
State and explain Kirchhoff’s Law.
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: Kirchhoff's circuit laws are two equalities in the lumped element model of electrical circuits that deal with current and potential differences (commonly known as voltage). Gustav Kirchhoff, a German physicist, was the first to describe them in 1845. Kirchhoff's rules, also known as Kirchhoff's laws, are widely used in electrical engineering. These laws apply in both time and frequency domains and serve as the foundation for network analysis.
Complete step by step answer:
Kirchhoff's law is made up of two separate laws:
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
Kirchhoff's first law, or the junction rule, is also known as KCL. The goal of this law is to keep the electric charge as low as possible. The amount of current flowing into a node is equal to the sum of currents flowing out of it, according to the law. KCL is used to perform the nodal analysis in Ohm's law.
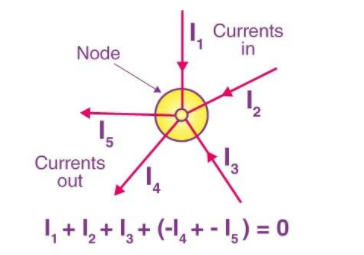
Currents ${I_1},{I_2}$ and ${I_3}$ entering the node are positive, while currents ${I_4}$ and ${I_5}$ leaving the nodes are negative. This can be mathematically expressed as follows:
${I_1} + {I_2} + {I_3} - {I_4} - {I_5} = 0$
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL)
Kirchhoff's second law, or loop law, is another name for KVL. This law is based on the principle of energy conservation. The sum of voltages in a closed-loop is zero, according to the law. The total amount of energy gained per unit charge equals the total amount of energy lost.
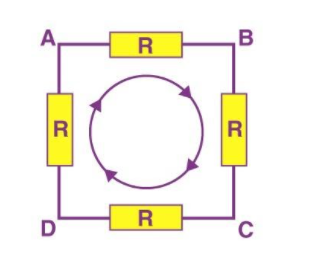
${V_{AB}} + {V_{BC}} + {V_{CD}} + {V_{DA}} = 0$
You'll notice that the voltage drops in all directions, whether negative or positive, and you'll end up back at the same point if you start at any point in the loop and keep going in the same direction. It's critical to keep the rotation going either anticlockwise or clockwise; otherwise, the final voltage value won't be zero.
Note: The current law assumes that the net charge in any wire, junction, or lumped component remains constant. This may not be the case when the electric field between parts of the circuit is non-negligible, such as when two wires are capacitively coupled. This happens in high-frequency AC circuits, where the lumped element model no longer works. In a transmission line, for example, the charge density in the conductor will be constantly oscillating.
Complete step by step answer:
Kirchhoff's law is made up of two separate laws:
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
Kirchhoff's first law, or the junction rule, is also known as KCL. The goal of this law is to keep the electric charge as low as possible. The amount of current flowing into a node is equal to the sum of currents flowing out of it, according to the law. KCL is used to perform the nodal analysis in Ohm's law.

Currents ${I_1},{I_2}$ and ${I_3}$ entering the node are positive, while currents ${I_4}$ and ${I_5}$ leaving the nodes are negative. This can be mathematically expressed as follows:
${I_1} + {I_2} + {I_3} - {I_4} - {I_5} = 0$
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL)
Kirchhoff's second law, or loop law, is another name for KVL. This law is based on the principle of energy conservation. The sum of voltages in a closed-loop is zero, according to the law. The total amount of energy gained per unit charge equals the total amount of energy lost.

${V_{AB}} + {V_{BC}} + {V_{CD}} + {V_{DA}} = 0$
You'll notice that the voltage drops in all directions, whether negative or positive, and you'll end up back at the same point if you start at any point in the loop and keep going in the same direction. It's critical to keep the rotation going either anticlockwise or clockwise; otherwise, the final voltage value won't be zero.
Note: The current law assumes that the net charge in any wire, junction, or lumped component remains constant. This may not be the case when the electric field between parts of the circuit is non-negligible, such as when two wires are capacitively coupled. This happens in high-frequency AC circuits, where the lumped element model no longer works. In a transmission line, for example, the charge density in the conductor will be constantly oscillating.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




