
A body falling freely from a given height $H$ hits an inclined plane in its path at a height. As a result of this impact the direction of the velocity of the body becomes horizontal. For what value of $\left( {\dfrac{h}{H}} \right)$ body will take a maximum time to reach the ground.
A) $\dfrac{1}{3}$
B) $\dfrac{1}{2}$
C) $\dfrac{2}{5}$
D) $\dfrac{2}{3}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To find the answer for the given solution, first we need to draw a reference diagram and then we should find the total time taken by the body to fall. From this we can calculate the value of $\left( {\dfrac{h}{H}} \right)$ in which the body will take a maximum time to reach the ground.
Complete step by step solution:
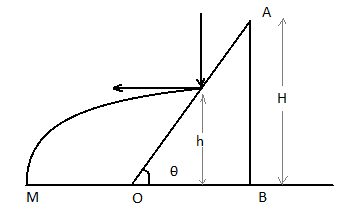
From above diagram the body which falls from height $H$ from the point $B$ from $h$ height above the ground. The path of the body after striking it will be like a parabola.
Then the time taken by the body to fall A to B is ${t_1}$.
$ \Rightarrow \left( {H - h} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t_1}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {t_1} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2\left( {H - h} \right)}}{g}} $
The time taken by the body which falls from B to M is ${t_2}$.
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t_2}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {t_2} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
Then the total time taken by the body to fall,
$ \Rightarrow T = {t_1} + {t_2}$
$ \Rightarrow T = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2(H - h)}}{g}} + \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
By taking the common elements out then the equation is,
$ \Rightarrow T = \sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}[(H - h)^{1/2} +{h}^{1/2}]} $
If the body reaches the maximum height then $\dfrac{{dt}}{{dh}} = 0$
We need to differentiate the above equation with respect to $h$we get,
$\dfrac{1}{2}{(H - h)^{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}}}( - 1) + \dfrac{1}{2}{h^{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow H - h = h$
$ \Rightarrow H = h + h$
$ \Rightarrow H = 2h$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Then the value of $\dfrac{h}{H}$ in which the body takes the maximum time to reach the ground is $\dfrac{1}{2}$.
Therefore the option (B) is correct.
Note: The above problem is based on kinematics that is motion in a straight line. The kinematics are used in day to day life everywhere, kinematics is a kind of mechanism in which dynamics can concern the forces. The main application of the kinematics is used in astrophysics that is robotics, biomechanics and also in mechanical engineering. Because it is used to describe the motion of the system to joint parts.
Complete step by step solution:

From above diagram the body which falls from height $H$ from the point $B$ from $h$ height above the ground. The path of the body after striking it will be like a parabola.
Then the time taken by the body to fall A to B is ${t_1}$.
$ \Rightarrow \left( {H - h} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t_1}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {t_1} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2\left( {H - h} \right)}}{g}} $
The time taken by the body which falls from B to M is ${t_2}$.
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t_2}^2$
$ \Rightarrow {t_2} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
Then the total time taken by the body to fall,
$ \Rightarrow T = {t_1} + {t_2}$
$ \Rightarrow T = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2(H - h)}}{g}} + \sqrt {\dfrac{{2h}}{g}} $
By taking the common elements out then the equation is,
$ \Rightarrow T = \sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}[(H - h)^{1/2} +{h}^{1/2}]} $
If the body reaches the maximum height then $\dfrac{{dt}}{{dh}} = 0$
We need to differentiate the above equation with respect to $h$we get,
$\dfrac{1}{2}{(H - h)^{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}}}( - 1) + \dfrac{1}{2}{h^{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow H - h = h$
$ \Rightarrow H = h + h$
$ \Rightarrow H = 2h$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{H} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Then the value of $\dfrac{h}{H}$ in which the body takes the maximum time to reach the ground is $\dfrac{1}{2}$.
Therefore the option (B) is correct.
Note: The above problem is based on kinematics that is motion in a straight line. The kinematics are used in day to day life everywhere, kinematics is a kind of mechanism in which dynamics can concern the forces. The main application of the kinematics is used in astrophysics that is robotics, biomechanics and also in mechanical engineering. Because it is used to describe the motion of the system to joint parts.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




