
Why is it meant by frequency?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Here in order to understand about the term frequency. Anything that happens at a repeated time interval. Let’s see this in detail.
Complete step by step solution:
Frequency is defined as the number of oscillations or vibrations per second. The below equation relates between frequency and time period.
\[f = \dfrac{1}{T}\]
Where, f is frequency and T is the time period.
The unit of time period is second written as s, and the unit of frequency is hertz denoted by Hz.
Suppose say if the time period is 10seconds, then by using the formula \[f = \dfrac{1}{{10}}\]. Then the frequency is 0.1 hertz. As the number of cycles increases, frequency also increases. One hertz is defined as one cycle per second. Then the cycle is defined as one complete cycle of AC or DC.
Time period is the time taken to complete one oscillation or vibration of a wave. Basically, frequency is something which repeats over a small period of time. We have discussed frequency till this point. Now let’s look at the word natural frequency. It is the frequency at which an object vibrates naturally in the absence of driving force.
Note:There are some relative terms to the frequency that we are going to discuss now. In the wave form the parts of the wave are represented clearly.
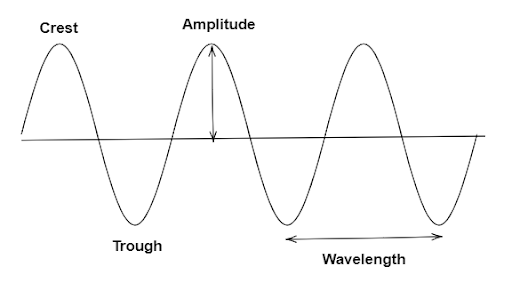
Parts of a wave are,
Wavelength- The distance between the two consecutive crests or troughs is known as wavelength of a wave and is denoted by \[\lambda \].
Amplitude- The maximum displacement of a particle from its mean position is called the amplitude of a wave and it is denoted by A.
Crest- The upper part of the wave in which there is a maximum displacement of the medium.
Trough- Lower part of the wave in which there is a minimum displacement of the medium.
Complete step by step solution:
Frequency is defined as the number of oscillations or vibrations per second. The below equation relates between frequency and time period.
\[f = \dfrac{1}{T}\]
Where, f is frequency and T is the time period.
The unit of time period is second written as s, and the unit of frequency is hertz denoted by Hz.
Suppose say if the time period is 10seconds, then by using the formula \[f = \dfrac{1}{{10}}\]. Then the frequency is 0.1 hertz. As the number of cycles increases, frequency also increases. One hertz is defined as one cycle per second. Then the cycle is defined as one complete cycle of AC or DC.
Time period is the time taken to complete one oscillation or vibration of a wave. Basically, frequency is something which repeats over a small period of time. We have discussed frequency till this point. Now let’s look at the word natural frequency. It is the frequency at which an object vibrates naturally in the absence of driving force.
Note:There are some relative terms to the frequency that we are going to discuss now. In the wave form the parts of the wave are represented clearly.

Parts of a wave are,
Wavelength- The distance between the two consecutive crests or troughs is known as wavelength of a wave and is denoted by \[\lambda \].
Amplitude- The maximum displacement of a particle from its mean position is called the amplitude of a wave and it is denoted by A.
Crest- The upper part of the wave in which there is a maximum displacement of the medium.
Trough- Lower part of the wave in which there is a minimum displacement of the medium.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




