




How Does the QRS Complex Show Ventricular Depolarization in the Heart?
The concept of What Does QRS Complex Represent In ECG is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively.
Understanding What Does QRS Complex Represent In ECG
What Does QRS Complex Represent In ECG refers to the main spike or complex visible in an electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) tracing. This concept is important in areas like cardiac physiology, heart electrical conduction, and diagnosing heart conditions. Understanding the QRS complex is crucial for NEET exam preparation, as questions often include ECG graph interpretation and the identification of cardiac events.
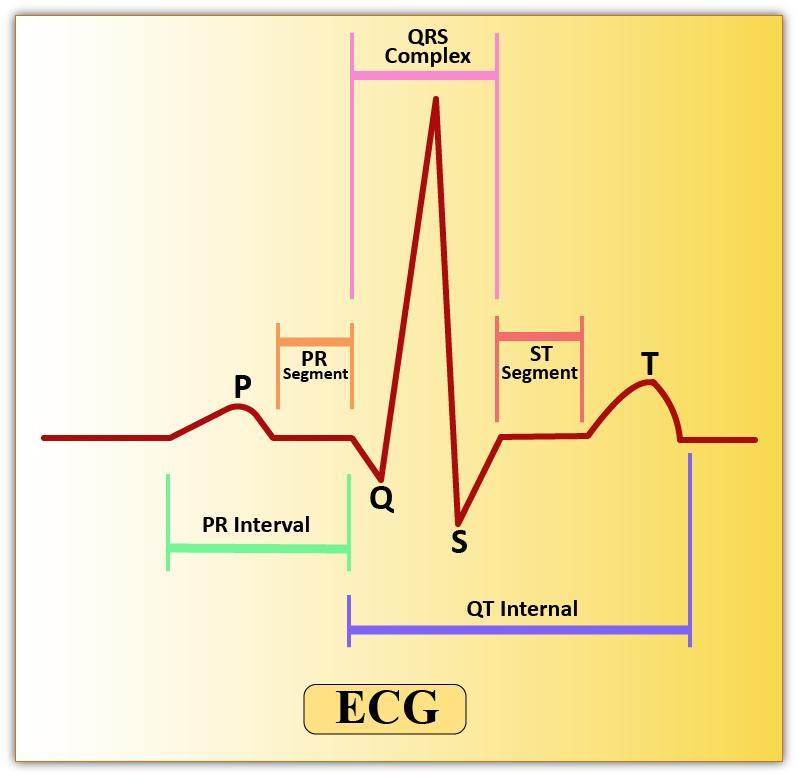
Role and Interpretation of QRS Complex in ECG
The QRS complex in ECG represents the rapid depolarization of the ventricles. This electrical event occurs right before the ventricles contract to pump blood to the lungs and the rest of the body. The QRS complex follows the P wave (atrial depolarization), and is succeeded by the T wave (ventricular repolarization).
- P wave: Indicates depolarization (and contraction) of the atria.
- QRS complex: Shows depolarization of the ventricles, marking the beginning of ventricular systole (contraction).
- T wave: Represents ventricular repolarization (relaxation phase) and end of systole.
On the ECG graph, the QRS complex starts with a downward deflection (Q), continues with a tall upward spike (R), and ends with another downward deflection (S). By counting the number of QRS complexes within one minute, you can estimate the heart rate.
Mechanism of QRS Complex Generation
The basic mechanism involves:
- The electrical impulse begins at the SA node in the right atrium.
- Impulse passes to the AV node, then via bundle of His and Purkinje fibers, leading to rapid depolarization of both ventricles.
- The QRS complex records the sum of this ventricular electrical activity on the ECG.
Here’s a helpful table to understand What Does QRS Complex Represent In ECG better:
ECG Component Table
| ECG Wave | Event Represented | Normal Duration |
|---|---|---|
| P wave | Atrial depolarization | 0.08 – 0.10 sec |
| QRS complex | Ventricular depolarization (ventricular contraction/systole) | 0.08 – 0.12 sec (80–120 ms) |
| T wave | Ventricular repolarization | ~0.16 sec |
Worked Example – Reading ECG for NEET
Let’s understand the process step by step:
1. Look at an ECG graph for the main tall spike after the P wave – this is the QRS complex.
2. Mark the start and end of the QRS complex—this section represents ventricular depolarization.
3. Count the number of QRS complexes in one minute to estimate the heart rate.
Final Understanding: The QRS complex is essential for diagnosing rhythm and conduction problems and is a high-yield point for NEET MCQs.
Practice Questions
- What event does the QRS complex represent in ECG?
- What is the difference between P wave and QRS complex?
- What is the normal duration of the QRS complex in humans?
