
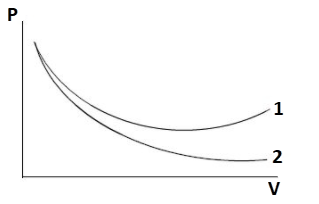
P-V plots for two gases adiabatically are shown in the figure. Plots 1 and 2 should correspond respectively:
A) $He$ and ${O_2}$
B) ${O_2}$ and $He$
C) $He$ and $Ar$
D) ${O_2}$ and ${N_2}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Notice the given ${{P - V}}$plot. Two curves are being plotted. The slope is high for the first curve as compared to the second curve. There are four gases i.e. ${O_2}$, $He$, $Ar$ and ${N_2}$. Distinguish the monoatomic, diatomic and triatomic gases from these four. Apply the relation for adiabatic change i.e., ${{P}}{{{V}}^{{\gamma }}}{{ = constant}}$ and differentiate the relation. After rearranging the terms, a relation between the slope and specific heat can be obtained. After that relate it with each option given in the question.
Complete solution:
Out of ${O_2}$, $He$, $Ar$ and ${N_2}$, only ${O_2}$ and ${N_2}$ are diatomic gases while $He$ and $Ar$ are monatomic gases.
For diatomic gases, the ratio of specific heats is $1.4$
For monoatomic gases, the ratio of specific heats is $1.67$
For adiabatic change, ${{P}}{{{V}}^{{\gamma }}}{{ = constant}}$
Taking derivative, we get
$\Rightarrow {{dp}}{{{V}}^{{\gamma }}}{{ + \gamma P}}{{{V}}^{{{\gamma - 1}}}}{{dV = 0}}$
On rearranging terms, we get
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{dp}}}}{{{{dV}}}}{{{V}}^{{\gamma }}}{{ + \gamma P}}{{{V}}^{{{\gamma - 1}}}}{{ = 0}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{{{dp}}}}{{{{dV}}}}{{{V}}^{{\gamma }}}{{ = - \gamma P}}{{{V}}^{{{\gamma - 1}}}}
\]
Thus, from the above relation we can conclude that slope of the curve varies as per ${{\gamma }}$.
It is clear from the given plot that slope of curve 2 is greater than that of curve 1.
$\therefore {{{\gamma }}_{{2}}}{{ > }}{{{\gamma }}_{{1}}}$
Curve 1 should be for diatomic gases like ${O_2}$ and ${N_2}$
Curve 2 should be for monoatomic gases like $He$ and $Ar$
Thus, curve 1 and curve 2 corresponds to ${O_2}$ and $He$, respectively.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct choice.
Note: In the first option, $He$ and ${O_2}$ gases are given. ${{He}}$ is monoatomic gas while ${O_2}$ is diatomic gas. In the second option, ${O_2}$ and $He$ gases are given. So, the point is ${{He}}$ will remain monoatomic gas while ${{{O}}_{{2}}}$ will remain diatomic gas but in first option for curve 1, ${{He}}$ is given and for curve 2, ${{{O}}_{{2}}}$ is given. Although the options are the same but the first gas is given for curve 1 and the second gas is for curve 2.
Complete solution:
Out of ${O_2}$, $He$, $Ar$ and ${N_2}$, only ${O_2}$ and ${N_2}$ are diatomic gases while $He$ and $Ar$ are monatomic gases.
For diatomic gases, the ratio of specific heats is $1.4$
For monoatomic gases, the ratio of specific heats is $1.67$
For adiabatic change, ${{P}}{{{V}}^{{\gamma }}}{{ = constant}}$
Taking derivative, we get
$\Rightarrow {{dp}}{{{V}}^{{\gamma }}}{{ + \gamma P}}{{{V}}^{{{\gamma - 1}}}}{{dV = 0}}$
On rearranging terms, we get
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{dp}}}}{{{{dV}}}}{{{V}}^{{\gamma }}}{{ + \gamma P}}{{{V}}^{{{\gamma - 1}}}}{{ = 0}} \\
\therefore \dfrac{{{{dp}}}}{{{{dV}}}}{{{V}}^{{\gamma }}}{{ = - \gamma P}}{{{V}}^{{{\gamma - 1}}}}
\]
Thus, from the above relation we can conclude that slope of the curve varies as per ${{\gamma }}$.
It is clear from the given plot that slope of curve 2 is greater than that of curve 1.
$\therefore {{{\gamma }}_{{2}}}{{ > }}{{{\gamma }}_{{1}}}$
Curve 1 should be for diatomic gases like ${O_2}$ and ${N_2}$
Curve 2 should be for monoatomic gases like $He$ and $Ar$
Thus, curve 1 and curve 2 corresponds to ${O_2}$ and $He$, respectively.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct choice.
Note: In the first option, $He$ and ${O_2}$ gases are given. ${{He}}$ is monoatomic gas while ${O_2}$ is diatomic gas. In the second option, ${O_2}$ and $He$ gases are given. So, the point is ${{He}}$ will remain monoatomic gas while ${{{O}}_{{2}}}$ will remain diatomic gas but in first option for curve 1, ${{He}}$ is given and for curve 2, ${{{O}}_{{2}}}$ is given. Although the options are the same but the first gas is given for curve 1 and the second gas is for curve 2.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




