
Name the blood vessel that brings oxygenated blood to the human heart.
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Heart is a conical muscular double pump structure that brings about circulation of blood by its pumping activity. The broader part is in above while the narrow-pointed apex is downwards and tilted towards left. Heart is reddish in colour with a size of our fist (12 cm length, 9 cm breadth) and a weight about 300 gm (250 gm in women).
Complete step-by-step answer:
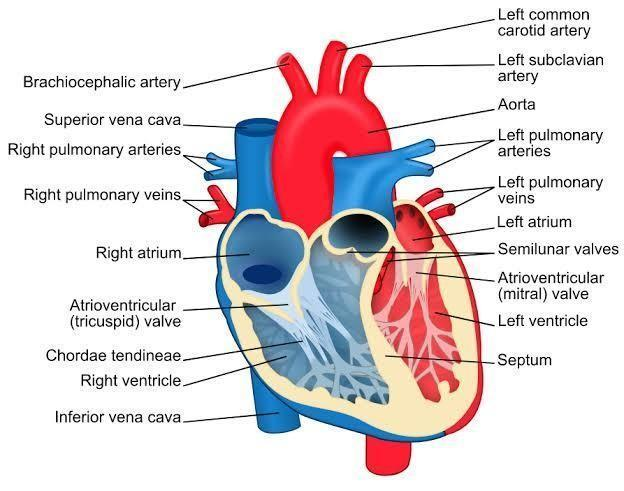
Heart is completely separated into chambers to prevent mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods. There are four chambers. Two upper or superior chambers are slighter and thin walled. They are called auricles of atria (sing. atrium). The other two inferior or bottom chambers are larger and thick walled. They are called ventricles.
> Deoxygenated blood from the whole body enters the right auricle through a superior vena cava (from upper parts of the body), inferior vena cava (from middle and lower parts of the body) and coronary sinus (from walls of the heart).
> Oxygenated blood is carried by pulmonary veins into the left auricle or atrium. Both the auricles get filled simultaneously. It is called diastole. They contract together or undergo systole to pour their blood into their respective ventricles.
This causes diastole of the two ventricles. The distended ventricles undergo systole or contraction to pass their bloods to the pulmonary arch from right side and (systemic) aorta from left side. A cardiac cycle consists of one filling and emptying of the heart chambers in 0.8 second duration. It comprises auricular systole, ventricular systole and joint diastole. Backward flow of blood is prevented by valves.
The separation between the right and left sides of the heart are helpful in separating oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods. This type of structure provides efficient supply of oxygen to all body parts. This type of heart structure is present in animals having high energy needs like birds and mammals. They spend a lot of extra energy for keeping the body from temperature constant.
In reptiles and amphibians, the requirements of energy are lesser as the body temperature varies with the temperature of the environment. Their heart is 3-chambered. Blending of oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods occurs in them.
So pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood to the heart.
Note: Heart beat is a rhythmic contraction and expansion of heart. The diastole is an expansion while the contraction is known as systole. Actually, the auricles and the ventricles both undergo diastole and systole individually but being forceful only ventricular contraction and expansion constitute the heartbeat. The rate of heart beat is 70-72/min in adult human male and 80/min in adult females.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Heart is completely separated into chambers to prevent mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods. There are four chambers. Two upper or superior chambers are slighter and thin walled. They are called auricles of atria (sing. atrium). The other two inferior or bottom chambers are larger and thick walled. They are called ventricles.
> Deoxygenated blood from the whole body enters the right auricle through a superior vena cava (from upper parts of the body), inferior vena cava (from middle and lower parts of the body) and coronary sinus (from walls of the heart).
> Oxygenated blood is carried by pulmonary veins into the left auricle or atrium. Both the auricles get filled simultaneously. It is called diastole. They contract together or undergo systole to pour their blood into their respective ventricles.
This causes diastole of the two ventricles. The distended ventricles undergo systole or contraction to pass their bloods to the pulmonary arch from right side and (systemic) aorta from left side. A cardiac cycle consists of one filling and emptying of the heart chambers in 0.8 second duration. It comprises auricular systole, ventricular systole and joint diastole. Backward flow of blood is prevented by valves.
The separation between the right and left sides of the heart are helpful in separating oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods. This type of structure provides efficient supply of oxygen to all body parts. This type of heart structure is present in animals having high energy needs like birds and mammals. They spend a lot of extra energy for keeping the body from temperature constant.
In reptiles and amphibians, the requirements of energy are lesser as the body temperature varies with the temperature of the environment. Their heart is 3-chambered. Blending of oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods occurs in them.
So pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood to the heart.

Note: Heart beat is a rhythmic contraction and expansion of heart. The diastole is an expansion while the contraction is known as systole. Actually, the auricles and the ventricles both undergo diastole and systole individually but being forceful only ventricular contraction and expansion constitute the heartbeat. The rate of heart beat is 70-72/min in adult human male and 80/min in adult females.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




