
According to Markownikoff rule, the product formed by the reaction of 1-butene with water is:
(A) Primary alcohol
(B) Secondary alcohol
(C) Tertiary alcohol
(D) None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: According to the Markownikoff rule, the major product formed in such reactions is the one where acidic hydrogen gets attached to the carbon atom having maximum number of hydrogen atoms while the halide ion attaches to the carbon atom having the least number of hydrogen atoms attached to it.
Complete step by step answer:
- First we will talk about Markownikoff rule.
This rule basically helps describe the outcome of a chemical addition reaction on asymmetrical alkenes. According to this rule: When we add a protic acid (HX) to an asymmetrical alkene, the acidic hydrogen will attach itself to the carbon atom having greater number of hydrogen substituents, while the halide group gets attached to the carbon atom having greater number of alkyl substituents.
In simple words: the hydrogen atom attaches to the carbon with most number of hydrogen atoms and halide attaches to the carbon atom having least number of hydrogen atoms.
For example: let us take propene and react it with HBr.
${H_3}C - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}{H_3}C - CH(Br) - C{H_3} + {H_3}C - C{H_2} - C{H_2}(Br)$
Where, ${H_3}C - CH(Br) - C{H_3}$ is a major product and ${H_3}C - C{H_2} - C{H_2}(Br)$ is the minor product.
-Now we will see the structure of 1-butene and then its reaction with water according to Markownikoff rule.
The structure of 1-butene is:
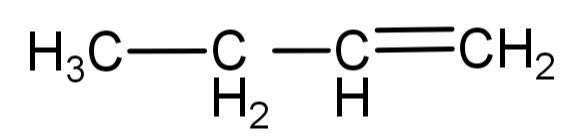
When it reacts with water, the hydroxyl group (-OH) gets attached to the carbon atom which has least number of hydrogen atoms (the secondary carbon) while the hydrogen ion will attach to the carbon atom with the most number of hydrogen atoms. The reaction will be:

So, the major product will be butan-2-ol which is a secondary alcohol.
The correct option will be: (B) Secondary alcohol.
Note: Here the carbon atom with least number of hydrogen atoms or the carbon with maximum alkyl groups is the major product because the tertiary and secondary carbocations formed as intermediates are more stable than primary carbocations. The stability order for carbocations is: Tertiary (${3^ \circ }$) > Secondary (${2^ \circ }$) > Primary (${1^ \circ }$).
Complete step by step answer:
- First we will talk about Markownikoff rule.
This rule basically helps describe the outcome of a chemical addition reaction on asymmetrical alkenes. According to this rule: When we add a protic acid (HX) to an asymmetrical alkene, the acidic hydrogen will attach itself to the carbon atom having greater number of hydrogen substituents, while the halide group gets attached to the carbon atom having greater number of alkyl substituents.
In simple words: the hydrogen atom attaches to the carbon with most number of hydrogen atoms and halide attaches to the carbon atom having least number of hydrogen atoms.
For example: let us take propene and react it with HBr.
${H_3}C - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{HBr}}{H_3}C - CH(Br) - C{H_3} + {H_3}C - C{H_2} - C{H_2}(Br)$
Where, ${H_3}C - CH(Br) - C{H_3}$ is a major product and ${H_3}C - C{H_2} - C{H_2}(Br)$ is the minor product.
-Now we will see the structure of 1-butene and then its reaction with water according to Markownikoff rule.
The structure of 1-butene is:
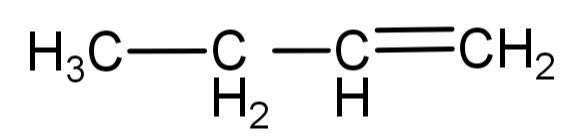
When it reacts with water, the hydroxyl group (-OH) gets attached to the carbon atom which has least number of hydrogen atoms (the secondary carbon) while the hydrogen ion will attach to the carbon atom with the most number of hydrogen atoms. The reaction will be:

So, the major product will be butan-2-ol which is a secondary alcohol.
The correct option will be: (B) Secondary alcohol.
Note: Here the carbon atom with least number of hydrogen atoms or the carbon with maximum alkyl groups is the major product because the tertiary and secondary carbocations formed as intermediates are more stable than primary carbocations. The stability order for carbocations is: Tertiary (${3^ \circ }$) > Secondary (${2^ \circ }$) > Primary (${1^ \circ }$).
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




