
The difference between amylase and amylopectin is __________.
(a)- \[Amylopectin\text{ }have\text{ }1\to 4\alpha -linkage\text{ }and\text{ }1\to 6\beta -linkage\]
(b)- \[Amylopectin\text{ }have\text{ }1\to 4\alpha -linkage\text{ }and\text{ }1\to 6\alpha -linkage\]
(c)- Amylose is made up of glucose and galactose.
(d)- \[Amylose\text{ }have\text{ }1\to 4\alpha -linkage\text{ }and\text{ }1\to 6\beta -linkage\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: One of the following has the branched-chain structure and one has the linear chain structure. Both of them are made up of glucose components only.
Complete step by step answer:
Starch is not only a single compound but is a mixture of two components-a water-soluble components called amylose (15-20%) and a water-insoluble component called amylopectin (80-85%). The aqueous solution of amylose gives a blue color with an iodine solution. Amylopectin, on the other hand, does not give blue color with iodine solution.
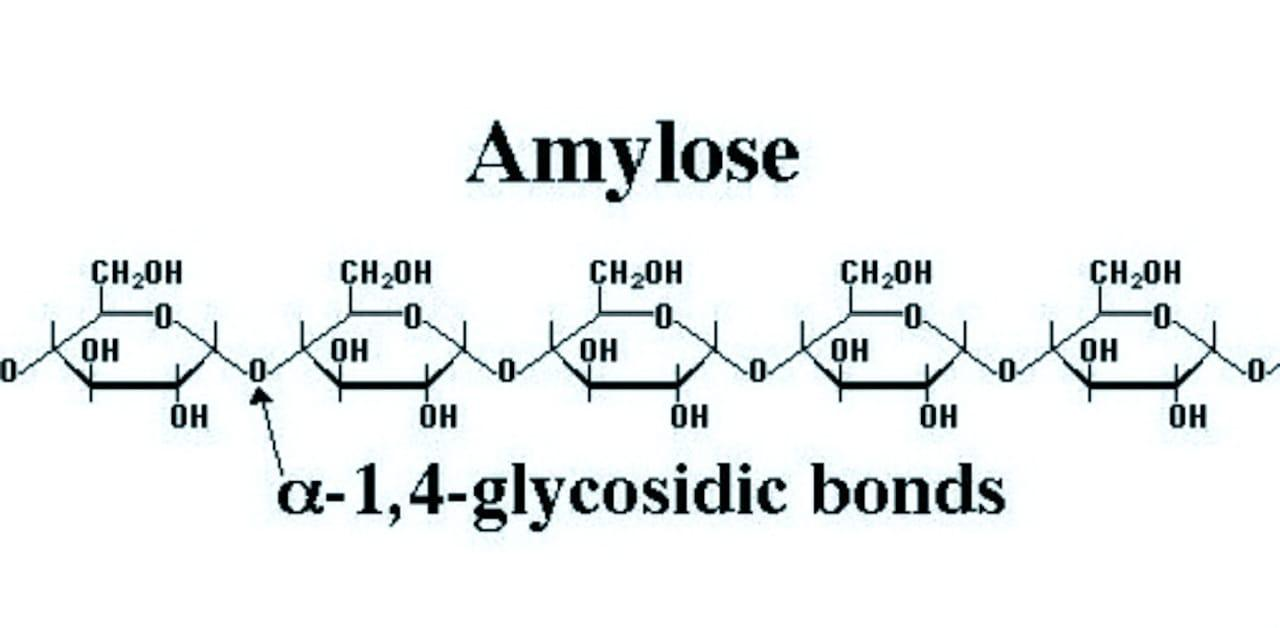
Structure of amylose: It is a linear polymer of \[\alpha -D-glu\cos e\] in which\[{{C}_{1}}\] of one glucose unit is attached to\[{{C}_{4}}\] of the other through\[\alpha -gly\cos idic\] linkage.
