
Find the quadrants in which the following points lie
[i] (3,2)
[ii] (-2,1)
[iii] (-1,-3)
[iv] (5,-1)
Answer
614.4k+ views
Hint: Plot these points on a graph paper and hence determine in which quadrant they lie.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Plotting point P(x,y) on a graph paper:
When plotting a point P(x,y), we move x units on x-axis and y units on the y-axis. If x is positive, then we move x units in the right direction. If x is negative, then we move on the x-axis in the left direction. If y is positive, then we move on the y-axis in the upwards direction. If y is negative, then we move on the y-axis in the downward direction. Finally, from these two positions we draw lines parallel to another axis, i.e. from a point on the x-axis we draw a line parallel to y-axis and from a point on y-axis, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis. The point at which these lines intersect gives the position of the point P(x,y) in the cartesian plane.
[i] Plotting (3,2):
We move 3 units on the x-axis in the rightward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the y-axis.
We move 2 units on the y-axis in the upward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis.
The lines intersect at point A.
The graph is shown below.
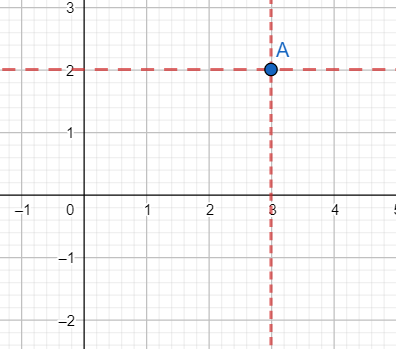
As is evident from the graph, A(3,2) lies in the first quadrant.
[ii] Plotting (-2,1):
We move 2 units on the x-axis in the leftward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the y-axis.
We move 1 unit on the y-axis in the upward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis.
The lines intersect at point A.
The graph is shown below.
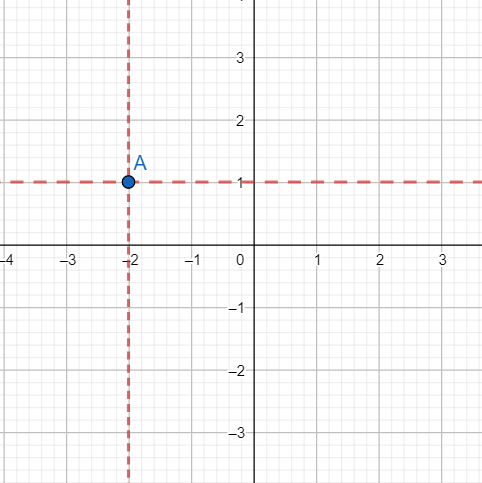
As is evident from the graph A(-2,1) lies in the second quadrant.
[iii] Plotting (-1,-3):
We move 1 unit on the x-axis in the leftward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the y-axis.
We move 3 units on the y-axis in the downward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis.
The lines intersect at point A.
The graph is shown below.
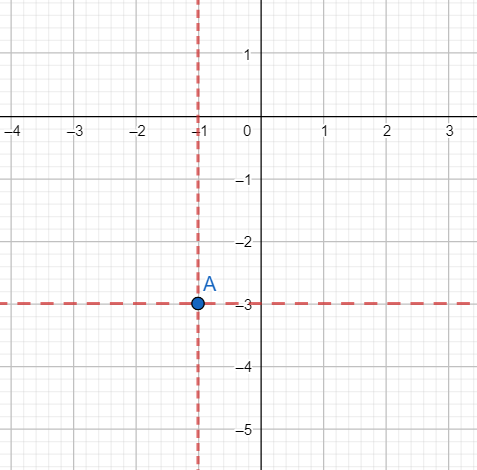
As is evident from the graph A(-1,-3) lies in the third quadrant.
[iv] Plotting (5,-1):
We move 5 units on the x-axis in the rightward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the y-axis.
We move 1 unit on the y-axis in the downward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis.
The lines intersect at point A.
The graph is shown below.
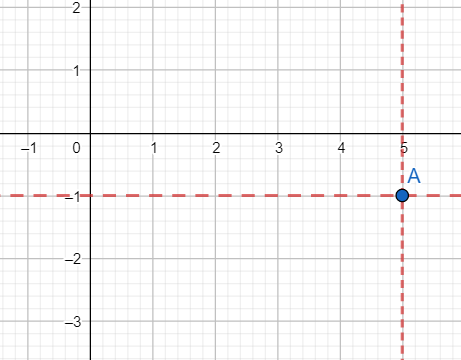
As is evident from the graph A(5,-1) lies in the fourth quadrant.
Note: Alternatively, we can find the quadrant by remembering the following rules:
If x and y both are positive, then (x,y) lies in the first quadrant.
If x is negative and y is positive, then (x,y) lies in the second quadrant.
If x and y both are negative, then (x,y) lies in the third quadrant.
If x is positive and y is negative, then (x,y) lies in the fourth quadrant.
Hence we can find the respective quadrants of each of the points above.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Plotting point P(x,y) on a graph paper:
When plotting a point P(x,y), we move x units on x-axis and y units on the y-axis. If x is positive, then we move x units in the right direction. If x is negative, then we move on the x-axis in the left direction. If y is positive, then we move on the y-axis in the upwards direction. If y is negative, then we move on the y-axis in the downward direction. Finally, from these two positions we draw lines parallel to another axis, i.e. from a point on the x-axis we draw a line parallel to y-axis and from a point on y-axis, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis. The point at which these lines intersect gives the position of the point P(x,y) in the cartesian plane.
[i] Plotting (3,2):
We move 3 units on the x-axis in the rightward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the y-axis.
We move 2 units on the y-axis in the upward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis.
The lines intersect at point A.
The graph is shown below.

As is evident from the graph, A(3,2) lies in the first quadrant.
[ii] Plotting (-2,1):
We move 2 units on the x-axis in the leftward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the y-axis.
We move 1 unit on the y-axis in the upward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis.
The lines intersect at point A.
The graph is shown below.

As is evident from the graph A(-2,1) lies in the second quadrant.
[iii] Plotting (-1,-3):
We move 1 unit on the x-axis in the leftward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the y-axis.
We move 3 units on the y-axis in the downward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis.
The lines intersect at point A.
The graph is shown below.

As is evident from the graph A(-1,-3) lies in the third quadrant.
[iv] Plotting (5,-1):
We move 5 units on the x-axis in the rightward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the y-axis.
We move 1 unit on the y-axis in the downward direction. From that position, we draw a line parallel to the x-axis.
The lines intersect at point A.
The graph is shown below.

As is evident from the graph A(5,-1) lies in the fourth quadrant.
Note: Alternatively, we can find the quadrant by remembering the following rules:
If x and y both are positive, then (x,y) lies in the first quadrant.
If x is negative and y is positive, then (x,y) lies in the second quadrant.
If x and y both are negative, then (x,y) lies in the third quadrant.
If x is positive and y is negative, then (x,y) lies in the fourth quadrant.
Hence we can find the respective quadrants of each of the points above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




