
Draw a diagram that explains the formation of an image by a plane mirror.
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: The images formed by a plane mirror are always virtual (rays appear to converge behind the mirror) and erect/upright, and formed on the opposite side of the mirror as the object(s). The image and object are at the same distance from a mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
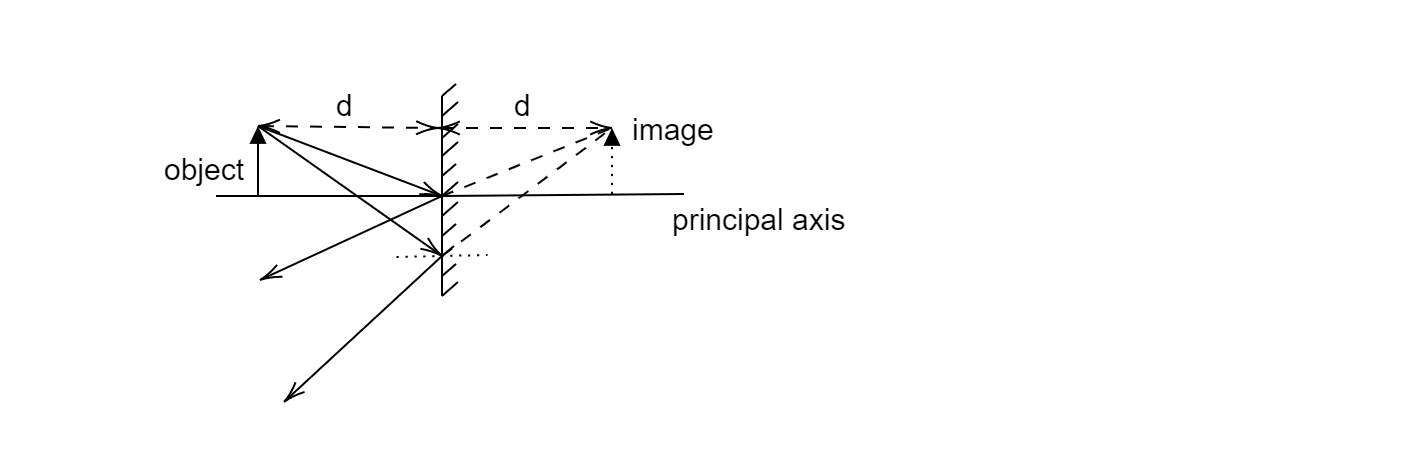
In the above image, we have drawn two rays from the top of the object and extended the reflected rays behind the mirror until they meet at a point. This point will be the image of the top of the object. The ray(s) incident from the bottom of the image will travel along the principal axis. It’s also clear from the diagram that the distance from the object to the mirror is equal to the distance from the mirror to the image (both equal to d).
Additional Information: While drawing the incident rays and the reflected rays, keep in mind that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection (angle is measured from the normal at the point(s) of incidence). The height of the image is exactly equal to the height of the object and hence we can say that a plane mirror has a magnification of 1 (magnification is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object).
Note: It is not mandatory to consider only the rays shown in the above diagram. Alternatively, we can consider one ray from the top of the object incident at the point of intersection of the principal axis and the mirror and the other ray from the top traveling parallel to the principal axis, incident normally at the mirror surface.
Complete step by step answer:

In the above image, we have drawn two rays from the top of the object and extended the reflected rays behind the mirror until they meet at a point. This point will be the image of the top of the object. The ray(s) incident from the bottom of the image will travel along the principal axis. It’s also clear from the diagram that the distance from the object to the mirror is equal to the distance from the mirror to the image (both equal to d).
Additional Information: While drawing the incident rays and the reflected rays, keep in mind that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection (angle is measured from the normal at the point(s) of incidence). The height of the image is exactly equal to the height of the object and hence we can say that a plane mirror has a magnification of 1 (magnification is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object).
Note: It is not mandatory to consider only the rays shown in the above diagram. Alternatively, we can consider one ray from the top of the object incident at the point of intersection of the principal axis and the mirror and the other ray from the top traveling parallel to the principal axis, incident normally at the mirror surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




