
The reaction of t-butyl bromide with sodium methoxide mainly produces:
A. isobutane
B. isobutylene
C. t-butyl methyl ether
D. sodium tert-butoxide
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Think about the standard name reaction mechanism that involves the reaction of an alkyl halide and alkoxide ion. Consider mechanisms for primary, secondary, as well as tertiary alkyl halides.
Complete step by step solution:
This kind of reaction is known as the Williamson synthesis. The alkyl halide reacts with a metal alkoxide. It forms an ether is the alkyl halide is primary and an alkene if the alkyl halide is secondary or tertiary.
For a primary alkyl halide, by the $S{{N}_{2}}$ mechanism, the alkoxide ion attacks the carbon attached to the halogen atom. This halogen atom is then displaced and an ether is formed. This reaction mechanism does not favour the formation of bulky ethers. Hence, if the alkyl halide is secondary or tertiary, the reaction that happens is an elimination reaction instead of a displacement reaction due to steric hindrance.
The elimination occurs by the ${{E}_{1}}cB$ mechanism of elimination and dehydrohalogenation takes place. Thus, an alkene is formed. The reaction that occurs will be:
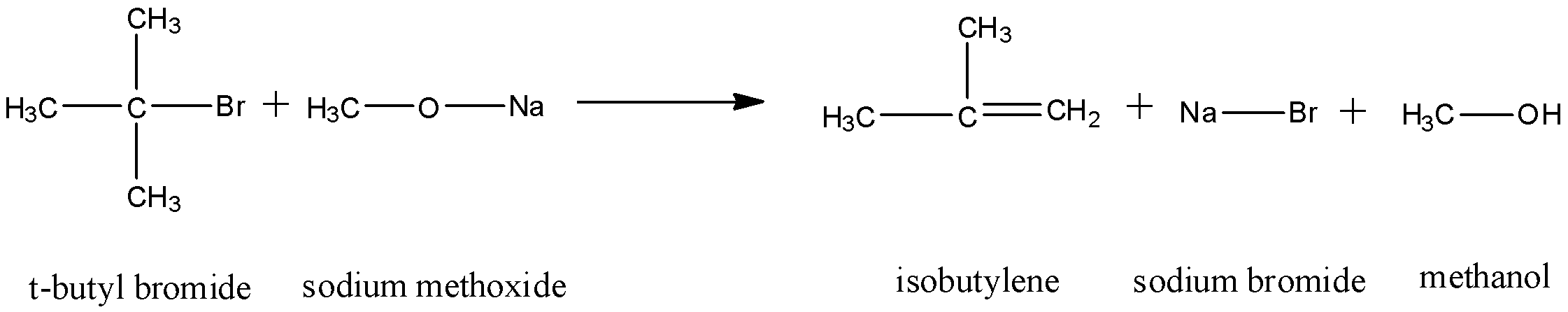
Thus, as we can see, dehydrohalogenation occurs on the tertiary carbon and an adjacent carbon. A double bond forms between them and formation of an alkene occurs.
Hence, the answer is ‘B. isobutylene’
Note: Please do not get confused due to the fact that this is a Williamson synthesis. Remember that only primary alkyl halides form ethers. Because of this, do not blindly mark your answer as ‘C. t-butyl methyl ether’. Always check if the alkyl halide is primary, secondary, or tertiary before working out the reaction and marking the answer.
Complete step by step solution:
This kind of reaction is known as the Williamson synthesis. The alkyl halide reacts with a metal alkoxide. It forms an ether is the alkyl halide is primary and an alkene if the alkyl halide is secondary or tertiary.
For a primary alkyl halide, by the $S{{N}_{2}}$ mechanism, the alkoxide ion attacks the carbon attached to the halogen atom. This halogen atom is then displaced and an ether is formed. This reaction mechanism does not favour the formation of bulky ethers. Hence, if the alkyl halide is secondary or tertiary, the reaction that happens is an elimination reaction instead of a displacement reaction due to steric hindrance.
The elimination occurs by the ${{E}_{1}}cB$ mechanism of elimination and dehydrohalogenation takes place. Thus, an alkene is formed. The reaction that occurs will be:

Thus, as we can see, dehydrohalogenation occurs on the tertiary carbon and an adjacent carbon. A double bond forms between them and formation of an alkene occurs.
Hence, the answer is ‘B. isobutylene’
Note: Please do not get confused due to the fact that this is a Williamson synthesis. Remember that only primary alkyl halides form ethers. Because of this, do not blindly mark your answer as ‘C. t-butyl methyl ether’. Always check if the alkyl halide is primary, secondary, or tertiary before working out the reaction and marking the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




