
In which of the following pairs 1st is more stable than 2nd?
(A) 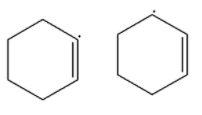
(B) 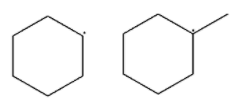
(C) 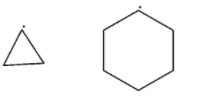
(D) $P{{h}_{3}}{{C}^{\bullet }},\text{ }{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}{{C}^{\bullet }}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The compounds in the given options have carbocation. The tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary and secondary is more stable than the primary. The carbocations are stabilized by either hyperconjugation effect or resonance effect.
Complete step by step answer:
All the compounds in the given options have carbocation.
-In the first option, the carbocation is attached to the carbon atom that has a double bond and the second compound has carbocation on the next carbon of the carbon atom having a double bond. So the resonance is possible in the second structure but not in the first structure. So the second is more stable than the first.
-In second option, in the first structure, the carbocation is on the secondary carbon atom and in the second structure, the carbocation is on the tertiary carbon atom. So the first structure has secondary carbocation and the second structure has tertiary carbocation. We know that tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary. Therefore, the second is more stable than the first.
-In third option, in the first structure, there is a ring of three carbon atoms and in the second structure, there is a ring of six carbon atoms. The ring of six carbon atoms is more stable than the ring of three carbon atoms. Therefore, the second is more stable than the first.
-In the last option, the first compound, the carbocation having carbon is attached to three phenyl groups that can be stabilized with resonance. But the second compound has carbocation having carbon attached to three methyl groups that is stabilized by hyperconjugation effect. The stability due to resonance is more prominent than the stability due to hyperconjugation. Hence, the first is more stable than the second.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (d)-$P{{h}_{3}}{{C}^{\bullet }},\text{ }{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}{{C}^{\bullet }}$.
Note: The flow of electrons from one part of the conjugated system to the other creating centers of low and high electron density due to the phenomenon of resonance is called resonance effect or R-effect. The reverse of the inductive effect when the alkyl group is attached to the unsaturated system or carbocation is known as the hyperconjugation effect.
Complete step by step answer:
All the compounds in the given options have carbocation.
-In the first option, the carbocation is attached to the carbon atom that has a double bond and the second compound has carbocation on the next carbon of the carbon atom having a double bond. So the resonance is possible in the second structure but not in the first structure. So the second is more stable than the first.
-In second option, in the first structure, the carbocation is on the secondary carbon atom and in the second structure, the carbocation is on the tertiary carbon atom. So the first structure has secondary carbocation and the second structure has tertiary carbocation. We know that tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary. Therefore, the second is more stable than the first.
-In third option, in the first structure, there is a ring of three carbon atoms and in the second structure, there is a ring of six carbon atoms. The ring of six carbon atoms is more stable than the ring of three carbon atoms. Therefore, the second is more stable than the first.
-In the last option, the first compound, the carbocation having carbon is attached to three phenyl groups that can be stabilized with resonance. But the second compound has carbocation having carbon attached to three methyl groups that is stabilized by hyperconjugation effect. The stability due to resonance is more prominent than the stability due to hyperconjugation. Hence, the first is more stable than the second.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (d)-$P{{h}_{3}}{{C}^{\bullet }},\text{ }{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}{{C}^{\bullet }}$.
Note: The flow of electrons from one part of the conjugated system to the other creating centers of low and high electron density due to the phenomenon of resonance is called resonance effect or R-effect. The reverse of the inductive effect when the alkyl group is attached to the unsaturated system or carbocation is known as the hyperconjugation effect.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




