
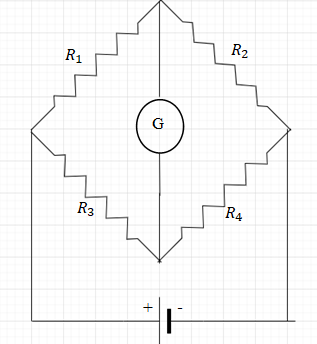
The Wheatstone bridge shown in fig. here gets balanced when the carbon resistor used as ${R_1}$ has the colour code (orange, Red, Brown). The resistors ${R_2}$ and ${R_4}$ are 80 and 40 respectively. Assuming that the colour code for the carbon resistors gives their accurate values, the colour code for carbon resistor, used as ${R_3}$, would be:
A) Red, Green, Brown.
B) Brown, Blue, Brown.
C) Grey, Black, Brown.
D) Brown, Blue, Black.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Resistor is an electrical component which has two terminals and it is used to decrease the flow of the current in the circuit. Wheatstone bridge is an arrangement of the resistors, ammeter, voltmeter, etc. and it is used to find the value of the unknown resistor.
Formula used:
The formula of the resistors in the balanced condition of the galvanometer is given by,
$\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_3}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_4}}}$
Where ${R_1}$ and ${R_3}$ are the resistors on one side of the galvanometer whereas ${R_2}$ and ${R_4}$ are resistors on the other side of the galvanometer.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the problem that Wheatstone gets balanced when the carbon resistor used as ${R_1}$ has the colour code (orange, Red, Brown) the resistors ${R_2}$ and ${R_4}$ are 80 and 40 respectively assuming that the colour code for the carbon resistors gives their accurate values then we need to find the colour code for resistor ${R_3}$.
When the current in the Galvanometer is balanced then the ratio of resistor are balanced on the either side of the galvanometer,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_3}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_4}}}$………eq. (1)
The colour code of the resistor ${R_1}$ is orange, red, brown which means the resistance would be 3,2,10 so the combined resistance would be\[320\Omega \].
Replacing the value of resistance${R_1}$,${R_2}$, and ${R_4}$ in the equation (1)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_3}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_4}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{320}}{{{R_3}}} = \dfrac{{80}}{{40}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{320}}{{{R_3}}} = 2$
$ \Rightarrow {R_3} = 160\Omega $.
The resistance of the resistor ${R_3}$ is equal to ${R_3} = 160\Omega $. The colour code according to the resistance is equal to Brown, Blue and Brown.
The correct answer for this problem is option B.
Note: The Wheatstone is a very important topic and it is asked frequently to find the unknown resistance. When the current in the galvanometer is balanced then the ratio of the resistors are equal. The resistors are colour coded according to their resistance value.
Formula used:
The formula of the resistors in the balanced condition of the galvanometer is given by,
$\dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_3}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_4}}}$
Where ${R_1}$ and ${R_3}$ are the resistors on one side of the galvanometer whereas ${R_2}$ and ${R_4}$ are resistors on the other side of the galvanometer.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the problem that Wheatstone gets balanced when the carbon resistor used as ${R_1}$ has the colour code (orange, Red, Brown) the resistors ${R_2}$ and ${R_4}$ are 80 and 40 respectively assuming that the colour code for the carbon resistors gives their accurate values then we need to find the colour code for resistor ${R_3}$.
When the current in the Galvanometer is balanced then the ratio of resistor are balanced on the either side of the galvanometer,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_3}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_4}}}$………eq. (1)
The colour code of the resistor ${R_1}$ is orange, red, brown which means the resistance would be 3,2,10 so the combined resistance would be\[320\Omega \].
Replacing the value of resistance${R_1}$,${R_2}$, and ${R_4}$ in the equation (1)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{{R_3}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{{R_4}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{320}}{{{R_3}}} = \dfrac{{80}}{{40}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{320}}{{{R_3}}} = 2$
$ \Rightarrow {R_3} = 160\Omega $.
The resistance of the resistor ${R_3}$ is equal to ${R_3} = 160\Omega $. The colour code according to the resistance is equal to Brown, Blue and Brown.
The correct answer for this problem is option B.
Note: The Wheatstone is a very important topic and it is asked frequently to find the unknown resistance. When the current in the galvanometer is balanced then the ratio of the resistors are equal. The resistors are colour coded according to their resistance value.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




