
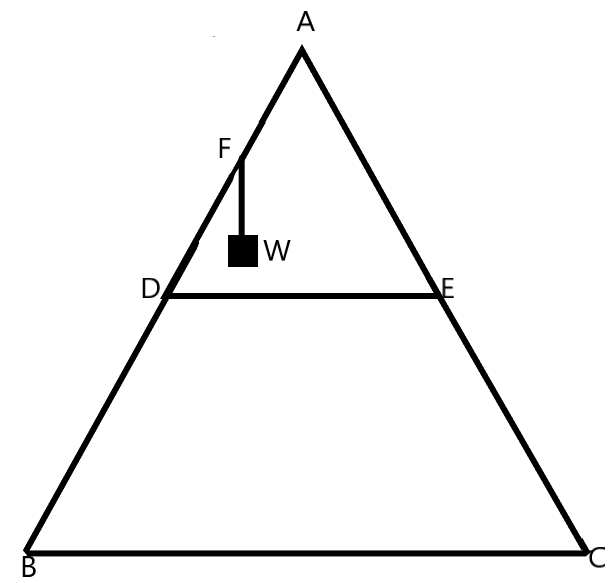
As shown in figure, the two sides of a step ladder BA and CA are 1.6 m long and hinged at A. A rope, DE of 0.5 m is tied half way up. A weight 40 kg is suspended from a point F, 1.2 m from B along the ladder BA. Assuming the floor to be frictionless and neglecting the weight of the ladder, find the tension in the rope and forces exerted by the floor on the ladder. (Take \[g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}\]) (Hint: Consider the equilibrium of each side of the ladder separately.)

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: We need to find the relation between the mass hanging on a side of the step ladder, the tension that is experienced by the rope on which the mass is hanging and the force acting on the floor due to this mass on one side of the ladder.
Complete answer:
We are given a step ladder which consists of two ladders of equal length attached at a point P and inclined at an equal angle with the vertical. A mass is hung on one ladder maintaining the equilibrium conditions.
We know that for the ladder to be at rest on the floor, the normal reaction acting at the base of the two ladders should be balancing the mass hung on the system. This can be given as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{N}_{B}}+{{N}_{C}}-mg=0\text{ } \\
& \Rightarrow {{N}_{B}}+{{N}_{C}}=40(9.8)\text{ } \\
& \therefore {{N}_{B}}+{{N}_{C}}=392N\text{ --}(1) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, for the system to be in rotational equilibrium, i.e., the torque at the point A on the step ladder should be balanced by the rotational moments of the two ladders. IN order to find the distances involved in equating the torque we need to find some of the lengths using very familiar triangular relations.
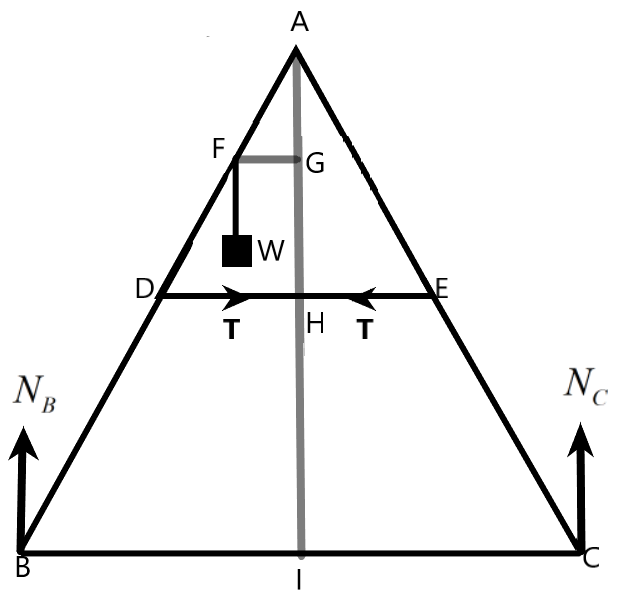
Consider \[\Delta \text{ABC}\], let D be the midpoint of the side AB, also, I is the midpoint of BC, therefore, from the geometry we can conclude that –
\[\begin{align}
& BC=2DE=1m, \\
& BI=2DH=0.5m \\
& \text{and,} \\
& AD=\dfrac{1}{2}BA=0.8m \\
\end{align}\]
Also, F is the midpoint of the side AD,
\[\therefore FG=\dfrac{1}{2}DH=0.125m\]
Now, we can find the side AH as –
\[\begin{align}
& AH=\sqrt{A{{D}^{2}}-D{{H}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AH=\sqrt{{{0.8}^{2}}-{{0.25}^{2}}} \\
& \therefore AH=0.76m \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we can find the balancing moment about the point A as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{N}_{B}}(BI)+T(AH)={{N}_{C}}(CI)+T(AH)+mg(FG) \\
& \Rightarrow {{N}_{B}}(0.5m)-{{N}_{C}}(0.5m)=(0.125)(40kg)(9.8) \\
& \therefore {{N}_{B}}-{{N}_{C}}=98N\text{ --(2)} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we can find the normal reaction at point B and C by solving equations (1) and (2) as –
\[\therefore {{N}_{B}}=245N\text{ and }{{N}_{C}}=147N\]
Now, we can find the tension on the rope along DE as –
\[\begin{align}
& mg(FG)+T(AH)={{N}_{B}}(BI) \\
& \Rightarrow (40)(9.8)(0.125)+0.76T-(245)(0.5)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow T=\dfrac{122.5-49}{0.76} \\
& \therefore T=96.71N \\
\end{align}\]
So, this is the required tension acting on the rope along DE.
The normal forces on the floor are given as 245N at point B and 147N at point C.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The equilibrium conditions for a step ladder are to be treated with extreme care. The normal reaction on one end of the system will be different from the other depending on the mass on the ladder and position of the mass as we have seen here.
Complete answer:
We are given a step ladder which consists of two ladders of equal length attached at a point P and inclined at an equal angle with the vertical. A mass is hung on one ladder maintaining the equilibrium conditions.

