
For the given reaction \[(B)\xleftarrow{NaB{{H}_{4}}}PhCH=CH-CHO\xrightarrow[2){{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}]{1)LAH,ether}(A)\]
The products (A) and (B) are:
(A) 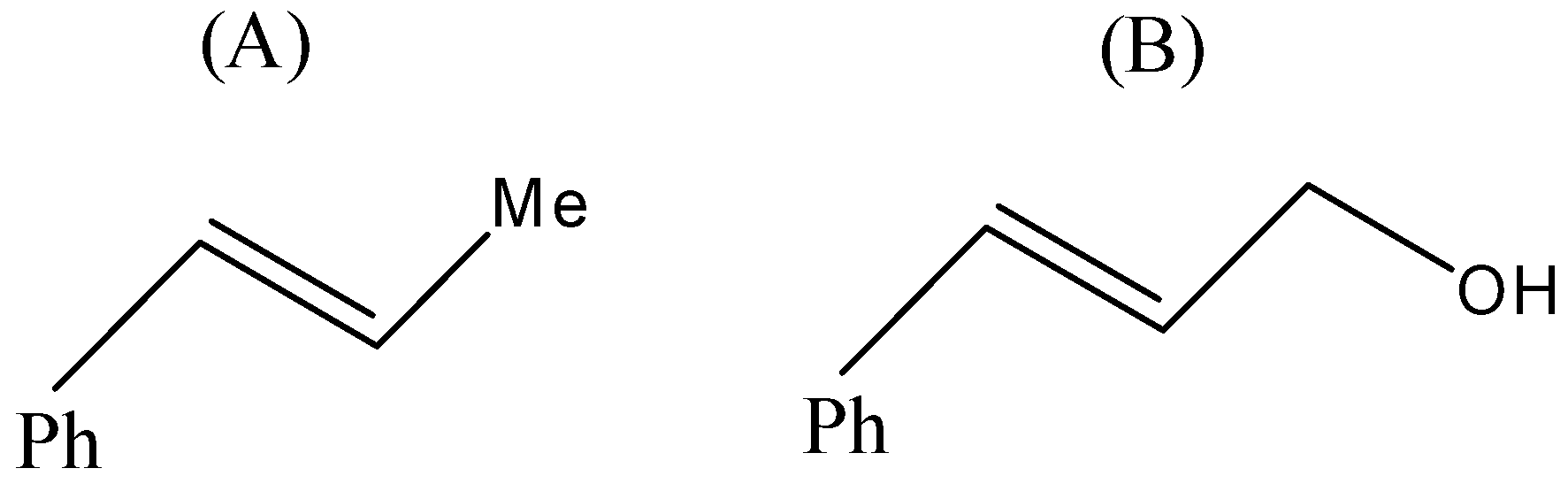
(B) 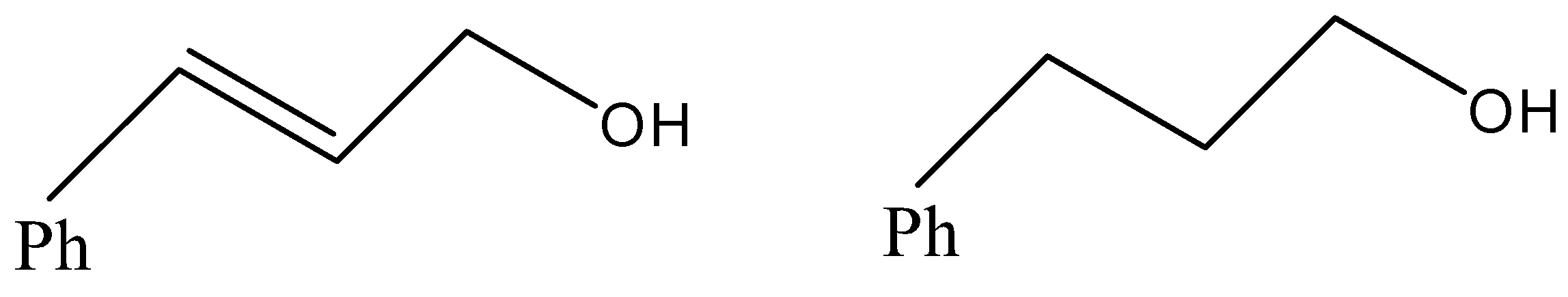
(C) 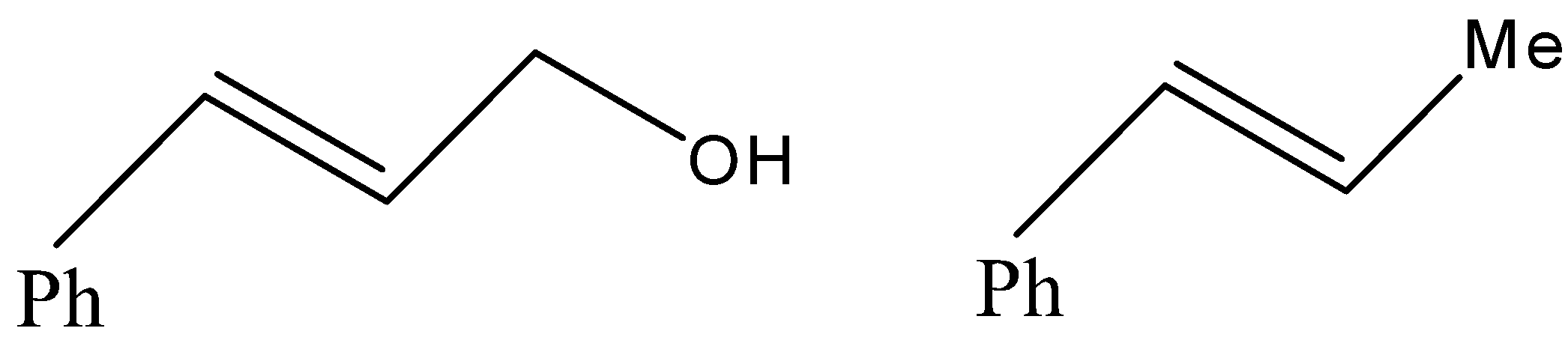
(D) 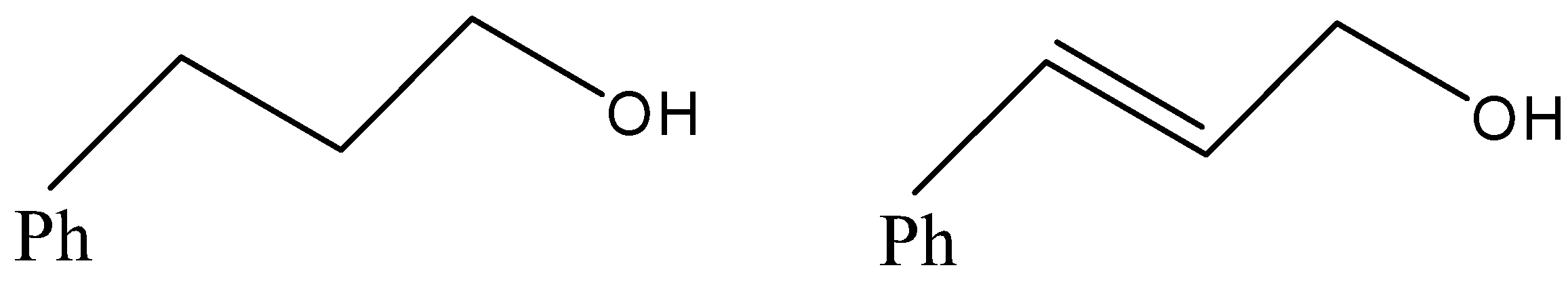
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: LAH stands for Lithium Aluminium Hydride and $NaB{{H}_{4}}$ is sodium borohydride. Both lithium aluminium hydride and sodium hydride are reducing agents but LAH is more stronger.
Complete step by step solution:
- It is known that Lithium Aluminium Hydride (LAH) is a strong, unselective reducing agent for polar double bonds and is a source of hydride ions.
- LAH will reduce aldehydes, ketones, esters, carboxylic acid chlorides, carboxylic acids and even carboxylate salts to alcohols. Also, it reduces amides and nitriles to amines.
