
A circuit is shown in the diagram given below.
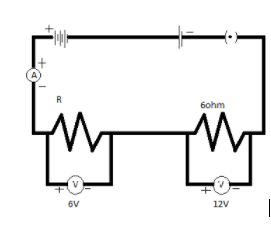
Find the value of R
Find the reading of the ammeter
Potential difference across the terminals of the battery.

Answer
518.1k+ views
Hint: Resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit. Resistance is measured in ohms, symbolized by the Greek letter omega (Ω). Ohms are named after Georg Simon Ohm (1784-1854), a German physicist who studied the relationship between voltage, current and resistance. As we know that
$\therefore V = IR$
Complete answer:
The value of R
Since R and $6\Omega $ resistors are in series, same current flows through them, i.e,
Current ‘I’ through the resistor can be
$\therefore I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Put the values
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{6V}}{R} = \dfrac{{12V}}{{6\Omega }}$
Simplify
$ \Rightarrow R = 3\Omega $
The reading of ammeter will be
Ammeter reading will be same as current through R,
$\therefore I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Put the value
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{6V}}{{3\Omega }}$
$ \Rightarrow I = 2A$
The potential difference across the terminal
$\therefore Potential\,Difference = {V_1} + {V_2}$
Put the value
\[ \Rightarrow Potential\,Difference = 12 + 6\]
\[ \Rightarrow Potential\,Difference = 18V\]
Additional information:
An ammeter (from ampere meter) is a measuring instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. The ammeter is usually connected in series with the circuit in which the current is to be measured.
Note: Potential difference is the difference in the amount of energy that charge carriers have between two points in a circuit. A potential difference of one Volt is equal to one Joule of energy being used by one Coulomb of charge when it flows between two points in a circuit.
$\therefore V = IR$
Complete answer:
The value of R
Since R and $6\Omega $ resistors are in series, same current flows through them, i.e,
Current ‘I’ through the resistor can be
$\therefore I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Put the values
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{6V}}{R} = \dfrac{{12V}}{{6\Omega }}$
Simplify
$ \Rightarrow R = 3\Omega $
The reading of ammeter will be
Ammeter reading will be same as current through R,
$\therefore I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Put the value
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{6V}}{{3\Omega }}$
$ \Rightarrow I = 2A$
The potential difference across the terminal
$\therefore Potential\,Difference = {V_1} + {V_2}$
Put the value
\[ \Rightarrow Potential\,Difference = 12 + 6\]
\[ \Rightarrow Potential\,Difference = 18V\]
Additional information:
An ammeter (from ampere meter) is a measuring instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. The ammeter is usually connected in series with the circuit in which the current is to be measured.
Note: Potential difference is the difference in the amount of energy that charge carriers have between two points in a circuit. A potential difference of one Volt is equal to one Joule of energy being used by one Coulomb of charge when it flows between two points in a circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