We know that for the ladder to be at rest on the floor, the normal reaction acting at the base of the two ladders should be balancing the mass hung on the system. This can be given as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{N}_{B}}+{{N}_{C}}-mg=0\text{ } \\
& \Rightarrow {{N}_{B}}+{{N}_{C}}=40(9.8)\text{ } \\
& \therefore {{N}_{B}}+{{N}_{C}}=392N\text{ --}(1) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, for the system to be in rotational equilibrium, i.e., the torque at the point A on the step ladder should be balanced by the rotational moments of the two ladders. IN order to find the distances involved in equating the torque we need to find some of the lengths using very familiar triangular relations.

Consider \[\Delta \text{ABC}\], let D be the midpoint of the side AB, also, I is the midpoint of BC, therefore, from the geometry we can conclude that –
\[\begin{align}
& BC=2DE=1m, \\
& BI=2DH=0.5m \\
& \text{and,} \\
& AD=\dfrac{1}{2}BA=0.8m \\
\end{align}\]
Also, F is the midpoint of the side AD,
\[\therefore FG=\dfrac{1}{2}DH=0.125m\]
Now, we can find the side AH as –
\[\begin{align}
& AH=\sqrt{A{{D}^{2}}-D{{H}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AH=\sqrt{{{0.8}^{2}}-{{0.25}^{2}}} \\
& \therefore AH=0.76m \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we can find the balancing moment about the point A as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{N}_{B}}(BI)+T(AH)={{N}_{C}}(CI)+T(AH)+mg(FG) \\
& \Rightarrow {{N}_{B}}(0.5m)-{{N}_{C}}(0.5m)=(0.125)(40kg)(9.8) \\
& \therefore {{N}_{B}}-{{N}_{C}}=98N\text{ --(2)} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we can find the normal reaction at point B and C by solving equations (1) and (2) as –
\[\therefore {{N}_{B}}=245N\text{ and }{{N}_{C}}=147N\]
Now, we can find the tension on the rope along DE as –
\[\begin{align}
& mg(FG)+T(AH)={{N}_{B}}(BI) \\
& \Rightarrow (40)(9.8)(0.125)+0.76T-(245)(0.5)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow T=\dfrac{122.5-49}{0.76} \\
& \therefore T=96.71N \\
\end{align}\]
So, this is the required tension acting on the rope along DE.
The normal forces on the floor are given as 245N at point B and 147N at point C.
This is the required solution.
Note:
The equilibrium conditions for a step ladder are to be treated with extreme care. The normal reaction on one end of the system will be different from the other depending on the mass on the ladder and position of the mass as we have seen here.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




