
When $CHC{{l}_{3}}$ is boiled with $NaOH$, It gives
A. Formic acid
B. Trihydroxy methane
C. Acetylene
D. Sodium formate
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Trichloromethane, or Chloroform is a famous chemical compound and the formula of this chemical compound is $CHC{{l}_{3}}$. Chloroform undergoes a nucleophilic substitution reaction $({{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}})$ in the presence of a strong base In a ${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$ reaction where a carbon – leaving group bond is broken and carbon-nucleophile bond formation takes place simultaneously.
Complete step by step solution:
Chloroform undergoes a nucleophilic ${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$ reaction in the presence of a strong base like sodium hydroxide,$NaOH$. Chloroform has three electronegative chlorine $(Cl)$ Chlorine has an inductive effect $(-I)$ and they strongly attract the electron from the central carbon atom. and also from the hydrogen atom Therefore central carbon atom goes electron deficient A incoming strong nucleophile-like $O{{H}^{-}}$ attacks on the electron-deficient carbon atom and substituted all the chlorine atoms $(Cl)$with three hydroxyl group $(OH)$
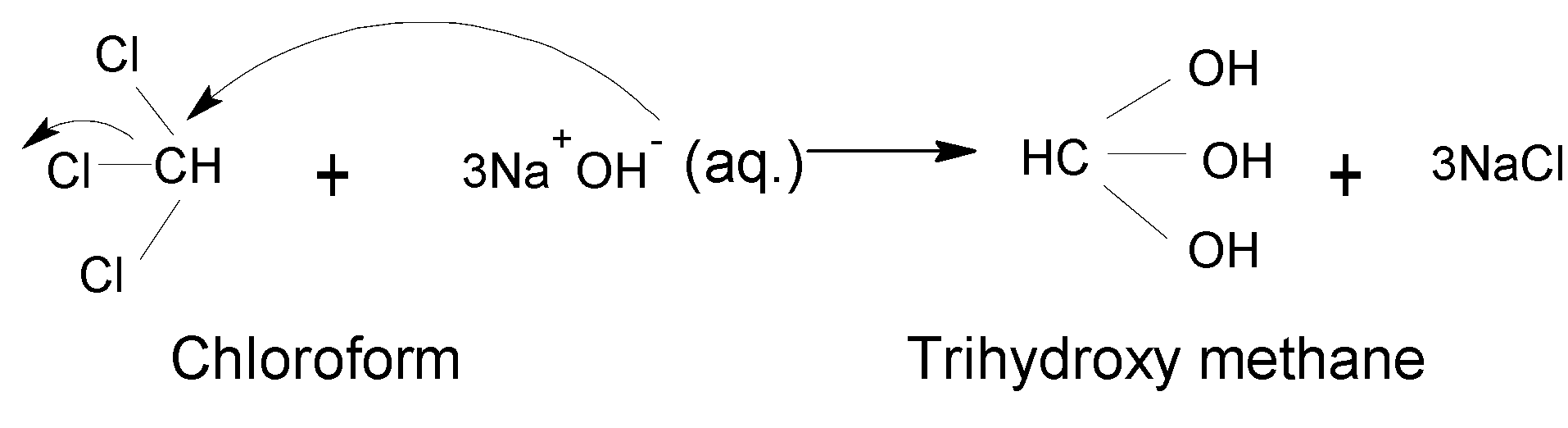
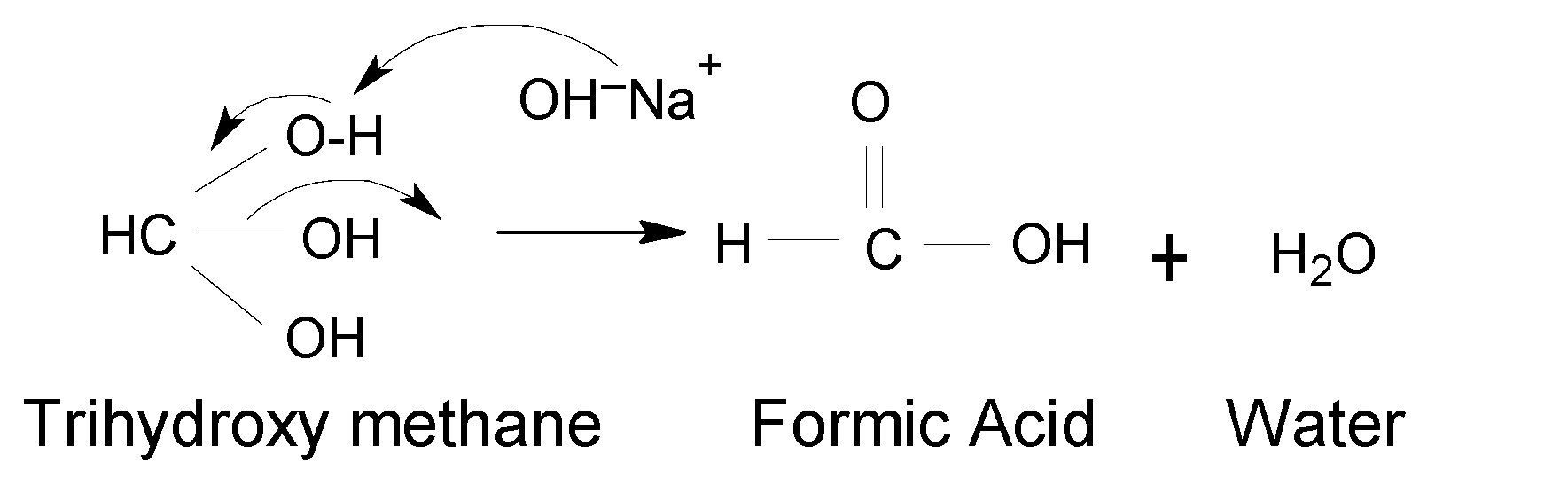
Finally, Trihydroxy methane is produced but it is very unstable. Because more than one $(OH)$ group on one carbon atom is very unstable as the carbon atom becomes more electropositive and it can easily attack even weak nucleophiles. It undergoes further reaction and converts to the final product as formic acid by removing one water molecule forming Trihydroxy methane. Thus, the final product is stable.
Thus, Option (A) is correct
Note: Chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide is a useful reagent in the very famous Reimer-Tiemann reaction via electrophilic substitution reaction. In this reaction, a carbene intermediate is formed and the product salicylaldehyde is used as a crucial reagent and has many applications in our daily lives.
Complete step by step solution:
Chloroform undergoes a nucleophilic ${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$ reaction in the presence of a strong base like sodium hydroxide,$NaOH$. Chloroform has three electronegative chlorine $(Cl)$ Chlorine has an inductive effect $(-I)$ and they strongly attract the electron from the central carbon atom. and also from the hydrogen atom Therefore central carbon atom goes electron deficient A incoming strong nucleophile-like $O{{H}^{-}}$ attacks on the electron-deficient carbon atom and substituted all the chlorine atoms $(Cl)$with three hydroxyl group $(OH)$

Finally, Trihydroxy methane is produced but it is very unstable. Because more than one $(OH)$ group on one carbon atom is very unstable as the carbon atom becomes more electropositive and it can easily attack even weak nucleophiles. It undergoes further reaction and converts to the final product as formic acid by removing one water molecule forming Trihydroxy methane. Thus, the final product is stable.

Thus, Option (A) is correct
Note: Chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide is a useful reagent in the very famous Reimer-Tiemann reaction via electrophilic substitution reaction. In this reaction, a carbene intermediate is formed and the product salicylaldehyde is used as a crucial reagent and has many applications in our daily lives.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




