
The reagent used for obtaining the osazone derivative of fructose is
A. \[N{H_2}OH\]
B. \[N{H_2}-N{H_2}\]
C. \[N{H_2}-NH{C_6}{H_5}\]
D. \[2,{\rm{ }}4 - DNP\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a ketogenic simple sugar set up in numerous plants. Osazones are a category of carbohydrate derivatives formed from the reaction of reducing sugars with excess phenylhydrazine at boiling temperatures.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Reducing sugar is any sugar that is apt to work as a reducing agent.
In an alkaline solution, a reducing sugar yields some aldehyde or ketone, which lets it work as a reducing agent, such as Benedict's reagent.
Every monosaccharide is a reducing sugar.
Fructose is a monosaccharide that has a ketone group.
So, it is a type of ketose that undergoes tautomerization to aldoses and then acts as reducing sugars.
Fructose in presence of excess phenylhydrazine forms an osazone derivative.
This reaction is a reduction of phenylhydrazine by fructose.
Fructose acts as a reducing agent by undergoing oxidation itself.
Hence, osazone is an oxidation product.
Step-1: The carbonyl group present in the fructose reacts with phenylhydrazine to form phenylhydrazone. During this phase, one molecule of hydrazine is used.
Step-2: This phenylhydrazone then reacts with two molecules of phenylhydrazine to form osazone.
The second molecule of phenylhydrazine oxidises the reactive hydroxyl group to develop the aldehyde group. This is because the ketone group had undergone a reaction in the first step itself.
Step-3: Lastly, the molecule of the phenylhydrazine that is left reacts with the newly created carbonyl group and converts fructose into osazone.
The mechanism is as follows:
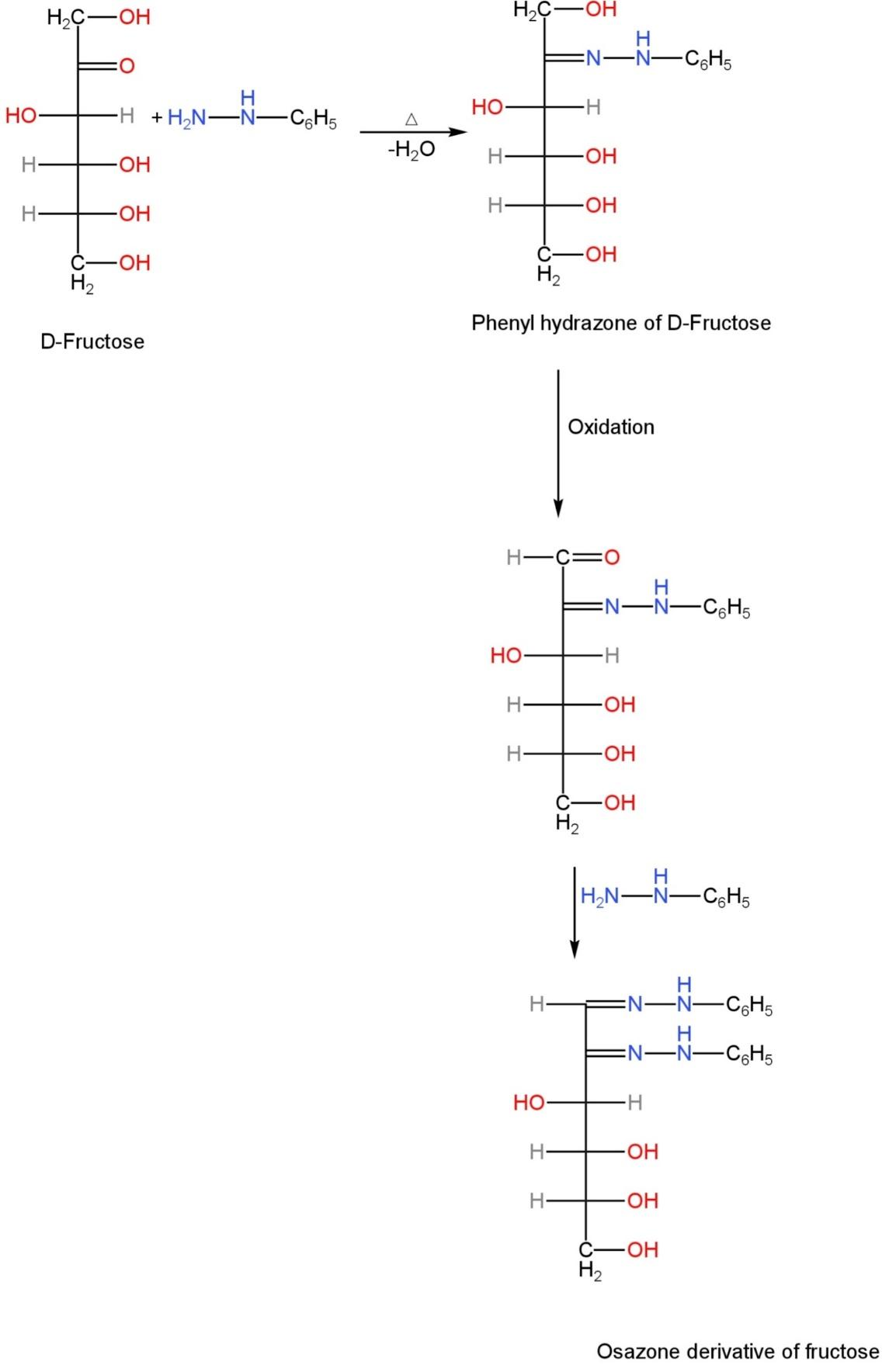
Image: Mechanism of conversion of fructose into its osazone derivative.
Out of the given options, option C i.e., \[N{H_2}-NH{C_6}{H_5}\] is the formula for phenylhydrazine.
So, option C is correct.
