
Why do we use a Polarimeter?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: A polarimeter is an instrument that is used to measure the angle of rotation when it is passing from polarised light. When the polarisation is passing to the sample tube, it starts exhibiting angular rotation toward the left and right.
Complete step by step solution:
A polarimeter is a device for finding the polarisation direction of light or we can say that it is used to find the angle of rotation when it is passing through the optically active fluid. The role of finding the rotation is to help us to find the concentration of the solutions.
A polarimeter consists of the polarised light source, a graduated circle to measure the angle of rotation, a sample tube, and a polarised light source. The figure of the polarimeter is shown below,
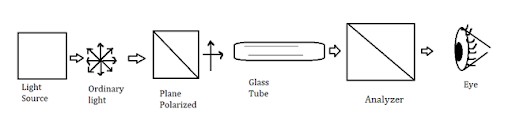
Image: Polarimeter
Working of the Polarimeter: As we can see in the figure, the monochromatic light is passing through the plane polarising plate which creates the polarised beam of light. This polarised beam of light is passing through a sample which contains ion the glass tube. When the beam is passed through the sample it will pass through the second plate known as the analyzer which helps to rotate the beam either via mutual rotation or automatic rotation. Which helps us to detect the concentration of the sample that is present.
Note : There are two main types of applications of the Polarimeter. One is quantitative and another is qualitative. In the quantitative application we can find out the concentration of the sample whereas in the quantitative application, it helps in chemistry to find out the D and L isomeric forms.
Complete step by step solution:
A polarimeter is a device for finding the polarisation direction of light or we can say that it is used to find the angle of rotation when it is passing through the optically active fluid. The role of finding the rotation is to help us to find the concentration of the solutions.
A polarimeter consists of the polarised light source, a graduated circle to measure the angle of rotation, a sample tube, and a polarised light source. The figure of the polarimeter is shown below,

Image: Polarimeter
Working of the Polarimeter: As we can see in the figure, the monochromatic light is passing through the plane polarising plate which creates the polarised beam of light. This polarised beam of light is passing through a sample which contains ion the glass tube. When the beam is passed through the sample it will pass through the second plate known as the analyzer which helps to rotate the beam either via mutual rotation or automatic rotation. Which helps us to detect the concentration of the sample that is present.
Note : There are two main types of applications of the Polarimeter. One is quantitative and another is qualitative. In the quantitative application we can find out the concentration of the sample whereas in the quantitative application, it helps in chemistry to find out the D and L isomeric forms.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