- Sodium borohydride is also used as a reducing agent in organic chemistry. It is commonly used to reduce ketones by donating hydride ions. This compound can be used in aqueous solution because it is not that reactive compared to LAH.
- Now, coming to the question, the compound which is reacted with both sodium borohydride and LAH is 3-Phenylprop-2-enal and its common name is cinnamaldehyde.
- We know that alkene gives electrophilic addition reaction so it will not react with sodium borohydride so sodium borohydride will only reduce the carbonyl group into corresponding alcohol. The reaction can be given as under.
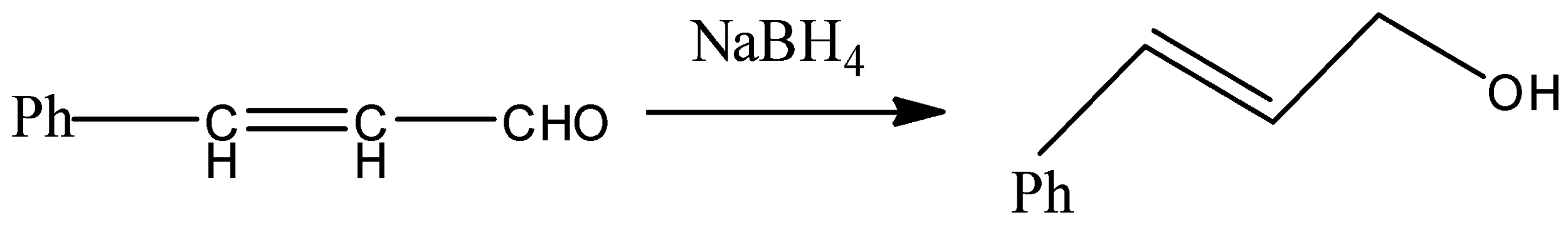
But since, the given compound is alpha-beta unsaturated aldehyde so there is conjugation between alkene and carbonyl, so with LAH carbonyl and alkenes also get reduced. That means we will get an alkene functional group converted into alkane as well.
