
For an AM-system the total power of modulated signal is 600W and that of carrier is 400W, the modulation index is
(A) 0.25
(B) 0.36
(C) 0.54
(D) 1
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint The modulation index for the total power of the modulated signal and carrier signal is related to total power and carrier power is given by ${P_T} = {P_C}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{m_a}^2}}{2}} \right)$ . Substitute the power values and simplify to get the modulation index.
Complete step-by-step answer
The process of changing the amplitude of a carrier wave in accordance with the amplitude of the audio frequency signal is known as amplitude modulation (AM).
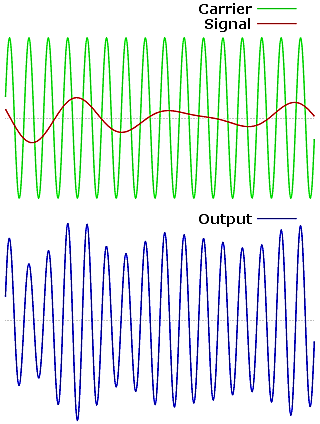
Power modulation index is given by,
${P_T} = {P_C}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{m_a}^2}}{2}} \right)$
Where, ${P_T}$ is the total power modulated, ${P_C}$ is the carrier power, and ${m_a}$ is the modulation index.
It is given in the question that,
Total power of modulated signal$ = 600W$
Carrier power$ = 400W$
Substitute the given data in the above expression.
$600 = 400\left( {1 + \dfrac{{m_a^2}}{2}} \right)$
$\dfrac{3}{2} = 1 + \dfrac{{m_a^2}}{2}$
$\dfrac{{m_a^2}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
${m_a} = 1$
Hence, the modulation index is 1 and the correct option is D.
Note Maximum power in the AM without distortion will occur when ${m_a} = 1$
If ${I_C}$is unmodulated current and${I_T}$ is total modulated current then,
$\dfrac{{{P_T}}}{{{P_C}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{I_T}}}{{{I_C}}}} \right)^2}$
The ratio of change of amplitude of carrier wave to the amplitude of original carrier wave is called modulation factor or degree of modulation to modulation index. It is also called modulation depth.
Complete step-by-step answer
The process of changing the amplitude of a carrier wave in accordance with the amplitude of the audio frequency signal is known as amplitude modulation (AM).

Power modulation index is given by,
${P_T} = {P_C}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{m_a}^2}}{2}} \right)$
Where, ${P_T}$ is the total power modulated, ${P_C}$ is the carrier power, and ${m_a}$ is the modulation index.
It is given in the question that,
Total power of modulated signal$ = 600W$
Carrier power$ = 400W$
Substitute the given data in the above expression.
$600 = 400\left( {1 + \dfrac{{m_a^2}}{2}} \right)$
$\dfrac{3}{2} = 1 + \dfrac{{m_a^2}}{2}$
$\dfrac{{m_a^2}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
${m_a} = 1$
Hence, the modulation index is 1 and the correct option is D.
Note Maximum power in the AM without distortion will occur when ${m_a} = 1$
If ${I_C}$is unmodulated current and${I_T}$ is total modulated current then,
$\dfrac{{{P_T}}}{{{P_C}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{I_T}}}{{{I_C}}}} \right)^2}$
The ratio of change of amplitude of carrier wave to the amplitude of original carrier wave is called modulation factor or degree of modulation to modulation index. It is also called modulation depth.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