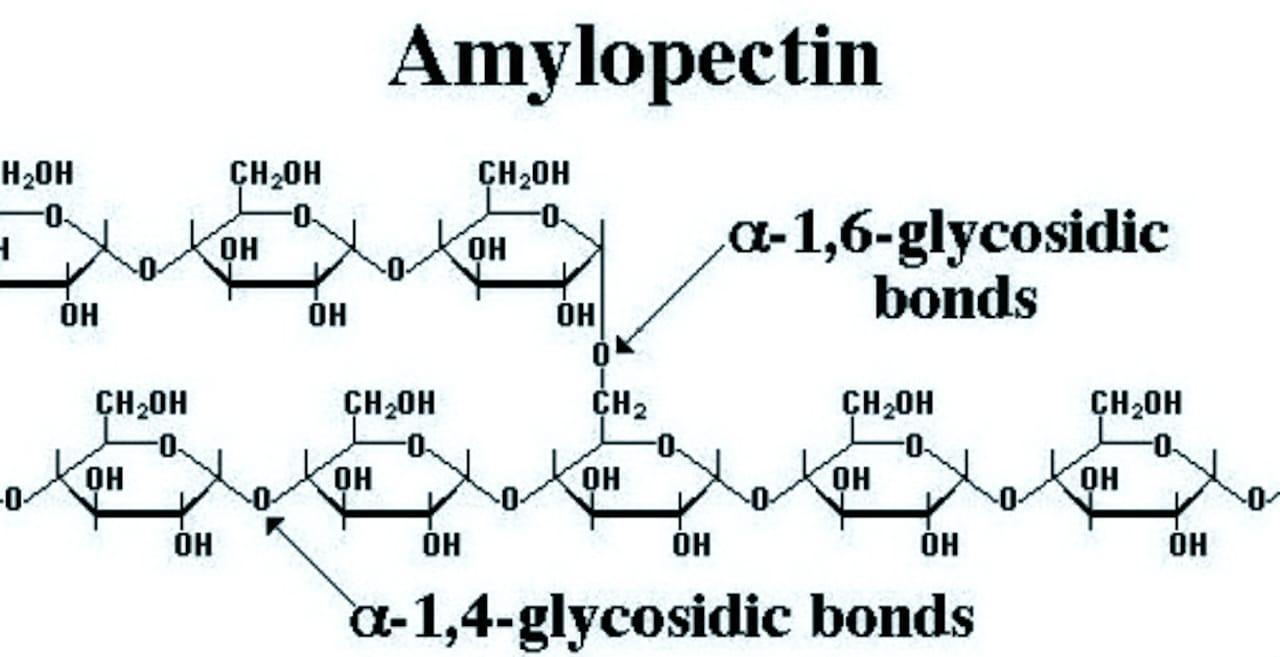
Structure of amylopectin: Amylopectin, on the other hand, is a highly branched polymer. It consists of a large number of short chains each containing 20-25 glucose units which are joined together through \[\alpha -gly\cos idic\] linkage involving \[{{C}_{1}}\] of one glucose unit with\[{{C}_{4}}\] of the other. The \[{{C}_{1}}\]of the terminal glucose unit in each chain is further linked to\[{{C}_{6}}\] of some other glucose unit in the next chain through \[{{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{6}}\]\[\alpha -gly\cos idic\] linkage. This gives amylopectin a highly branched structure.
Hence, from the above discussion option (b) is correct.
Note: You may get confused between \[\alpha -linkage\] and \[\beta -linkage\]. \[\alpha -linkage\] is formed when the bond is formed on the same side and \[\beta -linkage\]is formed when the bond is formed between the opposite side.
Complete step by step answer:
Starch is not only a single compound but is a mixture of two components-a water-soluble components called amylose (15-20%) and a water-insoluble component called amylopectin (80-85%). The aqueous solution of amylose gives a blue color with an iodine solution. Amylopectin, on the other hand, does not give blue color with iodine solution.
Structure of amylose: It is a linear polymer of \[\alpha -D-glu\cos e\] in which\[{{C}_{1}}\] of one glucose unit is attached to\[{{C}_{4}}\] of the other through\[\alpha -gly\cos idic\] linkage.

Structure of amylopectin: Amylopectin, on the other hand, is a highly branched polymer. It consists of a large number of short chains each containing 20-25 glucose units which are joined together through \[\alpha -gly\cos idic\] linkage involving \[{{C}_{1}}\] of one glucose unit with\[{{C}_{4}}\] of the other. The \[{{C}_{1}}\]of the terminal glucose unit in each chain is further linked to\[{{C}_{6}}\] of some other glucose unit in the next chain through \[{{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{6}}\]\[\alpha -gly\cos idic\] linkage. This gives amylopectin a highly branched structure.

Hence, from the above discussion option (b) is correct.
Note: You may get confused between \[\alpha -linkage\] and \[\beta -linkage\]. \[\alpha -linkage\] is formed when the bond is formed on the same side and \[\beta -linkage\]is formed when the bond is formed between the opposite side.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




