
A ladder 5 m long is leaning against a wall. The foot of the ladder is pulled out along the ground away from the wall at a rate of 2\[m{{s}^{-1}}\]. How fast is the height of the ladder on the wall decreasing at the instant when the floor of the ladder is 4 m away from the wall?
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: We need to find the relation between the height of the ladder and the speed at which the ladder is pulled off from the wall with the speed at which the height of the ladder decreases with the wall. We can use the triangle relations to solve this.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given that a ladder is kept against a wall. It is said that the ladder is pulled from the bottom such that the base is moved away from the wall. This change in position is followed by the height of the ladder decreasing vertically.
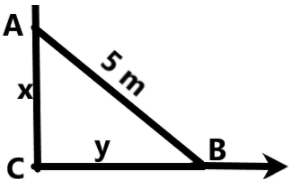
According to the Pythagoras theorem, the sum of the squares of the two sides of the right-angled triangle will be equal to the square of the hypotenuse. Here, we can understand from the figure that the hypotenuse is the length of the ladder which is always a constant, i.e., 5 m. So, at any time, the relation between the two sides and the length of the ladder can be given as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{z}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{5}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=25 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we know that the distance between the wall and the base of the ladder, y is increased at a rate of 2 \[m{{s}^{-1}}\], we can differentiate the above relation between the sides to get the rate of change of the height (x). This is given by –
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=25 \\
& \text{Differentiating with respect to time,} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x\dfrac{dx}{dt}+2y\dfrac{dy}{dt}=0 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \text{but,} \\
& \dfrac{dy}{dt}=2m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x\dfrac{dx}{dt}+4y=0 \\
& \therefore \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{4y}{2x}=\dfrac{2y}{x} \\
\end{align}\]
We can substitute any value in y and x such that it follows the Pythagoras theorem. We are given that y is 4 m. So, we can get the speed at which the height of the ladder decreases as –
\[\begin{align}
& y=4m \\
& \therefore x=3m \\
& \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{-2y}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{-2(4)}{3} \\
& \therefore \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{-8}{3}m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
The speed at which the height of the ladder decreases with the wall is \[\dfrac{8}{3}m{{s}^{-1}}\].
This is the required solution.
Note:
The speed at which the height of the ladder decreases with the wall is given with a negative sign. This is because as the distance ‘y’ from the wall to the base of the ladder is increasing the height of the ladder ‘x’ is decreasing, so the speed is negative.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given that a ladder is kept against a wall. It is said that the ladder is pulled from the bottom such that the base is moved away from the wall. This change in position is followed by the height of the ladder decreasing vertically.

According to the Pythagoras theorem, the sum of the squares of the two sides of the right-angled triangle will be equal to the square of the hypotenuse. Here, we can understand from the figure that the hypotenuse is the length of the ladder which is always a constant, i.e., 5 m. So, at any time, the relation between the two sides and the length of the ladder can be given as –
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{z}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{5}^{2}} \\
& \therefore {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=25 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we know that the distance between the wall and the base of the ladder, y is increased at a rate of 2 \[m{{s}^{-1}}\], we can differentiate the above relation between the sides to get the rate of change of the height (x). This is given by –
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=25 \\
& \text{Differentiating with respect to time,} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x\dfrac{dx}{dt}+2y\dfrac{dy}{dt}=0 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \text{but,} \\
& \dfrac{dy}{dt}=2m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x\dfrac{dx}{dt}+4y=0 \\
& \therefore \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{4y}{2x}=\dfrac{2y}{x} \\
\end{align}\]
We can substitute any value in y and x such that it follows the Pythagoras theorem. We are given that y is 4 m. So, we can get the speed at which the height of the ladder decreases as –
\[\begin{align}
& y=4m \\
& \therefore x=3m \\
& \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{-2y}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{-2(4)}{3} \\
& \therefore \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{-8}{3}m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}\]
The speed at which the height of the ladder decreases with the wall is \[\dfrac{8}{3}m{{s}^{-1}}\].
This is the required solution.
Note:
The speed at which the height of the ladder decreases with the wall is given with a negative sign. This is because as the distance ‘y’ from the wall to the base of the ladder is increasing the height of the ladder ‘x’ is decreasing, so the speed is negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




