
Explain with the suitable diagram the conducting system of the human heart.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint:Your heart is a muscle. It's a little to the left of the centre of your chest, and it's around the size of your fist. There are a lot of muscles all over your body — in your arms, in your legs, in your back, and in your back. But the muscle of the heart is unique regardless of what it does. The heart is pumping blood across your body. The blood supplies the body with the oxygen and nutrients it requires. It also carries the waste away.
Complete answer:
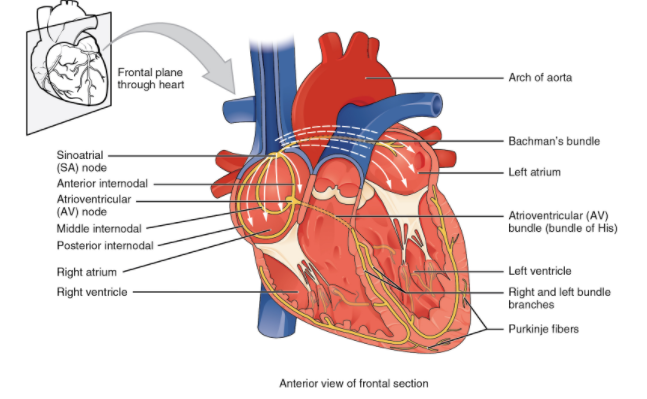
A network of specialized cardiac muscle cells responsible for the coordinated contraction of each cardiac cycle that activates and transmits electrical impulses cardiac is the cardiac conduction system. These special cells are capable of producing an action potential on their own (self-excitation) and transmitting it to other nearby cells (conduction), including cardiomyocytes.
It is possible to separate the sections of the heart conduction system into those that produce action potential (nodal tissue) and those that conduct them (fibre conducting). While all sections have the capacity to produce potential for action and therefore heart contractions, the primary impulse initiator and regulator in a healthy heart is the sinoatrial (SA) node. This feature makes the SA node the heart's biochemical pacemaker. The impulse originating from the SA node is sequentially obtained and performed by other sections and then transferred to myocardial cells. Myocardial cells contract synchronously upon activation by the action potential, resulting in a heartbeat. With the presence of intercalated discs and gap junctions, the transmission of electrical impulses and synchronous contraction of cardiomyocytes is facilitated.
Note:A rhythm abnormality or arrhythmia may result from any abnormality of the conducting pathway, whether congenital or acquired. An arrhythmia simply means that, as it should, the heart is not beating at the right time. These may take the form of beating the heart too rapidly (tachycardia) or too slowly (bradycardia). Abnormal sites that produce an electrical impulse (ectopic beats) may also be present.
Complete answer:
A network of specialized cardiac muscle cells responsible for the coordinated contraction of each cardiac cycle that activates and transmits electrical impulses cardiac is the cardiac conduction system. These special cells are capable of producing an action potential on their own (self-excitation) and transmitting it to other nearby cells (conduction), including cardiomyocytes.
It is possible to separate the sections of the heart conduction system into those that produce action potential (nodal tissue) and those that conduct them (fibre conducting). While all sections have the capacity to produce potential for action and therefore heart contractions, the primary impulse initiator and regulator in a healthy heart is the sinoatrial (SA) node. This feature makes the SA node the heart's biochemical pacemaker. The impulse originating from the SA node is sequentially obtained and performed by other sections and then transferred to myocardial cells. Myocardial cells contract synchronously upon activation by the action potential, resulting in a heartbeat. With the presence of intercalated discs and gap junctions, the transmission of electrical impulses and synchronous contraction of cardiomyocytes is facilitated.
| Parts | Nodal tissue: Sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) nodeConducting fibres:internodal and interatrial conduction pathways, bundles of Hs, bundle branches, subendocardial branches. |
| Sinoatrial node | Contains cardiac pacemaker cells(p)Pacemaker of the heartSupplied by SA nodal branch of right coronary artery |
| Internodal conduction pathway | Anterior, middle, Posterior |
| Interatrial conduction pathway | Conducts impulses to the left atriumSupplied by SA nodal artery |
| Atrioventricular node | Second pacemaker of heartSupplied by AV nodal artery |
| Bundles | Atrioventricular bundle of His-Oval, quadrangular, triangularRight and left bundlesSubendocardial branches(purkinje fibres) |
| Physiology | Impulse begins at the SA node of the internal and inter-atrial conduction pathways-> AV node -> AV bundle (of His) ->bundle branches -> sub-endocardial branch.Sympathetic: increase the activity rate of the SA nodeParasympathetic: decreases the operation rate of the SA node |
| Clinical notes | Sick sinus syndrome, wolff-parkinson white syndrome |

Note:A rhythm abnormality or arrhythmia may result from any abnormality of the conducting pathway, whether congenital or acquired. An arrhythmia simply means that, as it should, the heart is not beating at the right time. These may take the form of beating the heart too rapidly (tachycardia) or too slowly (bradycardia). Abnormal sites that produce an electrical impulse (ectopic beats) may also be present.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