- Draw a labelled diagram of a standard ECG tracing and mark the QRS complex.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing QRS complex with the T wave (T wave is for repolarization, not contraction).
- Mixing up atrial (P wave) and ventricular events (QRS complex).
- Forgetting the normal QRS duration for MCQs: Remember, prolonged QRS (>0.12 sec) indicates conduction block.
Abnormalities and Clinical Significance
Changes in the QRS complex are key for clinical diagnosis. A widened or prolonged QRS complex can indicate bundle branch block or hyperkalemia. An increased R-wave amplitude suggests ventricular hypertrophy, while abnormal Q waves may point to myocardial infarction (heart attack). NEET questions may test your ability to spot these features in diagram-based questions.
Real-World Applications
The concept of What Does QRS Complex Represent In ECG is used in fields like medicine, emergency care, physiology research, and surgery. Doctors and nurses rely on the QRS complex to monitor patient heart activity in real time. Vedantu helps students relate such concepts to practical healthcare and go beyond NCERT for NEET success.
Related Topics and Internal Links
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Human Circulatory System
- Human Heart
- Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
- Neural Control and Coordination
- MCQs on ECG
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Heart: Pump of the Circulatory System
- Facts About Heart
In this article, we explored What Does QRS Complex Represent In ECG, its key processes, real-life significance, and how to solve questions based on it. To learn more and build confidence, keep practicing with Vedantu.
FAQs on What Does the QRS Complex Represent in ECG?
1. What does the QRS complex represent in ECG, as per NEET syllabus?
The QRS complex in an ECG represents the depolarization of the ventricles, which initiates ventricular contraction or ventricular systole. It follows the P wave (atrial depolarization) and precedes the T wave (ventricular repolarization), making it the most prominent part of the ECG trace.
2. How can I easily remember QRS complex vs P wave vs T wave for NEET?
To distinguish the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave quickly for NEET, remember:
• P wave = atrial depolarization (atria contract)
• QRS complex = ventricular depolarization (ventricles contract)
• T wave = ventricular repolarization (ventricles relax)
Use mnemonics like “P for Pumped atria, QRS for Quick pump of ventricles, T for Tank refill (relaxation).” This helps avoid confusion during exams.
3. What is the normal QRS complex duration in adults?
The normal duration of the QRS complex in adults is typically between 80 to 120 milliseconds (0.08 to 0.12 seconds). Durations longer than this may indicate conduction delays such as bundle branch block or other cardiac abnormalities.
4. What are the causes of abnormal QRS patterns in ECG?
Abnormalities in the QRS complex can be caused by:
• Bundle branch block (causing widened QRS duration)
• Ventricular hypertrophy (increased R or S wave amplitude)
• Myocardial infarction (abnormal Q waves)
• Electrolyte imbalances like hyperkalemia
These changes help in diagnosing cardiac conditions in NEET clinical questions.
5. How is QRS complex used to find heart rate in ECG?
The number of QRS complexes counted in one minute on an ECG trace corresponds to the heart rate. Since each QRS complex indicates one ventricular contraction, counting these complexes over time allows calculation of beats per minute (bpm), essential for interpreting cardiac rhythm in NEET exams.
6. Why do some students confuse QRS with T wave in MCQs?
Confusion between QRS complex and T wave often occurs because both involve ventricular activity on the ECG. However, QRS shows depolarization (contraction) and appears as a sharp spike, while T wave shows repolarization (relaxation) and is a smoother upward deflection. Clear differentiation is crucial for NEET MCQs.
7. Can P wave or T wave ever overlap with QRS in the ECG graph?
Normally, the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave appear sequentially without overlap. However, in certain arrhythmias or rapid heart rates, waves may overlap or obscure each other, complicating interpretation. Understanding normal wave timing helps avoid errors in NEET exam ECG analysis.
8. How to quickly spot the J-point on an ECG for NEET diagrams?
The J-point is located at the junction where the end of the QRS complex meets the beginning of the ST segment. It is the first inflection point after the downward S wave. Recognizing this point is important for identifying ST elevation/depression relevant in NEET clinical questions.
9. What is a common silly mistake when filling QRS values in OMR sheets?
A frequent error is confusing the QRS duration with the interval between two consecutive QRS complexes (heart rate interval). Remember:
• QRS duration = width of one complex
• RR interval = time between two complexes
This distinction prevents incorrect answers in NEET OMR sheets.
10. How is QRS complex linked to real clinical conditions (NEET extra)?
The QRS complex provides vital clues for diagnosing:
• Myocardial infarction (abnormal Q waves)
• Ventricular hypertrophy (increased R or S amplitude)
• Bundle branch blocks (prolonged QRS duration)
Understanding these helps NEET aspirants correlate ECG changes with real cardiac pathologies.























