
Draw and explain the clover-like life structure of nucleic acid and molecules.
Answer
518.4k+ views
Hint: Nucleotides are monomers that are the building blocks of DNA and RNA polymers. Each nucleotide consists of three components- a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. These DNA or RNA nucleic acids are macromolecules made of these nucleotide units.
Complete answer:
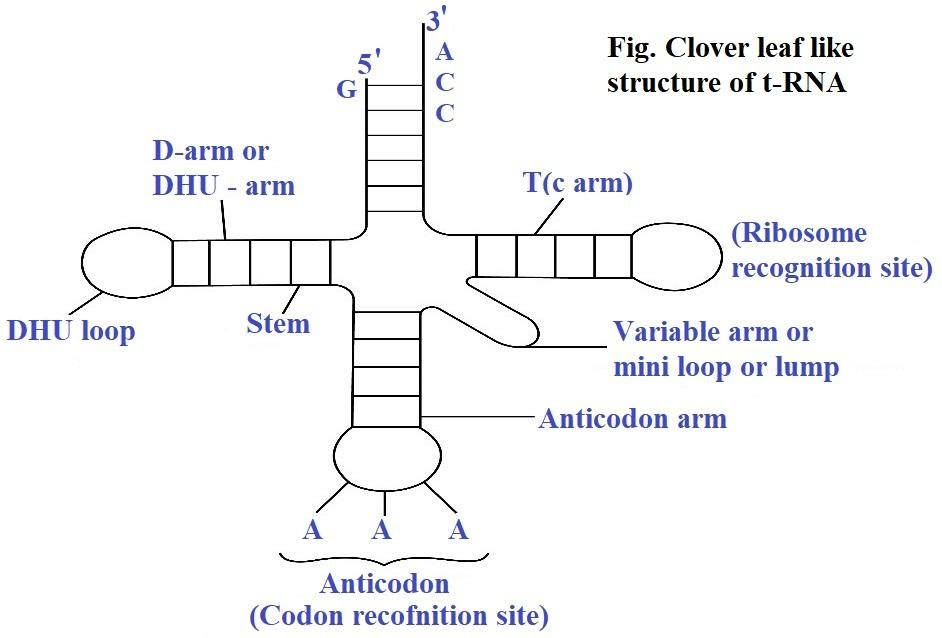
A special type of RNA nucleic acid, discovered by Franck Crick, known as the transfer RNA or tRNA is a short chain of the nucleotide of RNA. The tRNA decodes the sequence of mRNA into a protein for gene expression. The tRNA is a three-leaf clover structure with special hairpin-like loops.
Each tRNA molecule has two important parts, the anticodon and the specific site for attaching amino acid. Anticodon is a sequence presence on the hairpin loop of tRNA, which is responsible for recognizing and decoding an mRNA codon.
In the cloverleaf model, the tRNA is folded to form five arms which are single chains. The folding is from $3$’ to $5$’ which lies adjacent to each other. The loops are not paired, and the arm which is not folded into a loop is called the acceptor arm. It is the site for amino acid-binding. The DNA arm is the second arm that recognizes the amino acid activating synthetase enzyme. There is a variable arm as the fourth arm and the T-arm is the ribosome recognition site.
Note:
According to Frank Crick, about \[15\] percent of the total RNA structure consists of tRNA. Most of the tRNA is soluble RNA or sRNA before it postulates genetic code. The role of tRNA is to attach to the codons on the mRNA template and add a corresponding amino acid in the polypeptide chain. tRNA is, therefore, known as translator RNA because it translates the language of RNA into proteins.
Complete answer:
A special type of RNA nucleic acid, discovered by Franck Crick, known as the transfer RNA or tRNA is a short chain of the nucleotide of RNA. The tRNA decodes the sequence of mRNA into a protein for gene expression. The tRNA is a three-leaf clover structure with special hairpin-like loops.
Each tRNA molecule has two important parts, the anticodon and the specific site for attaching amino acid. Anticodon is a sequence presence on the hairpin loop of tRNA, which is responsible for recognizing and decoding an mRNA codon.
In the cloverleaf model, the tRNA is folded to form five arms which are single chains. The folding is from $3$’ to $5$’ which lies adjacent to each other. The loops are not paired, and the arm which is not folded into a loop is called the acceptor arm. It is the site for amino acid-binding. The DNA arm is the second arm that recognizes the amino acid activating synthetase enzyme. There is a variable arm as the fourth arm and the T-arm is the ribosome recognition site.

Note:
According to Frank Crick, about \[15\] percent of the total RNA structure consists of tRNA. Most of the tRNA is soluble RNA or sRNA before it postulates genetic code. The role of tRNA is to attach to the codons on the mRNA template and add a corresponding amino acid in the polypeptide chain. tRNA is, therefore, known as translator RNA because it translates the language of RNA into proteins.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




