
How would you determine the formal charges on each atom in the carbonate ion \[C{{O}_{3}}{{^{2}}^{-}}\text{ }?\]
Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: We know the concept of the formal charge of an atom in a molecule is defined as the hypothetical charge an atom has if we could easily re-distribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. The Alternate way of understanding this is that formal charge results when we take it into consideration the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom and when we subtract the nonbonding electron and then again subtract the numbers of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We acquired the formal charges by understanding the Lewis structure; we got the number of electrons from their respective atomic numbers of each element and added $2$ electron to represent the charge. The formal charge which lies on the most electro negatively attached atom i.e. the oxygen atoms is given by:
\[C{{O}_{3}}{{^{2}}^{-}}\text{ }\left( 3\times 6 \right)+4+2\text{ }=\text{ }24\]
Here the valence electron is to distribute around $4$ centers.
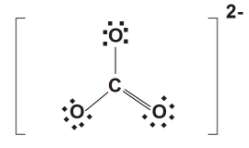
A Lewis structure of $O=C{{(-{{O}^{-}})}^{2}}$ give neutral double oxygen a neutral carbon and two anionic oxygen atom of compound associated with other $7$ valence electrons and of course we can draw resonance structure to show equality of the oxygen atom.
Note:
i) Note that the hypothetical formal charges are here to determine the most appropriate Lewis Structure. ii) A structure in which formal charges are as close as to zero and is possibly most preferable.
iii) Most likely resonance occurs in cases where two Lewis Structures with identical arrangement of atom along with stimuli different distribution of electron can be written with it.
iv) The actual distribution of Electron and the resonance is the hybrid an average of the distribution which indicates by the individual Lewis structures the resonance form.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We acquired the formal charges by understanding the Lewis structure; we got the number of electrons from their respective atomic numbers of each element and added $2$ electron to represent the charge. The formal charge which lies on the most electro negatively attached atom i.e. the oxygen atoms is given by:
\[C{{O}_{3}}{{^{2}}^{-}}\text{ }\left( 3\times 6 \right)+4+2\text{ }=\text{ }24\]
Here the valence electron is to distribute around $4$ centers.

A Lewis structure of $O=C{{(-{{O}^{-}})}^{2}}$ give neutral double oxygen a neutral carbon and two anionic oxygen atom of compound associated with other $7$ valence electrons and of course we can draw resonance structure to show equality of the oxygen atom.
Note:
i) Note that the hypothetical formal charges are here to determine the most appropriate Lewis Structure. ii) A structure in which formal charges are as close as to zero and is possibly most preferable.
iii) Most likely resonance occurs in cases where two Lewis Structures with identical arrangement of atom along with stimuli different distribution of electron can be written with it.
iv) The actual distribution of Electron and the resonance is the hybrid an average of the distribution which indicates by the individual Lewis structures the resonance form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




