
What do you mean by short-circuiting of a circuit?
Answer
519k+ views
Hint: Short-circuiting of an electric circuit usually occurs when the insulation over the wires breaks or there is a voltage fluctuation in the circuit. During a short circuit, the voltage across two nodes in an electric circuit becomes equal.
Complete step by step answer:
Short-circuiting in an electric circuit is defined as that condition during which the overall resistance or impedance of the circuit becomes zero or almost negligible, thereby allowing the flow of a large amount of current through the circuit. In such a condition, the current flows in the circuit in an involuntary path. Short-circuiting occurs when the live wires come in contact with the neutral wires, either directly or via a conductor.
A short circuit is represented in the diagram below:
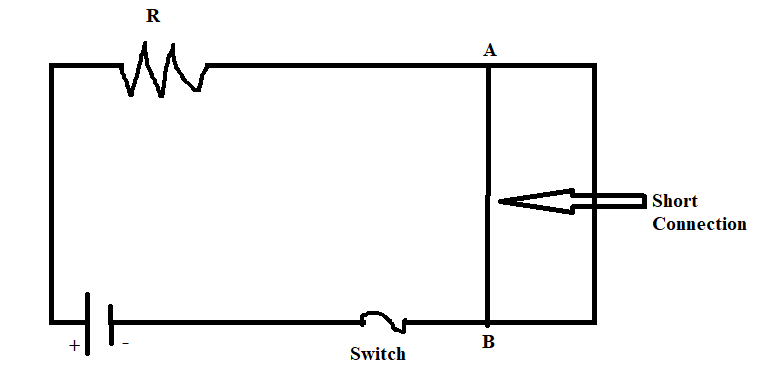
Note: In an ideal situation, a short circuit would mean zero resistance and no voltage drop across these nodes, however, in the case of a real circuit, the resistance becomes very less but not zero, thereby allowing a very high amount of current to flow through it.
The most common scenario of a short circuit is observed when the positive and the negative terminals of a battery are connected by a conducting wire. As the wire possesses very low resistance, it allows a high amount of current to flow through it. This flow of high current in a very short time leads to the heating of the battery and may cause it to explode and cause hazardous damages.
However, damages caused by a short circuit of any form can be reduced or prevented by the use of fuses, circuit breakers, etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Short-circuiting in an electric circuit is defined as that condition during which the overall resistance or impedance of the circuit becomes zero or almost negligible, thereby allowing the flow of a large amount of current through the circuit. In such a condition, the current flows in the circuit in an involuntary path. Short-circuiting occurs when the live wires come in contact with the neutral wires, either directly or via a conductor.
A short circuit is represented in the diagram below:

Note: In an ideal situation, a short circuit would mean zero resistance and no voltage drop across these nodes, however, in the case of a real circuit, the resistance becomes very less but not zero, thereby allowing a very high amount of current to flow through it.
The most common scenario of a short circuit is observed when the positive and the negative terminals of a battery are connected by a conducting wire. As the wire possesses very low resistance, it allows a high amount of current to flow through it. This flow of high current in a very short time leads to the heating of the battery and may cause it to explode and cause hazardous damages.
However, damages caused by a short circuit of any form can be reduced or prevented by the use of fuses, circuit breakers, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




