
Which solid will have the weakest intermolecular forces?
(a) Ice
(b) Phosphorous
(c) Naphthalene,
(d) Sodium Fluoride
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The London dispersion force, Van der waals interaction, and hydrogen bonding are the weakest intermolecular forces in comparison with covalent and ionic bonds.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The London dispersion force, Van der waals, and Hydrogen bonding are the three major intermolecular forces.
The London dispersion and Van der waals forces are the weakest intermolecular forces than the hydrogen bonding.
The hydrogen bond is formed when nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine are attached to a hydrogen atom. For example, \[N{H_3}\] and \[{H_2}O\] molecules possess hydrogen bonding.
In ice, every single water molecule is connected to four neighbouring water molecules via hydrogen bonding interaction (Image 1).
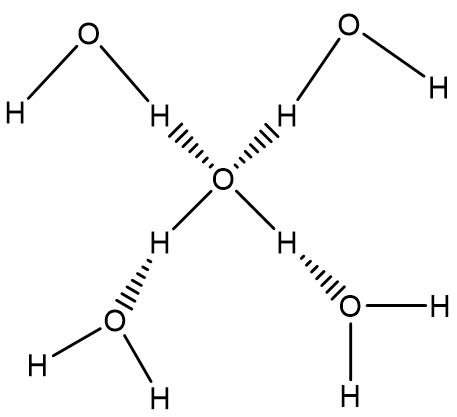
Image 1: Hydrogen bonding interaction in ice.
In the case of phosphorus, the four P atoms are bonded to each other by a covalent bond and form a tetrahedral geometry (Image 2).
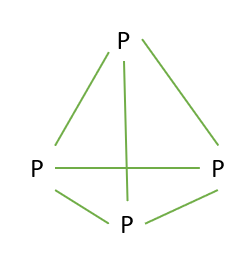
Image 2: Covalent bonding in phosphorus (\[{P_4}\] ) molecules.
Similarly, naphthalene is a covalent molecule, in which the hydrogen and carbon atoms are bonded by means of a covalent bond (image 3). It is found that covalent bonds are stronger than that hydrogen bonding.
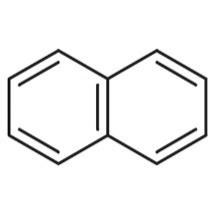
Image 3: Structure of naphthalene molecule.
Whereas, silver fluoride is an ionic compound, in which the silver and fluoride ions are fused together by means of strong ionic bond. It is found that ionic bonds are also stronger than hydrogen bonds.
the above statements, conclude that the hydrogen bond is a weaker intermolecular force than the covalent and ionic bonds.
Note: The hydrogen bonding interaction is also known as dipole-dipole interaction. The strength of hydrogen bonding depends upon the electronegativity of the element attached to the hydrogen atom.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The London dispersion force, Van der waals, and Hydrogen bonding are the three major intermolecular forces.
The London dispersion and Van der waals forces are the weakest intermolecular forces than the hydrogen bonding.
The hydrogen bond is formed when nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine are attached to a hydrogen atom. For example, \[N{H_3}\] and \[{H_2}O\] molecules possess hydrogen bonding.
In ice, every single water molecule is connected to four neighbouring water molecules via hydrogen bonding interaction (Image 1).

Image 1: Hydrogen bonding interaction in ice.
In the case of phosphorus, the four P atoms are bonded to each other by a covalent bond and form a tetrahedral geometry (Image 2).

Image 2: Covalent bonding in phosphorus (\[{P_4}\] ) molecules.
Similarly, naphthalene is a covalent molecule, in which the hydrogen and carbon atoms are bonded by means of a covalent bond (image 3). It is found that covalent bonds are stronger than that hydrogen bonding.

Image 3: Structure of naphthalene molecule.
Whereas, silver fluoride is an ionic compound, in which the silver and fluoride ions are fused together by means of strong ionic bond. It is found that ionic bonds are also stronger than hydrogen bonds.
the above statements, conclude that the hydrogen bond is a weaker intermolecular force than the covalent and ionic bonds.
Note: The hydrogen bonding interaction is also known as dipole-dipole interaction. The strength of hydrogen bonding depends upon the electronegativity of the element attached to the hydrogen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




