
Work done by normal reaction is zero during the motion of the block:
A) From point A to B only
B) From point B to C only
C) From A to C
D) None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question you have to remember the concepts of the work-energy theorem and the use of force for finding work done. The work-energy theorem states that the work done by all the forces that are acting on a particle will be equal to the change in the kinetic energy of that particle.
Complete step by step solution:
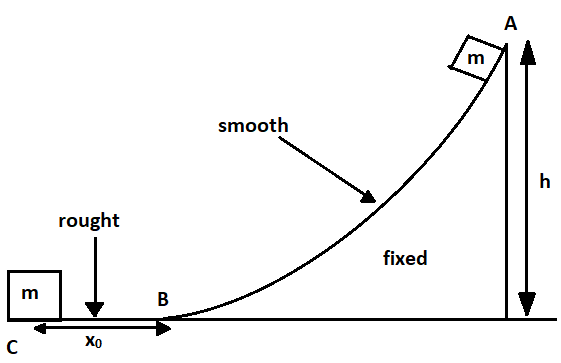
In the question, it is given a small block of mass m, which is released from point A on a fixed smooth wedge as shown in the above figure. The top of the wedge is marked as A and the bottom as B and at point C the block stops moving because of the roughness of the floor.
We have to find the portion where the work done by the normal reaction is zero during the motion of the block
We already know that the normal reaction is always perpendicular to the direction of motion.
So, it means that the work done by the normal reaction is equal to zero from point A to C as the normal reaction is perpendicular to the displacement of the block.
Hence, from the above discussion, it is clear that the work done by the normal reaction is zero during the motion of the block will be from point A to C.
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note: Always keep in mind that the normal reaction is the force that is applied by the surface in reaction to the weight that the object exerts on the surface. The normal reaction force is perpendicular to the surface that an object contacts. For example, the table surface that prevents an object from falling from the table.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question, it is given a small block of mass m, which is released from point A on a fixed smooth wedge as shown in the above figure. The top of the wedge is marked as A and the bottom as B and at point C the block stops moving because of the roughness of the floor.
We have to find the portion where the work done by the normal reaction is zero during the motion of the block
We already know that the normal reaction is always perpendicular to the direction of motion.
So, it means that the work done by the normal reaction is equal to zero from point A to C as the normal reaction is perpendicular to the displacement of the block.
Hence, from the above discussion, it is clear that the work done by the normal reaction is zero during the motion of the block will be from point A to C.
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note: Always keep in mind that the normal reaction is the force that is applied by the surface in reaction to the weight that the object exerts on the surface. The normal reaction force is perpendicular to the surface that an object contacts. For example, the table surface that prevents an object from falling from the table.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




