
Explain the structure of chromosomes with diagrams.
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: Every living individual organism either microscopic or macroscopic possess genetic material, which carries life encoding information that is used to form a new life. The genetic material presents either naked or covered by a nuclear membrane, prokaryote and eukaryotes respectively.
Complete solution:
Chromosomes are the thread-like structure that is present in the condensed form either in the nucleus or cell cytoplasm. The number of the chromosome is different in different species that regulate the life processes.
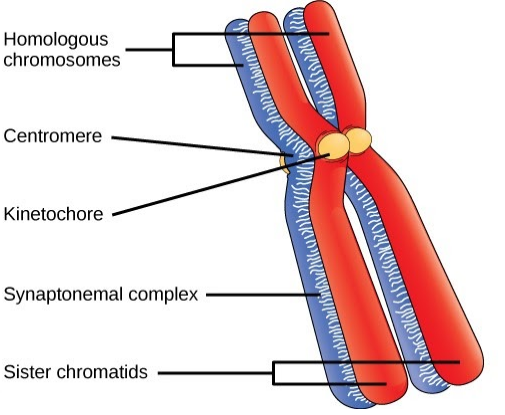
Chromosomes are made up of a long thread of DNA molecules, which is double-stranded in most of the species, most of the eukaryotic chromosomes include packaging proteins called histone protein, which form nucleosomes and together they form a condensed structure called chromosomes.
DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid which is the genetic material and encodes protein during the translation process, DNA is made up of purine and pyrimidine nitrogenous base pairs that are opposite to each other and form double and triple hydrogen bond in between, the backbone is made up of deoxyribose sugar and a phosphate group. The long chain of DNA stretch is right-handed coiled and attached with histone protein molecule which stabilises the negatively charged DNA structure and Along with histone protein DNA for nucleosome and number of nucleosomes coiled together and give rise to chromosome structure.
Note:
Chromosomes are divided into two types that named as autosome and sex chromosome which function different and encode a different protein which is used the various development process in the individual. Their number may vary in different species, in case of human 23 pair of chromosomes are found in which 22 are autosome and last 23rd act as sex chromosomes.
Complete solution:
Chromosomes are the thread-like structure that is present in the condensed form either in the nucleus or cell cytoplasm. The number of the chromosome is different in different species that regulate the life processes.

Chromosomes are made up of a long thread of DNA molecules, which is double-stranded in most of the species, most of the eukaryotic chromosomes include packaging proteins called histone protein, which form nucleosomes and together they form a condensed structure called chromosomes.
DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid which is the genetic material and encodes protein during the translation process, DNA is made up of purine and pyrimidine nitrogenous base pairs that are opposite to each other and form double and triple hydrogen bond in between, the backbone is made up of deoxyribose sugar and a phosphate group. The long chain of DNA stretch is right-handed coiled and attached with histone protein molecule which stabilises the negatively charged DNA structure and Along with histone protein DNA for nucleosome and number of nucleosomes coiled together and give rise to chromosome structure.
Note:
Chromosomes are divided into two types that named as autosome and sex chromosome which function different and encode a different protein which is used the various development process in the individual. Their number may vary in different species, in case of human 23 pair of chromosomes are found in which 22 are autosome and last 23rd act as sex chromosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




