
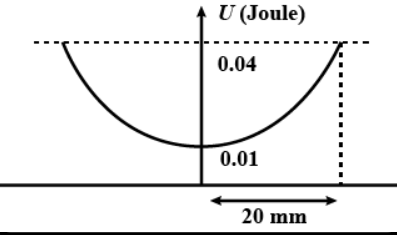
The variation in potential energy of a harmonic oscillator is as shown in the figure. The spring constant is
A. \[1 \times {10^2}N{m^{ - 1}}\]
B. \[1.5 \times {10^2}N{m^{ - 1}}\]
C. \[0.0667 \times {10^2}N{m^{ - 1}}\]
D. \[3 \times {10^2}N{m^{ - 1}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The term potential energy refers to the energy that has been stored or the energy that has been caused by its location. The potential energy of an object changes mostly when the object is lower or higher than its original position.
Formula Used:
\[PE = {V_0} + \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
where PE is the potential energy, \[{V_0}\] is the initial energy, k is the spring constant and x is the displacement travelled by the string.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given that the initial energy of the harmonic oscillator is 0.01 J and its final potential energy is 0.04 J. The spring of the harmonic oscillator has travelled 20 mm or 0.02 m. We have to find the spring constant of the oscillator. Let \[{V_0}\] be the initial potential energy, PE be the final potential energy, x be the distance travelled by the string, and k be the spring constant.
By using the formula of the potential energy of the harmonic oscillator, we get,
\[PE = {V_0} + \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} \\
\Rightarrow 0.04 = 0.01 + \dfrac{1}{2}k{\left( {0.02} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow 0.03 = 0.0002k \\
\Rightarrow k = 150N{m^{ - 1}} \]
Writing the result in the scientific notation we get,
\[k = 150N{m^{ - 1}} \\
\Rightarrow k = 1.5 \times 100N{m^{ - 1}} \\
\therefore k = 1.5 \times {10^2}N{m^{ - 1}} \]
So, option B, \[1.5 \times {10^2}N{m^{ - 1}}\] is the required solution.
Note: As the harmonic oscillator initially had some potential energy and after applying the spring its potential energy gets increased so to calculate the spring constant we only need the energy generated by the spring. So, for the energy generated only by spring, we subtract the initial potential energy from the final potential energy.
Formula Used:
\[PE = {V_0} + \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
where PE is the potential energy, \[{V_0}\] is the initial energy, k is the spring constant and x is the displacement travelled by the string.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been given that the initial energy of the harmonic oscillator is 0.01 J and its final potential energy is 0.04 J. The spring of the harmonic oscillator has travelled 20 mm or 0.02 m. We have to find the spring constant of the oscillator. Let \[{V_0}\] be the initial potential energy, PE be the final potential energy, x be the distance travelled by the string, and k be the spring constant.
By using the formula of the potential energy of the harmonic oscillator, we get,
\[PE = {V_0} + \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} \\
\Rightarrow 0.04 = 0.01 + \dfrac{1}{2}k{\left( {0.02} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow 0.03 = 0.0002k \\
\Rightarrow k = 150N{m^{ - 1}} \]
Writing the result in the scientific notation we get,
\[k = 150N{m^{ - 1}} \\
\Rightarrow k = 1.5 \times 100N{m^{ - 1}} \\
\therefore k = 1.5 \times {10^2}N{m^{ - 1}} \]
So, option B, \[1.5 \times {10^2}N{m^{ - 1}}\] is the required solution.
Note: As the harmonic oscillator initially had some potential energy and after applying the spring its potential energy gets increased so to calculate the spring constant we only need the energy generated by the spring. So, for the energy generated only by spring, we subtract the initial potential energy from the final potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




