
Draw a flowchart to show the process of cloning.
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: In biotechnology, cloning is a process of creating clones (exact copies of parents) of organisms, copies of cells or DNA (deoxyribo nucleic acid) fragments. The term clone is derived from ancient work. The term clone was coined by Herbert J. Webber.
Complete answer:
Types of the cloning:
There are two types of cloning-
1.Reproductive cloning – Reproductive cloning involves the implantation of a cloned embryo in the uterus of a surrogate mother. The embryo develops into the fetus.
2.Therapeutic cloning – Therapeutic cloning is used to clone embryos for the purpose of extracting stem cells from them. In therapeutic cloning, the cloned embryo is not implanted into the uterus of the surrogate mother.
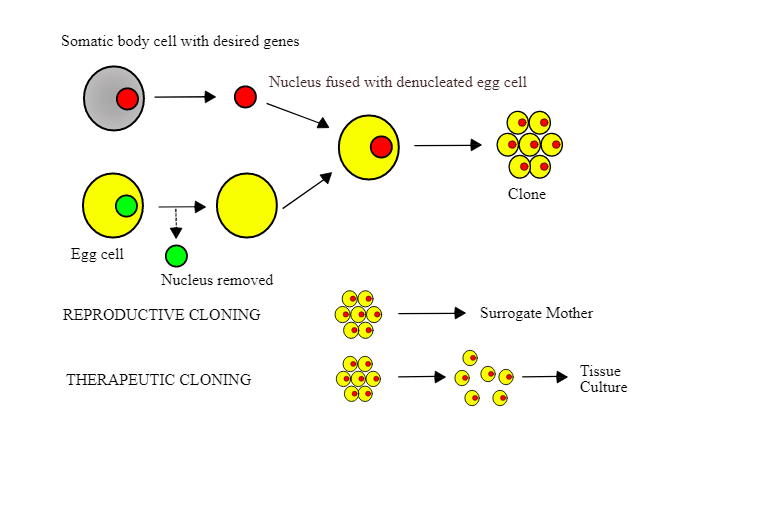
Process of cloning:
1.First the nucleus is isolated from the somatic cell (cells of the whole body) of an organism.
2.The nucleus of the egg cell is removed in order to make it enucleated (without nucleus).
3.The nucleus of the somatic cell is transplanted into the enucleated egg cell in order to make a clone..
4.In reproductive cloning, this cloned egg cell is transplanted to the uterus of the surrogate mother.
5.In therapeutic cloning the cloned egg cell grows artificially.
Note: With the help of the reproductive cloning, Ian Wilmut and his colleagues make a sheep whose name is Dolly sheep. The newly cloned egg cell contains the nucleus of the mammary gland. The Dolly sheep was cloned by fusing the nucleus from a mammary gland of a Finn Dorset ewe into an enucleated egg cell which was taken from a Scottish Blackface ewe.
Complete answer:
Types of the cloning:
There are two types of cloning-
1.Reproductive cloning – Reproductive cloning involves the implantation of a cloned embryo in the uterus of a surrogate mother. The embryo develops into the fetus.
2.Therapeutic cloning – Therapeutic cloning is used to clone embryos for the purpose of extracting stem cells from them. In therapeutic cloning, the cloned embryo is not implanted into the uterus of the surrogate mother.

Process of cloning:
1.First the nucleus is isolated from the somatic cell (cells of the whole body) of an organism.
2.The nucleus of the egg cell is removed in order to make it enucleated (without nucleus).
3.The nucleus of the somatic cell is transplanted into the enucleated egg cell in order to make a clone..
4.In reproductive cloning, this cloned egg cell is transplanted to the uterus of the surrogate mother.
5.In therapeutic cloning the cloned egg cell grows artificially.
Note: With the help of the reproductive cloning, Ian Wilmut and his colleagues make a sheep whose name is Dolly sheep. The newly cloned egg cell contains the nucleus of the mammary gland. The Dolly sheep was cloned by fusing the nucleus from a mammary gland of a Finn Dorset ewe into an enucleated egg cell which was taken from a Scottish Blackface ewe.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




