
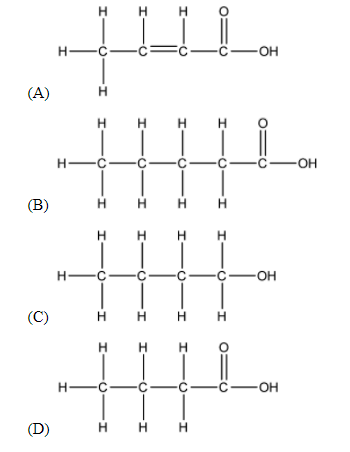
The correct structural formula of butanoic acid is:
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The term ‘-oic acid’ suffix suggests the presence of a carboxylic acid functional group in the organic compound but prefix suggests the presence of four carbons in the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s get familiar about nomenclature.In general, an IUPAC name always has three essential features:
i) A root or base indicating a major chain or ring of carbon atoms found in the molecular structure.
ii) A suffix or other element(s) which represents the functional groups that may be present in the compound.
iii) Names of substituent groups, other than hydrogen, that complete the molecular structure.
With these rules in mind, let us now analyse the name ‘butanoic acid’.
The prefix ‘but-’ means that the longest Carbon chain of the required structure contains 4 Carbon atoms. Thus, we can easily eliminate (B) as a possible answer.
As the suffix ‘-oic acid’ suggests, the functional group of the compound is carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acid can be shown as –COOH. This further narrows our possible answers down to (A) and (D).
The middle part of the name ‘-an-’ suggests that there are no unsaturated bonds in the longest Carbon chain, thus we can eliminate option (A) as an answer. Thus, we can safely conclude that the answer to this question is (D).
Thus, the answer to the above question is option (D).
Note: Here, we are given only ‘butanoic acid’ as the name of the compound, so terminal carbon will be of carboxylic acid functional group. When any specific number is given before the name of the compound (i.e. 2-butanoic acid), then it will suggest the position of the carboxylic acid functional group and we will then have to choose the structure accordingly.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s get familiar about nomenclature.In general, an IUPAC name always has three essential features:
i) A root or base indicating a major chain or ring of carbon atoms found in the molecular structure.
ii) A suffix or other element(s) which represents the functional groups that may be present in the compound.
iii) Names of substituent groups, other than hydrogen, that complete the molecular structure.
With these rules in mind, let us now analyse the name ‘butanoic acid’.
The prefix ‘but-’ means that the longest Carbon chain of the required structure contains 4 Carbon atoms. Thus, we can easily eliminate (B) as a possible answer.
As the suffix ‘-oic acid’ suggests, the functional group of the compound is carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acid can be shown as –COOH. This further narrows our possible answers down to (A) and (D).
The middle part of the name ‘-an-’ suggests that there are no unsaturated bonds in the longest Carbon chain, thus we can eliminate option (A) as an answer. Thus, we can safely conclude that the answer to this question is (D).
Thus, the answer to the above question is option (D).
Note: Here, we are given only ‘butanoic acid’ as the name of the compound, so terminal carbon will be of carboxylic acid functional group. When any specific number is given before the name of the compound (i.e. 2-butanoic acid), then it will suggest the position of the carboxylic acid functional group and we will then have to choose the structure accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




