
A tube filled with water and closed at both ends uniformly rotates in a horizontal plane about the OO' axis. The manometers A and B fixed in the tube at distances ${r_1}$ and ${r_2}$ from rotational axis indicate pressure ${p_1}$ and ${p_2}$ , respectively. Determine the angular velocity $\omega $ of rotation of the tube:
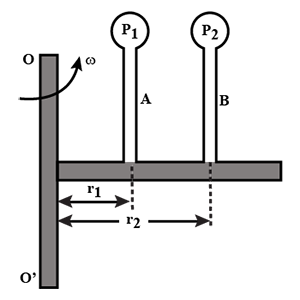
(A) $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2({p_2} - {p_1})}}{{\rho (r_1^2 - r_2^2)}}} $
(B) $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2({p_2} - {p_1})}}{{\rho (r_1^2 + r_2^2)}}} $
(C) $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2(r_2^2 - r_1^2)}}{{({p_2} - {p_1})}}} $
(D) $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2({p_2} - {p_1})}}{{\rho {r_1}{r_2}}}} $
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint We know Bernoulli equation relates the speed of the fluid at a point, the pressure at that point and the height of that point above the reference level. Bernoulli equation is given by:
$P + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2} = $ constant
Since height is the same for both A and B hence $\rho gh$ term can be neglected.
Complete Step by step solution
On applying Bernoulli equation separately for A and B we get,
For A, ${p_1}$ is the reading shown in the barometer.
Hence, \[{p_1} + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_1}^2 = \] constant…… (1)
For B, ${p_2}$ is the reading shown in the barometer.
Hence, \[{p_2} + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_2^2 = \] constant…… (2)
From equation (1) and (2) we get
\[
{p_1} + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_1^2 = {p_2} + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_2^2 \\
{p_1} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_1^2 = {p_2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_2^2 \\
\]
Now we know that $v = r\omega $
Therefore, above equation becomes
\[
{p_1}\rho {({r_1}\omega )^2} = {p_2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {({r_2}\omega )^2} \\
({p_2} - {p_1}) = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho ({r_1}^2 - {r_2}^2){\omega ^2} \\
\therefore {\omega ^2} = \dfrac{{2({p_2} - {p_1})}}{{\rho ({r_1}^2 - {r_2}^2)}} \\
\\
\]
$\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2({p_2} - {p_1})}}{{\rho (r_1^2 - r_2^2)}}} $
Hence the required angular velocity is, $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2({p_2} - {p_1})}}{{\rho (r_1^2 - r_2^2)}}} $
Option (A) is correct.
Note Bernoulli equation is just the application of work-energy theorem in the case of fluid flow. In the Bernoulli equation we make a few assumptions like the fluid is ideal i.e. incompressible and nonviscous, it has constant density, both points lie on a streamline, flow is steady and there is no friction.
$P + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2} = $ constant
Since height is the same for both A and B hence $\rho gh$ term can be neglected.
Complete Step by step solution
On applying Bernoulli equation separately for A and B we get,
For A, ${p_1}$ is the reading shown in the barometer.
Hence, \[{p_1} + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_1}^2 = \] constant…… (1)
For B, ${p_2}$ is the reading shown in the barometer.
Hence, \[{p_2} + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_2^2 = \] constant…… (2)
From equation (1) and (2) we get
\[
{p_1} + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_1^2 = {p_2} + \rho gh + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_2^2 \\
{p_1} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_1^2 = {p_2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho v_2^2 \\
\]
Now we know that $v = r\omega $
Therefore, above equation becomes
\[
{p_1}\rho {({r_1}\omega )^2} = {p_2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {({r_2}\omega )^2} \\
({p_2} - {p_1}) = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho ({r_1}^2 - {r_2}^2){\omega ^2} \\
\therefore {\omega ^2} = \dfrac{{2({p_2} - {p_1})}}{{\rho ({r_1}^2 - {r_2}^2)}} \\
\\
\]
$\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2({p_2} - {p_1})}}{{\rho (r_1^2 - r_2^2)}}} $
Hence the required angular velocity is, $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2({p_2} - {p_1})}}{{\rho (r_1^2 - r_2^2)}}} $
Option (A) is correct.
Note Bernoulli equation is just the application of work-energy theorem in the case of fluid flow. In the Bernoulli equation we make a few assumptions like the fluid is ideal i.e. incompressible and nonviscous, it has constant density, both points lie on a streamline, flow is steady and there is no friction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




