
With which part the mRNA should be bound to initiate the translation?
A. The smaller ribosomal sub-unit
B. The larger ribosomal sub-unit
C. The whole ribosome
D. No such specificity exists.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) is a variety of the RNA (Ribonucleic acid) which is required in the living being for the formation of protein.
Complete step by step answer:
RNA termed ribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that is present in the living thing cells that has some similarity with the DNA (Deoxy-ribonucleic acid). RNA is a single-stranded backbone-like structure having alternating phosphate groups and sugar ribose whereas in the DNA, the alternating deoxy-ribose group is found in repetitions. The bases attached to the sugar in nucleic acid- are Adenine(A), Uracil(U), Cytosine(C), and Guanine(G).
The different types of RNA present in the living being are rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA.
rRNA: Ribosomal RNA is used to synthesise organelle known as ribosomes which are exported to the cytoplasm to help translate the information. The rRNA molecules are synthesised in an organelle of the nucleus of a cell called the nucleolus.
tRNA: Transfer ribonucleic acid is a type of molecule required to decode the mRNA in protein. Its specific function is to synthesise a protein from an mRNA molecule.
mRNA: Messenger RNA, a blueprint of the protein which helps synthesise that protein. The transcription process creates mRNA where an enzyme, RNA polymerase, gets converted into primary transcript mRNA or pre-mRNA.
Proteins are synthesised by the ribosome which is present in the nucleolus. The ribosome consists of about 80 different proteins with structural RNA. When the protein is not in an active or inactive state, it consists of the 2 sub-unit in which one is larger and the other is a small sub-unit.
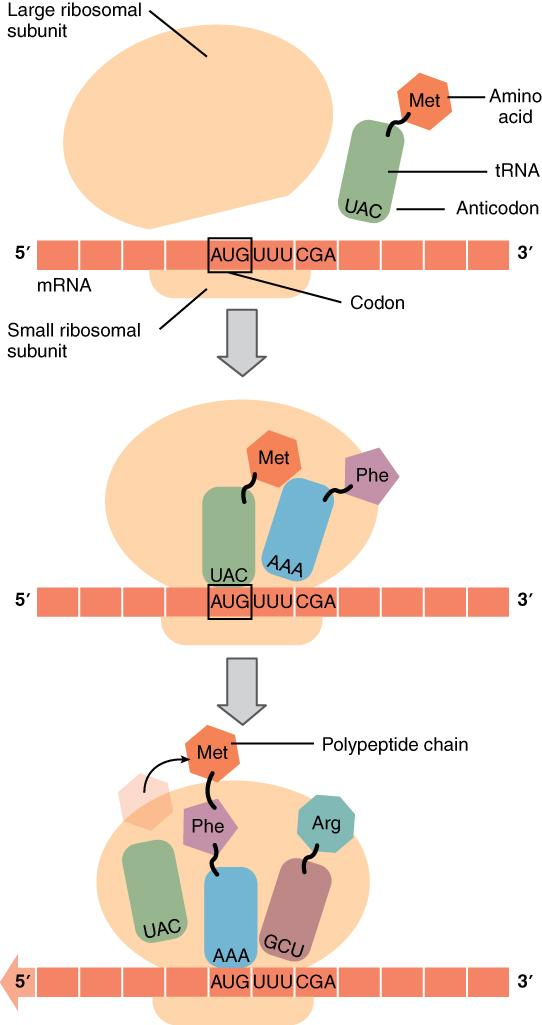
Image: Diagrammatic representation of process of Translation
Therefore, correct option to this question is A
Note: RRNA (Ribonucleic acid) is quite similar to DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), the difference is the positioning of the groups. DNA consists of the blueprint called gene and the RNA converts that blueprint into protein.
Complete step by step answer:
RNA termed ribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that is present in the living thing cells that has some similarity with the DNA (Deoxy-ribonucleic acid). RNA is a single-stranded backbone-like structure having alternating phosphate groups and sugar ribose whereas in the DNA, the alternating deoxy-ribose group is found in repetitions. The bases attached to the sugar in nucleic acid- are Adenine(A), Uracil(U), Cytosine(C), and Guanine(G).
The different types of RNA present in the living being are rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA.
rRNA: Ribosomal RNA is used to synthesise organelle known as ribosomes which are exported to the cytoplasm to help translate the information. The rRNA molecules are synthesised in an organelle of the nucleus of a cell called the nucleolus.
tRNA: Transfer ribonucleic acid is a type of molecule required to decode the mRNA in protein. Its specific function is to synthesise a protein from an mRNA molecule.
mRNA: Messenger RNA, a blueprint of the protein which helps synthesise that protein. The transcription process creates mRNA where an enzyme, RNA polymerase, gets converted into primary transcript mRNA or pre-mRNA.
Proteins are synthesised by the ribosome which is present in the nucleolus. The ribosome consists of about 80 different proteins with structural RNA. When the protein is not in an active or inactive state, it consists of the 2 sub-unit in which one is larger and the other is a small sub-unit.

Image: Diagrammatic representation of process of Translation
Therefore, correct option to this question is A
Note: RRNA (Ribonucleic acid) is quite similar to DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), the difference is the positioning of the groups. DNA consists of the blueprint called gene and the RNA converts that blueprint into protein.
Recently Updated Pages
Area of an Octagon Formula Explained Simply

Absolute Pressure Formula Explained: Key Equation & Examples

Central Angle of a Circle Formula Explained Quickly

Difference Between Vapor and Gas: JEE Main 2026

Difference Between Atom and Molecule: JEE Main 2026

Carbon Dioxide Formula - Definition, Uses and FAQs

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 1 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

JEE Mains 2026 January 21 Shift 2 Question Paper with Solutions PDF - Complete Exam Analysis

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 2 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Human Reproduction (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 4 Principles of Inheritance and Variation (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health (2025-26)

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

One Day International Cricket