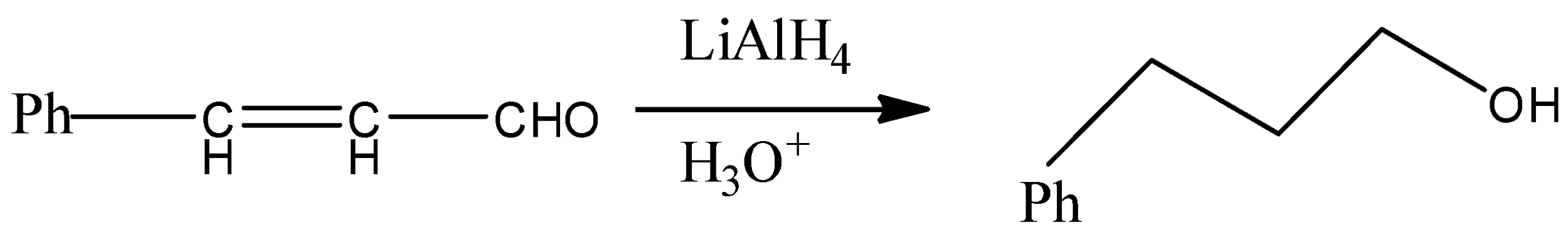
Therefore, from above we can conclude that option (D) is the correct option to the given question.
Note:
It should be remembered that in order to reduce aldehyde or ketone selectively without reducing carbon-carbon double bond in the same molecule, a reducing agent hydroborane known as 9-BBN is also used. Also, you should remember that catalytic hydrogenation can reduce both the double bond and carbonyl group simultaneously.
Complete step by step solution:
- It is known that Lithium Aluminium Hydride (LAH) is a strong, unselective reducing agent for polar double bonds and is a source of hydride ions.
- LAH will reduce aldehydes, ketones, esters, carboxylic acid chlorides, carboxylic acids and even carboxylate salts to alcohols. Also, it reduces amides and nitriles to amines.
- Sodium borohydride is also used as a reducing agent in organic chemistry. It is commonly used to reduce ketones by donating hydride ions. This compound can be used in aqueous solution because it is not that reactive compared to LAH.
- Now, coming to the question, the compound which is reacted with both sodium borohydride and LAH is 3-Phenylprop-2-enal and its common name is cinnamaldehyde.
- We know that alkene gives electrophilic addition reaction so it will not react with sodium borohydride so sodium borohydride will only reduce the carbonyl group into corresponding alcohol. The reaction can be given as under.
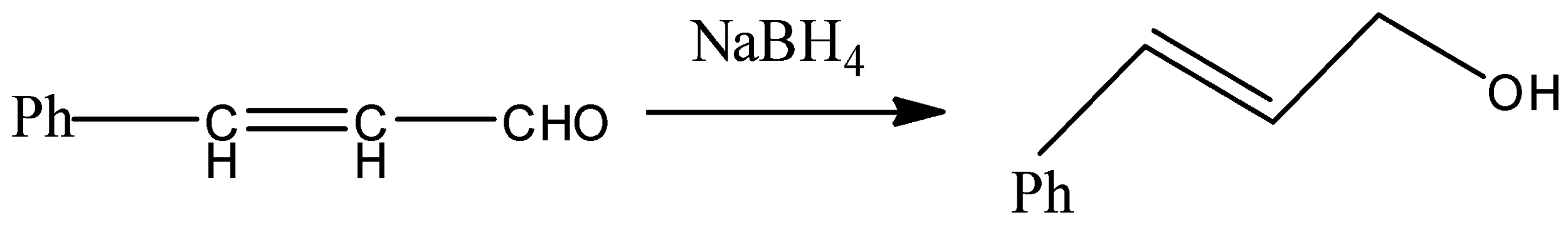
But since, the given compound is alpha-beta unsaturated aldehyde so there is conjugation between alkene and carbonyl, so with LAH carbonyl and alkenes also get reduced. That means we will get an alkene functional group converted into alkane as well.

Therefore, from above we can conclude that option (D) is the correct option to the given question.
Note:
It should be remembered that in order to reduce aldehyde or ketone selectively without reducing carbon-carbon double bond in the same molecule, a reducing agent hydroborane known as 9-BBN is also used. Also, you should remember that catalytic hydrogenation can reduce both the double bond and carbonyl group simultaneously.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




