
A battery has an e.m.f of $4{\text{V}}$ and an internal resistance $r$ . When this battery is connected to an external resistance of $2\Omega $, a current of $1{\text{A}}$ flows in the circuit. Find the current that flows if the terminals of the battery are connected directly.
A. $1{\text{A}}$
B. ${\text{2A}}$
C. ${\text{4A}}$
D. infinite
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint:According to Ohm’s law, the current in the circuit will be proportional to the applied potential difference in the circuit and inversely proportional to the resistance offered to the flow of current by the circuit. Here the e.m.f of the battery remains constant but the resistance changes when the battery terminals are connected directly.
Formulae Used:
The current in a circuit is given by, $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$ where $V$ is the potential difference and $R$ is the net resistance offered by the circuit.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Sketch a circuit diagram depicting the two cases.
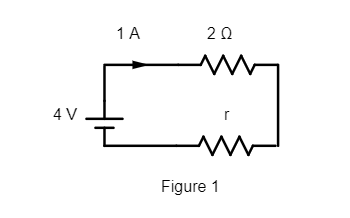
In figure 1, the battery of $V = 4{\text{V}}$ whose internal resistance is $r$ is connected to an external resistance ${r_{ext}} = 2\Omega $ and the current through the circuit is found to be $I = 1{\text{A}}$ .
Here the total resistance offered by the circuit will be $R = r + {r_{ext}} = \left( {r + 2} \right)\Omega $ .
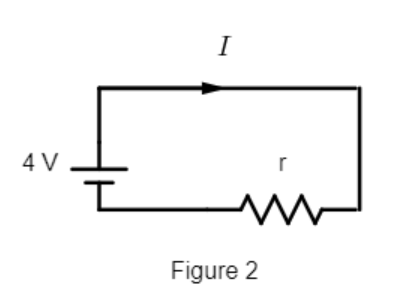
In figure 2, the external resistance is removed and the battery is connected directly. The only resistance offered will be its own internal resistance.
Here the total resistance will be $R = r$
Step 2: Using Ohm’s law, express the current in the circuit in both cases.
Ohm’s law gives the current in a circuit as $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$ where $V$ is the potential difference and $R$ is the net resistance offered by the circuit.
The current in the circuit in case 1 will be $I = \dfrac{V}{{r + {r_{ext}}}} = 1{\text{A}}$ .
Substituting the values for ${r_{ext}} = 2\Omega $ and $V = 4{\text{V}}$ in the above relation we get, $\dfrac{4}{{r + 2}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow r + 2 = 4$ or $r = 2\Omega $
Thus the internal resistance of the battery is $r = 2\Omega $ .
Now the current in the circuit when the battery is connected without the external resistance will be $I = \dfrac{V}{r}$
Substituting for $r = 2\Omega $ and $V = 4{\text{V}}$ in the above relation we get, $I = \dfrac{4}{2} = 2{\text{A}}$
Thus the required current in the circuit will be $I = 2{\text{A}}$ .
So the correct option is B.
Note:- The current is inversely proportional to the resistance offered by the circuit. Connecting the battery terminals directly suggests that the external resistance of the circuit to be removed. Then the current in the circuit must increase and it did. The internal resistance of the battery is a resistance offered by the battery itself. The resistance within the battery will generate heat in the circuit.
Formulae Used:
The current in a circuit is given by, $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$ where $V$ is the potential difference and $R$ is the net resistance offered by the circuit.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Sketch a circuit diagram depicting the two cases.

In figure 1, the battery of $V = 4{\text{V}}$ whose internal resistance is $r$ is connected to an external resistance ${r_{ext}} = 2\Omega $ and the current through the circuit is found to be $I = 1{\text{A}}$ .

Here the total resistance offered by the circuit will be $R = r + {r_{ext}} = \left( {r + 2} \right)\Omega $ .
In figure 2, the external resistance is removed and the battery is connected directly. The only resistance offered will be its own internal resistance.
Here the total resistance will be $R = r$
Step 2: Using Ohm’s law, express the current in the circuit in both cases.
Ohm’s law gives the current in a circuit as $I = \dfrac{V}{R}$ where $V$ is the potential difference and $R$ is the net resistance offered by the circuit.
The current in the circuit in case 1 will be $I = \dfrac{V}{{r + {r_{ext}}}} = 1{\text{A}}$ .
Substituting the values for ${r_{ext}} = 2\Omega $ and $V = 4{\text{V}}$ in the above relation we get, $\dfrac{4}{{r + 2}} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow r + 2 = 4$ or $r = 2\Omega $
Thus the internal resistance of the battery is $r = 2\Omega $ .
Now the current in the circuit when the battery is connected without the external resistance will be $I = \dfrac{V}{r}$
Substituting for $r = 2\Omega $ and $V = 4{\text{V}}$ in the above relation we get, $I = \dfrac{4}{2} = 2{\text{A}}$
Thus the required current in the circuit will be $I = 2{\text{A}}$ .
So the correct option is B.
Note:- The current is inversely proportional to the resistance offered by the circuit. Connecting the battery terminals directly suggests that the external resistance of the circuit to be removed. Then the current in the circuit must increase and it did. The internal resistance of the battery is a resistance offered by the battery itself. The resistance within the battery will generate heat in the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