Note: This reaction needs a free carbonyl group. So, reducing sugars like glucose, and fructose undergoes this type of reaction. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar that does not constitute an osazone. Sucrose is a disaccharide sugar made up of glucose and fructose subunits. It has glycosidic bonds with the carbon atoms of fructose and glucose and its transition into an open-chain form with an aldehyde group is not possible as they contain a cyclic structure.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Reducing sugar is any sugar that is apt to work as a reducing agent.
In an alkaline solution, a reducing sugar yields some aldehyde or ketone, which lets it work as a reducing agent, such as Benedict's reagent.
Every monosaccharide is a reducing sugar.
Fructose is a monosaccharide that has a ketone group.
So, it is a type of ketose that undergoes tautomerization to aldoses and then acts as reducing sugars.
Fructose in presence of excess phenylhydrazine forms an osazone derivative.
This reaction is a reduction of phenylhydrazine by fructose.
Fructose acts as a reducing agent by undergoing oxidation itself.
Hence, osazone is an oxidation product.
Step-1: The carbonyl group present in the fructose reacts with phenylhydrazine to form phenylhydrazone. During this phase, one molecule of hydrazine is used.
Step-2: This phenylhydrazone then reacts with two molecules of phenylhydrazine to form osazone.
The second molecule of phenylhydrazine oxidises the reactive hydroxyl group to develop the aldehyde group. This is because the ketone group had undergone a reaction in the first step itself.
Step-3: Lastly, the molecule of the phenylhydrazine that is left reacts with the newly created carbonyl group and converts fructose into osazone.
The mechanism is as follows:

Image: Mechanism of conversion of fructose into its osazone derivative.
Out of the given options, option C i.e., \[N{H_2}-NH{C_6}{H_5}\] is the formula for phenylhydrazine.
So, option C is correct.
Note: This reaction needs a free carbonyl group. So, reducing sugars like glucose, and fructose undergoes this type of reaction. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar that does not constitute an osazone. Sucrose is a disaccharide sugar made up of glucose and fructose subunits. It has glycosidic bonds with the carbon atoms of fructose and glucose and its transition into an open-chain form with an aldehyde group is not possible as they contain a cyclic structure.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




