
When carbon and oxygen bond, the molecules contain how many pairs of bonding electrons?
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: The valence electrons are those electrons which take part in chemical bonding. The valence electrons in carbon is 4 and the valence electrons in oxygen is 6. The bonding electrons are those which form bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
There are many compounds where the carbon atom and oxygen atoms bond to form a compound. The number of carbon atoms and oxygen atoms can be more than one.
In carbon monoxide, the carbon atom is directly bonded to the oxygen atom. The molecular formula of carbon monoxide is CO. In carbon monoxide the carbon atom is bonded to oxygen atom by triple bond where one sigma bond is present and two pi bonds. The atomic number of carbon is 6 and the electronic configuration of carbon is $[He]2{s^2}2{p^2}$. The valence electrons in carbon is 4. The atomic number oxygen is 8 and the electronic configuration is $[He]2{s^2}2{p^4}$. The valence electrons in oxygen in 6. The total valence electrons in a carbon monoxide molecule is 10. For forming a triple bond between the carbon and oxygen atom, three electrons are shared by each atom. Total 6 valence electrons are used for bonding and are called bonding electrons and four valence electrons are the non-bonding electrons which are present as two electron pairs in carbon atom and oxygen atom.
The structure of carbon monoxide is shown below.
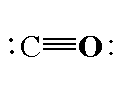
Note:
The other examples where the carbon and oxygen atoms are bonded is carbon dioxide, ethers which are represented as R-O-R where R is the alkyl group. In carbon dioxide the carbon atom is bonded with two oxygen with double bond. In ether the carbon is bonded with oxygen by double bond.
Complete step by step answer:
There are many compounds where the carbon atom and oxygen atoms bond to form a compound. The number of carbon atoms and oxygen atoms can be more than one.
In carbon monoxide, the carbon atom is directly bonded to the oxygen atom. The molecular formula of carbon monoxide is CO. In carbon monoxide the carbon atom is bonded to oxygen atom by triple bond where one sigma bond is present and two pi bonds. The atomic number of carbon is 6 and the electronic configuration of carbon is $[He]2{s^2}2{p^2}$. The valence electrons in carbon is 4. The atomic number oxygen is 8 and the electronic configuration is $[He]2{s^2}2{p^4}$. The valence electrons in oxygen in 6. The total valence electrons in a carbon monoxide molecule is 10. For forming a triple bond between the carbon and oxygen atom, three electrons are shared by each atom. Total 6 valence electrons are used for bonding and are called bonding electrons and four valence electrons are the non-bonding electrons which are present as two electron pairs in carbon atom and oxygen atom.
The structure of carbon monoxide is shown below.
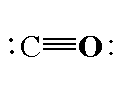
Note:
The other examples where the carbon and oxygen atoms are bonded is carbon dioxide, ethers which are represented as R-O-R where R is the alkyl group. In carbon dioxide the carbon atom is bonded with two oxygen with double bond. In ether the carbon is bonded with oxygen by double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE




