
Which would exhibit co-ordination isomerism:
A) $\left[ Cr{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{6}} \right]\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$
B) $\left[ Co{{\left( en \right)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}} \right]$
C) $\left[ Cr{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{6}} \right]C{{l}_{3}}$
D) ${{\left[ Cr{{\left( en \right)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}} \right]}^{+}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Coordination isomerism is exhibited by the complexes having two or more coordination spheres and there is a tendency to interchange ligands between the anionic and cationic entities of the different metal ions present within the complex. In simple words, coordination isomerism involves the switching of metal ions in between the coordination complexes.
Complete answer:In coordination chemistry, the complexes with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of ligands are known as isomers, and the phenomenon is known as isomerism. It is broadly categorized into two parts i.e., Structural isomerism and Stereoisomerism.
Structural isomerism: The isomerism in which the complex consists of the same number of atoms bonded to the central metal atom but may differ in structure or type of bonding. Structural isomerism is further categorized into four parts i.e., Ionization isomerism, Coordination isomerism, Linkage isomerism, and Hydrate or Solvate isomerism.
Coordination isomerism: It is the type of isomerism that occurs in the complexes consisting of anionic and cation parts within two different coordination spheres or we can say that must have the complex anionic and complex cationic parts and an interchange of ligands is observed between the anionic and the cationic part of the coordination spheres. Thus, we can say that in coordination isomerism, there are two complexes bound with each other in which one complex consists of a positive charge while the other is having a negative charge and the exchange of ligands takes place between anionic and cationic entities of the compound. The concept is explained with the help of an example as shown below:
${{\left[ Zn{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{4}} \right]}^{2+}}{{\left[ CuC{{l}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}\leftrightarrow {{\left[ Cu{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{4}} \right]}^{2+}}{{\left[ ZnC{{l}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}$
Thus, among the given options, the complex which will exhibit coordination isomerism is $\left[ Cr{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{6}} \right]\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$ as follows:
$\left[ Cr{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{6}} \right]\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]\leftrightarrow \left[ Co{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{6}} \right]\left[ Cr{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$
Therefore, option (A) is the correct answer.
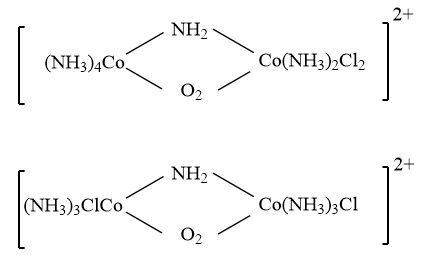
Note: It is important to note that the coordination isomerism can also be exhibited by the polynuclear complexes and bridging complexes by changing the position of the ligands with respect to different metal atoms present within the complex. An example for the same is shown below:
Complete answer:In coordination chemistry, the complexes with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of ligands are known as isomers, and the phenomenon is known as isomerism. It is broadly categorized into two parts i.e., Structural isomerism and Stereoisomerism.
Structural isomerism: The isomerism in which the complex consists of the same number of atoms bonded to the central metal atom but may differ in structure or type of bonding. Structural isomerism is further categorized into four parts i.e., Ionization isomerism, Coordination isomerism, Linkage isomerism, and Hydrate or Solvate isomerism.
Coordination isomerism: It is the type of isomerism that occurs in the complexes consisting of anionic and cation parts within two different coordination spheres or we can say that must have the complex anionic and complex cationic parts and an interchange of ligands is observed between the anionic and the cationic part of the coordination spheres. Thus, we can say that in coordination isomerism, there are two complexes bound with each other in which one complex consists of a positive charge while the other is having a negative charge and the exchange of ligands takes place between anionic and cationic entities of the compound. The concept is explained with the help of an example as shown below:
${{\left[ Zn{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{4}} \right]}^{2+}}{{\left[ CuC{{l}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}\leftrightarrow {{\left[ Cu{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{4}} \right]}^{2+}}{{\left[ ZnC{{l}_{4}} \right]}^{2-}}$
Thus, among the given options, the complex which will exhibit coordination isomerism is $\left[ Cr{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{6}} \right]\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$ as follows:
$\left[ Cr{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{6}} \right]\left[ Co{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]\leftrightarrow \left[ Co{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{6}} \right]\left[ Cr{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]$
Therefore, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: It is important to note that the coordination isomerism can also be exhibited by the polynuclear complexes and bridging complexes by changing the position of the ligands with respect to different metal atoms present within the complex. An example for the same is shown below:

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




