
A solid sphere of radius ${{R}_{1}}$ and volume charge density $\rho =\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{r}$ is enclosed by a hollow sphere of radius ${{R}_{2}}$ with negative surface charge density $\sigma $, such that the total charge in the system is zero, ${{\rho }_{0}}$ is positive constant and $r$ is the distance from the centre of the sphere. The ratio $\dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}}$ is ?
Answer
518.7k+ views
Hint:Surface charge density is the measure of charge per unit area. Volume charge density is the measure of charge distributed over a volume. Keep in mind the difference between sphere and a hollow sphere.
Complete step by step answer:
The charge density is a measure of charge per unit area or volume over which it is distributed. It can be either positive or negative.
Linear charge density: Linear charge density is represented by ratio of charge and length over which it is distributed. It is represented by $\lambda =\dfrac{q}{l}$
Surface charge density: Surface charge density is represented by the ratio of charge and the area over which it is distributed. It is represented by $\sigma =\dfrac{q}{A}$
Volume charge density: Volume charge density is the ratio of charge and the volume over which it is distributed. It is represented by
$\rho =\dfrac{q}{v}$
Where $q$ is the charge, $l$ is the length, $A$ is the area of the surface and $v$ is the volume of the body.
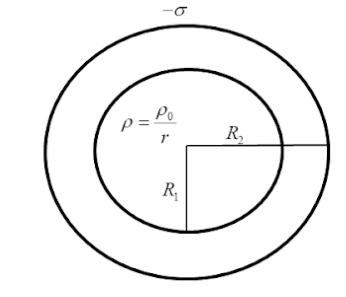
Charge on the outer sphere: $-4\pi R_{2}^{2}\sigma $
Charge on the inner sphere: For calculating charge on the inner sphere, let’s assume that the sphere with radius ${{R}_{2}}$ has another shell inside it with radius $r$ and thickness $d$r.The volume of the shell is equal to surface area $\times $ thickness.
Volume of shell: $\int{4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr}$
Charge : $\int{dQ}$=$\int{\rho \times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr}$
$\int{dQ}$=$\int{\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{r}\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr}$........(given that $\rho =\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{r}$)
$\int{dQ}$=$\int{{{\rho }_{0}}\times 4\pi rdr}$
Integrating from $0$ to $Q$ and from $0$ to ${{R}_{1}}$, we get
$\int\limits_{0}^{Q}{dQ}=\int\limits_{0}^{{{R}_{1}}}{{{\rho }_{0}}\times 4\pi rdr}$
$\Rightarrow Q=2\pi {{\rho }_{0}}R_{1}^{2}$
Therefore the charge on the inner sphere is $2\pi {{\rho }_{0}}R_{1}^{2}$. According to the question, total charge in the system is zero.
Hence, charge on outer sphere+charge on inner sphere=0
$(-4\pi R_{2}^{2}\sigma )+2\pi {{\rho }_{0}}R_{1}^{2}=0$
$\Rightarrow 2\pi {{\rho }_{0}}R_{1}^{2}=4\pi R_{2}^{2}\sigma $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{R_{2}^{2}}{R_{1}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{2\sigma }$
$\therefore \dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{2\sigma }}$
Hence, the ratio $\dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}}$ is $\sqrt{\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{2\sigma }}$.
Note:Keeping in mind the volume for a shell can save time and solve the problem much faster. When stuck, switch to the basic formulas and start from scratch. Remember there is a difference between a solid sphere and a hollow sphere.
Complete step by step answer:
The charge density is a measure of charge per unit area or volume over which it is distributed. It can be either positive or negative.
Linear charge density: Linear charge density is represented by ratio of charge and length over which it is distributed. It is represented by $\lambda =\dfrac{q}{l}$
Surface charge density: Surface charge density is represented by the ratio of charge and the area over which it is distributed. It is represented by $\sigma =\dfrac{q}{A}$
Volume charge density: Volume charge density is the ratio of charge and the volume over which it is distributed. It is represented by
$\rho =\dfrac{q}{v}$
Where $q$ is the charge, $l$ is the length, $A$ is the area of the surface and $v$ is the volume of the body.

Charge on the outer sphere: $-4\pi R_{2}^{2}\sigma $
Charge on the inner sphere: For calculating charge on the inner sphere, let’s assume that the sphere with radius ${{R}_{2}}$ has another shell inside it with radius $r$ and thickness $d$r.The volume of the shell is equal to surface area $\times $ thickness.
Volume of shell: $\int{4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr}$
Charge : $\int{dQ}$=$\int{\rho \times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr}$
$\int{dQ}$=$\int{\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{r}\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr}$........(given that $\rho =\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{r}$)
$\int{dQ}$=$\int{{{\rho }_{0}}\times 4\pi rdr}$
Integrating from $0$ to $Q$ and from $0$ to ${{R}_{1}}$, we get
$\int\limits_{0}^{Q}{dQ}=\int\limits_{0}^{{{R}_{1}}}{{{\rho }_{0}}\times 4\pi rdr}$
$\Rightarrow Q=2\pi {{\rho }_{0}}R_{1}^{2}$
Therefore the charge on the inner sphere is $2\pi {{\rho }_{0}}R_{1}^{2}$. According to the question, total charge in the system is zero.
Hence, charge on outer sphere+charge on inner sphere=0
$(-4\pi R_{2}^{2}\sigma )+2\pi {{\rho }_{0}}R_{1}^{2}=0$
$\Rightarrow 2\pi {{\rho }_{0}}R_{1}^{2}=4\pi R_{2}^{2}\sigma $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{R_{2}^{2}}{R_{1}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{2\sigma }$
$\therefore \dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{2\sigma }}$
Hence, the ratio $\dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}}$ is $\sqrt{\dfrac{{{\rho }_{0}}}{2\sigma }}$.
Note:Keeping in mind the volume for a shell can save time and solve the problem much faster. When stuck, switch to the basic formulas and start from scratch. Remember there is a difference between a solid sphere and a hollow sphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




