
What is the definition of Wavefront?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:A wavefront is defined as the locus of all points which are in the same phase, in other words, a wavefront is an imaginary surface, which can be visualized as the collection of all points oscillating in the same phase.
Complete step by step solution:
A wavefront is defined as a virtual surface where all the points of a particular wave are always in phase. Therefore for an oscillating wave as shown below by the red solid curves the virtual surface marked with the solid black vertical lines can be called the wavefront, because all points on the black solid lines are in phase. Depending on the nature of the wave motion a wavefront can be circular, planar, or in any symmetric geometric shape.
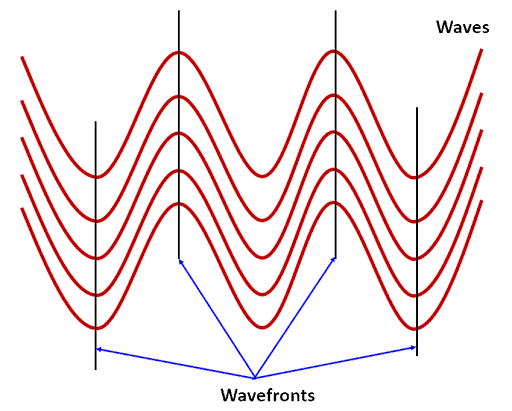
Image: Schematic to show the wavefronts
Some interesting properties of a wavefront can be summarized as follows:
- In the above image we have shown a stationary wavefront, but in reality a wavefront is always propagating in the direction of the motion of the wave, which can be also understood by the fact that all the particles are oscillating about their mean equilibrium position with time and space.
- The wavefront of an electromagnetic wave is always perpendicular to the direction of the propagation of the wave.
- Each wavefront gives origin to the another wavefront, which is obtained by the surface tangent (called envelope) of the collection of the wavelets and therefore helps to visualize the propagation of the wave.
Note: The wavefront always presents the collection of the points oscillating in the same phase and therefore always propagating in the same direction of the wave. The speed of the wavefront can be calculated using Huygen's principle, which states that the collection of all the wavelets give origin to the new wavefront and propagate with a speed related to the wave motion.
Complete step by step solution:
A wavefront is defined as a virtual surface where all the points of a particular wave are always in phase. Therefore for an oscillating wave as shown below by the red solid curves the virtual surface marked with the solid black vertical lines can be called the wavefront, because all points on the black solid lines are in phase. Depending on the nature of the wave motion a wavefront can be circular, planar, or in any symmetric geometric shape.

Image: Schematic to show the wavefronts
Some interesting properties of a wavefront can be summarized as follows:
- In the above image we have shown a stationary wavefront, but in reality a wavefront is always propagating in the direction of the motion of the wave, which can be also understood by the fact that all the particles are oscillating about their mean equilibrium position with time and space.
- The wavefront of an electromagnetic wave is always perpendicular to the direction of the propagation of the wave.
- Each wavefront gives origin to the another wavefront, which is obtained by the surface tangent (called envelope) of the collection of the wavelets and therefore helps to visualize the propagation of the wave.
Note: The wavefront always presents the collection of the points oscillating in the same phase and therefore always propagating in the same direction of the wave. The speed of the wavefront can be calculated using Huygen's principle, which states that the collection of all the wavelets give origin to the new wavefront and propagate with a speed related to the wave motion.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




