
A air bubble of radius 1 cm in water has an upward acceleration $9.8cm{s^{ - 2}}$. The density of water is $1gc{m^{ - 3}}$ and water offers negligible drag force on the bubble. The mass of the bubble is
(A) $1.52g$
(B) $4.51g$
(C) $3.15g$
(D) $4.15g$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we will balance all three forces acting on the air bubble which are gravity, upward force, and the buoyant force which acts in an upward direction, and then we will solve for the mass of the air bubble.
Formula used:
1. Force due to gravity on a body of mass m is:
$F = mg$
Where g is acceleration due to gravity $g = 980cm{s^{ - 2}}$
2. Force on a body of mass m and acceleration a is given by:
$F = ma$
3. The buoyant force on a body of volume V in water having density $\rho $ is:
$B = V\rho g$
Complete answer:
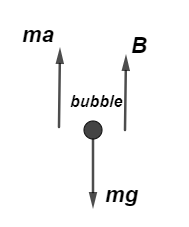
From the free body diagram of the air bubble we can see that by balancing all the three forces acting on the bubble, we get
$ma = B - mg \to (i)$
Now, volume of bubble is calculated as $V = \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}$ where $r = 1cm$
$V = \dfrac{4}{3}(3.14){(1)^3}$
$V = 4.19c{m^3} $
and density of water is given as $\rho = 1gc{m^{ - 3}}$
So, Buoyant force is given by $B = V\rho g$
$B = 4.19 \times 1 \times 980 $
$B = 4106.2gcm{s^{ - 2}} $
Now, due to upward acceleration force is $F = ma$ where $a = 9.8cm{s^{ - 2}}$
$F = 9.8m$ ‘m’ is the mass of the air bubble and force due to gravity on the bubble is given by $mg$ which is equal to $980m$
Using all the three forces values, put in equation (i) we get
$ 9.8m = 4106.2 - 980m$
$989.8m = 4106.2 $
$m = 4.15g $
So, the mass of the air bubble is $4.15g$
Hence, the correct option is (D) $4.15g$.
Note:It should be remembered that Archimedes found that when a body is immersed in water it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body and this force is known as buoyant force.
Formula used:
1. Force due to gravity on a body of mass m is:
$F = mg$
Where g is acceleration due to gravity $g = 980cm{s^{ - 2}}$
2. Force on a body of mass m and acceleration a is given by:
$F = ma$
3. The buoyant force on a body of volume V in water having density $\rho $ is:
$B = V\rho g$
Complete answer:

From the free body diagram of the air bubble we can see that by balancing all the three forces acting on the bubble, we get
$ma = B - mg \to (i)$
Now, volume of bubble is calculated as $V = \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}$ where $r = 1cm$
$V = \dfrac{4}{3}(3.14){(1)^3}$
$V = 4.19c{m^3} $
and density of water is given as $\rho = 1gc{m^{ - 3}}$
So, Buoyant force is given by $B = V\rho g$
$B = 4.19 \times 1 \times 980 $
$B = 4106.2gcm{s^{ - 2}} $
Now, due to upward acceleration force is $F = ma$ where $a = 9.8cm{s^{ - 2}}$
$F = 9.8m$ ‘m’ is the mass of the air bubble and force due to gravity on the bubble is given by $mg$ which is equal to $980m$
Using all the three forces values, put in equation (i) we get
$ 9.8m = 4106.2 - 980m$
$989.8m = 4106.2 $
$m = 4.15g $
So, the mass of the air bubble is $4.15g$
Hence, the correct option is (D) $4.15g$.
Note:It should be remembered that Archimedes found that when a body is immersed in water it experiences an upward force that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body and this force is known as buoyant force.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




