
What are carbocations? Discuss their various types.
Answer
519k+ views
Hint: As the name suggests, it is a cation, meaning it has a positive charge and ‘carbo’ refers to a carbon atom.There are various types of carbocations which we will learn through this question.
Complete answer:
-Carbocations are the beggars in organic chemistry, Basically it is a molecule in which a carbon atom has a positive charge and three bonds. It is also known as carbonium ion. They are called beggars because these are electron deficient species(as they have six valence electrons) and thus are very reactive and unstable.
-General structure of carbocation is
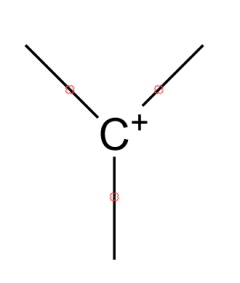
-These bonds are kept empty because anything can come at this place.
-Generally there are four types of carbocation. These are:
-Methyl carbocation: When all bonds attached to \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\] are substituted with hydrogen atoms, it is called methyl carbocation.
-Primary carbocation: When any two of bonds attached to \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\]are substituted with hydrogen atoms and the remaining bond is substituted with \[C{{H}_{3}}\] group, it is called primary carbocation.
-Secondary carbocation: When any two of bonds attached to \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\]are substituted with \[C{{H}_{3}}\] group and the remaining bond is substituted with hydrogen atom, it is called secondary carbocation.
-Tertiary carbocation: When all bonds attached to \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\] are substituted with \[C{{H}_{3}}\] group, it is called tertiary carbocation.
-Carbocation stability increases as methyl substitution increases around the electron deficient \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\]. The methyl groups are electron donating groups and therefore stabilize the positive charge by inductive effect. So tertiary carbocation is the most stable among the above listed carbocations.
Note:
There are other types of carbocation also like allylic carbocation(If there is a carbon-carbon double bond next to the carbon with the positive charge), benzylic carbocation(If the carbon having a positive charge is immediately next to a benzene ring). Resonance stabilized carbocation is more stable than the carbocation stabilized by inductive effect.
Complete answer:
-Carbocations are the beggars in organic chemistry, Basically it is a molecule in which a carbon atom has a positive charge and three bonds. It is also known as carbonium ion. They are called beggars because these are electron deficient species(as they have six valence electrons) and thus are very reactive and unstable.
-General structure of carbocation is

-These bonds are kept empty because anything can come at this place.
-Generally there are four types of carbocation. These are:
-Methyl carbocation: When all bonds attached to \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\] are substituted with hydrogen atoms, it is called methyl carbocation.
-Primary carbocation: When any two of bonds attached to \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\]are substituted with hydrogen atoms and the remaining bond is substituted with \[C{{H}_{3}}\] group, it is called primary carbocation.
-Secondary carbocation: When any two of bonds attached to \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\]are substituted with \[C{{H}_{3}}\] group and the remaining bond is substituted with hydrogen atom, it is called secondary carbocation.
-Tertiary carbocation: When all bonds attached to \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\] are substituted with \[C{{H}_{3}}\] group, it is called tertiary carbocation.
-Carbocation stability increases as methyl substitution increases around the electron deficient \[{{C}^{\oplus }}\]. The methyl groups are electron donating groups and therefore stabilize the positive charge by inductive effect. So tertiary carbocation is the most stable among the above listed carbocations.
Note:
There are other types of carbocation also like allylic carbocation(If there is a carbon-carbon double bond next to the carbon with the positive charge), benzylic carbocation(If the carbon having a positive charge is immediately next to a benzene ring). Resonance stabilized carbocation is more stable than the carbocation stabilized by inductive effect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




