
The value for crystal field stabilisation energy is zero for:
(A) ${ K }_{ 2 }\left[ Mn{ F }_{ 6 } \right]$
(B) ${ K }_{ 3 }\left[ Fe(CN)_{ 6 } \right]$
(C) ${ K }_{ 3 }\left[ Fe{ F }_{ 6 } \right]$
(D) ${ K }_{ 4 }\left[ Fe(CN)_{ 6 } \right]$
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Crystal field stabilization energy: Crystal field stabilization energy is the energy of electronic configuration in the ligand field - Electronic configuration in the isotropic field.
Complete answer step-by-step:
> The splitting pattern in each complex compound is octahedral. If a strong field ligand is present, then back pairing will take place as in the case of B and D, and splitting energy can never be zero, since no electron can go into ${ e }_{ g }$ orbitals.
But if a strong field is not present, then back pairing will not take place as in the case of A and C.
> The splitting pattern in ${ K }_{ 3 }\left[ Fe{ F }_{ 6 } \right]$ is;
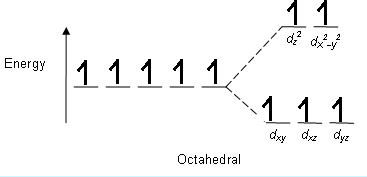
Atomic number of Fe = ${ 26 }$
Electronic configuration = $\left[ Ar \right] { 3d }^{ 6 }{ 4s }^{ 2 }$
For, ${ Fe }^{ +3 } = \left[ Ar \right] { 3d }^{ 5 } or { t }_{ 2g }^{ 3 }{ e }_{ g }^{ 2 }$
The crystal field splitting energy for octahedral complexes are given by;
CFSE = ${ -0.4\times }{ t }_{ 2g }{ +0.6\times }{ e }_{ g }$
By putting the values, we get
CFSE = ${ -0.4\times 3 }{ +0.6\times 2 }$
CFSE = 0
Now, for ${ K }_{ 2 }\left[ Mn{ F }_{ 6 } \right]$
Atomic number of Mn = ${ 25 }$
Electronic configuration = $\left[ Ar \right] { 3d }^{ 5 }{ 4s }^{ 2 }$
For, ${ Mn }^{ +3 } = \left[ Ar \right] { 3d }^{ 4 }or { t }_{ 2g }^{ 3 }{ e }_{ g }^{ 1 }$
The crystal field splitting energy for octahedral complexes are given by;
CFSE = ${ -0.4\times }{ t }_{ 2g }{ +0.6\times }{ e }_{ g }$
By putting the values, we get
CFSE = ${ -0.4\times 3 }{ +0.6\times 1 }$
CFSE = ${ -0.6 } \Delta _{ 0 }$
Hence, we can say that the value for crystal field stabilization energy is zero for ${ K }_{ 3 }\left[ Fe{ F }_{ 6 } \right]$.
The correct option is C.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may use the crystal field splitting energy formula for tetrahedral, not octahedral. But all the compounds are octahedral so do not confuse between them.
Complete answer step-by-step:
> The splitting pattern in each complex compound is octahedral. If a strong field ligand is present, then back pairing will take place as in the case of B and D, and splitting energy can never be zero, since no electron can go into ${ e }_{ g }$ orbitals.
But if a strong field is not present, then back pairing will not take place as in the case of A and C.
> The splitting pattern in ${ K }_{ 3 }\left[ Fe{ F }_{ 6 } \right]$ is;

Atomic number of Fe = ${ 26 }$
Electronic configuration = $\left[ Ar \right] { 3d }^{ 6 }{ 4s }^{ 2 }$
For, ${ Fe }^{ +3 } = \left[ Ar \right] { 3d }^{ 5 } or { t }_{ 2g }^{ 3 }{ e }_{ g }^{ 2 }$
The crystal field splitting energy for octahedral complexes are given by;
CFSE = ${ -0.4\times }{ t }_{ 2g }{ +0.6\times }{ e }_{ g }$
By putting the values, we get
CFSE = ${ -0.4\times 3 }{ +0.6\times 2 }$
CFSE = 0
Now, for ${ K }_{ 2 }\left[ Mn{ F }_{ 6 } \right]$
Atomic number of Mn = ${ 25 }$
Electronic configuration = $\left[ Ar \right] { 3d }^{ 5 }{ 4s }^{ 2 }$
For, ${ Mn }^{ +3 } = \left[ Ar \right] { 3d }^{ 4 }or { t }_{ 2g }^{ 3 }{ e }_{ g }^{ 1 }$
The crystal field splitting energy for octahedral complexes are given by;
CFSE = ${ -0.4\times }{ t }_{ 2g }{ +0.6\times }{ e }_{ g }$
By putting the values, we get
CFSE = ${ -0.4\times 3 }{ +0.6\times 1 }$
CFSE = ${ -0.6 } \Delta _{ 0 }$
Hence, we can say that the value for crystal field stabilization energy is zero for ${ K }_{ 3 }\left[ Fe{ F }_{ 6 } \right]$.
The correct option is C.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may use the crystal field splitting energy formula for tetrahedral, not octahedral. But all the compounds are octahedral so do not confuse between them.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

AssertionIn electrolytic refining of metal impure metal class 12 chemistry JEE_Main

JEE Main Syllabus 2026: Download Detailed Subject-wise PDF

Other Pages
Alcohol Phenol and Ether Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Hindi Medium (2025-26)

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 1 56/2/1 2025: Question Paper, Answers & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students




