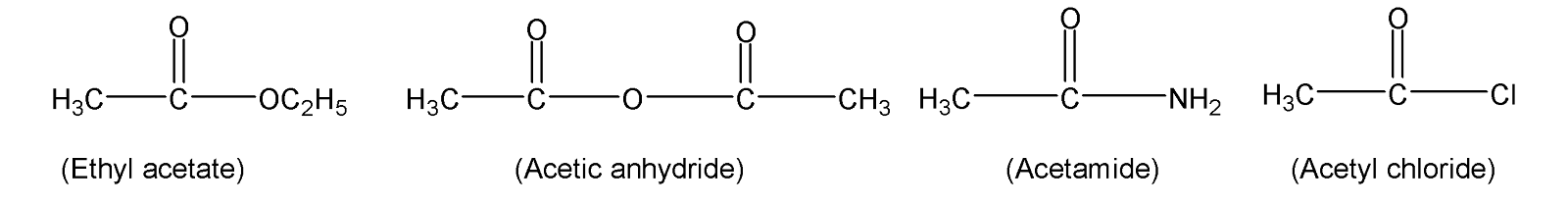
Now we can see there are four different substituents attached to the acyl group and the reactivity order is
$C{{l}^{-}}As the electronegativity of Oxygen is greater than nitrogen so the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen participates in conjugation more than oxygen’s lone pair. As a result electrophilicity of the acyl group decreases and reactivity decreases.


Lone pair of oxygen stabilizes the acyl group in acetic anhydride and also another carbonyl group is stabilized in the same manner. Also, chlorine has $(-I)$effect and pulls the electron density more strongly from the oxygen atom of the acyl group and making it more electrophilic or more reactive than the other three compounds.
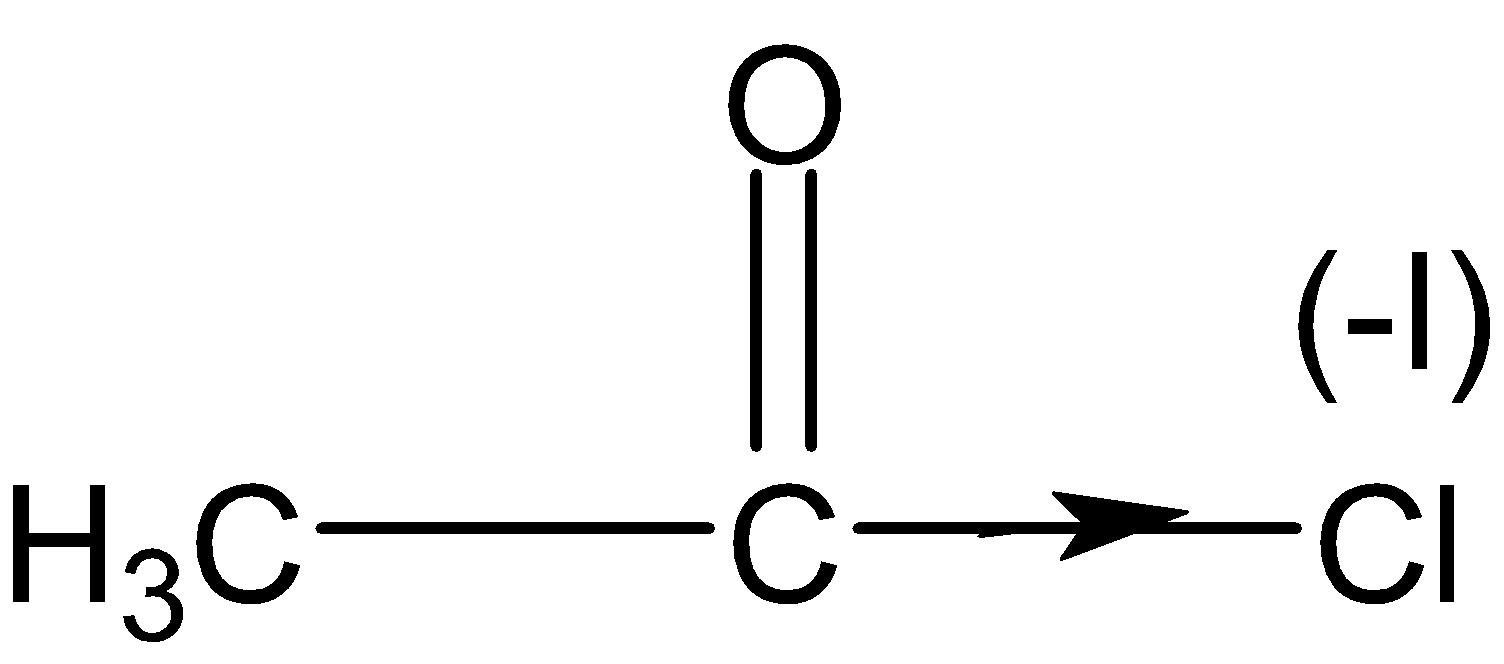
Therefore acetyl chloride is the most reactive compound.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: In this type of problem the most dominant factor is the reactivity of the attached substituent to the acyl group. Therefore we must understand the reason behind their reactivity and for this, we just need to have a basic idea of inductive effect, resonance effect, mesomeric effect, nucleophilicity, electrophilicity, etc.
Complete answer:Carboxylic acid derivatives such as ester, acid anhydride, amide, etc. undergoes a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction in which the acyl group ($R-C=O$) is a more reactive one. The reactivity of the acyl group depends on the substitution attached to it. If the attached substituent is an electron-donating group, then the electrophilicity of the acyl group is decreased or the acyl group is less reactive.
If the attached substitution is an electron-withdrawing group then the reactivity is increased as the electrophilicity of the acyl group increases.
Here we have four compounds Ethyl acetate with chemical formula$C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$, acetic anhydride with chemical formula ${{(C{{H}_{3}}O)}_{2}}O$, acetamide has a chemical formula$C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}$, and acetyl chloride with a chemical formula $C{{H}_{3}}COCl$.

Now we can see there are four different substituents attached to the acyl group and the reactivity order is
$C{{l}^{-}}


Lone pair of oxygen stabilizes the acyl group in acetic anhydride and also another carbonyl group is stabilized in the same manner. Also, chlorine has $(-I)$effect and pulls the electron density more strongly from the oxygen atom of the acyl group and making it more electrophilic or more reactive than the other three compounds.

Therefore acetyl chloride is the most reactive compound.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: In this type of problem the most dominant factor is the reactivity of the attached substituent to the acyl group. Therefore we must understand the reason behind their reactivity and for this, we just need to have a basic idea of inductive effect, resonance effect, mesomeric effect, nucleophilicity, electrophilicity, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




