
Which selection is an example of a molecule with a linear shape?
A)\[C{O_2}\]
B)\[AlC{l_3}\]
C)\[BeB{r_2}\]
D)\[NC{l_3}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: VSEPR Theory is helpful to predict the shape of the molecules from the electron pairs that surround the central atoms of the molecule. It was first shown by Sidgwick and Powell in 1940. It is based on the assumption that the molecule will take a shape such that electronic repulsion in the valence shell of that atom is minimized.
Complete Step-by-Step answer:
According to VSEPR Theory, the following steps must be followed so as to predict the shape of a molecule.
The least electronegative atom must be selected as the central atom since this atom has the highest ability to share its electrons with the other atoms surrounding the molecule.
The total number of electrons that belong to the outermost shell of the central atom must be counted.
The total number of electrons that belong to other atoms and used in bonds with the central atom must be counted irrespective of the lone pairs available on the other atoms.
At last, these two values must be added in order to obtain the valence shell electron pair number or the VSEP number.
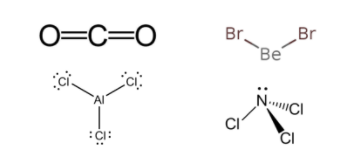
In \[C{O_2}\] , carbon is contributing four electrons for bond formation, and each oxygen atom is donating a pair of electrons i.e. VSEP number is 2. Both the electron groups around the central carbon atom forms bond pairs with carbon as it is the least electronegative atom here. If we focus only on central atom as per VSEPR, the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atoms do not play a role in determining the molecular geometry. To reduce repulsion, the molecular geometry comes out to be linear.
In \[AlC{l_3}\] , aluminium being the least electronegative atom contributes three electrons and each chlorine atom donates one electron to it i.e. its VSEP number is 3. So, its molecular geometry will be trigonal planar.
In \[BeB{r_2}\], Be is the least electronegative atom contributes two electrons and each bromine atom donates one electron to it i.e. its VSEP number is 2. But it has a lone pair on beryllium which leads to repulsion between bond pair-lone pair. So, its molecular geometry will be V-shape or linear if symmetric.
In \[NC{l_3}\] , N is the least electronegative atom contributes three electrons and each chlorine atom donates one electron to it i.e. its VSEP number is 3. But it has a lone pair on nitrogen which leads to repulsion between bond pair-lone pair. So, its molecular geometry will be trigonal pyramidal.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: There comes a steric number i.e. the sum of number of lone pairs and number of atoms attached to the central atom. It is similar to VSPER number. In 3D arrangement of bonds, the solid line represents a bond in the plane of the paper and a dotted line represents a bond going away from you into the paper, and a wedge shows a bond coming towards you as you can see in \[NC{l_3}\] .
Complete Step-by-Step answer:
According to VSEPR Theory, the following steps must be followed so as to predict the shape of a molecule.
The least electronegative atom must be selected as the central atom since this atom has the highest ability to share its electrons with the other atoms surrounding the molecule.
The total number of electrons that belong to the outermost shell of the central atom must be counted.
The total number of electrons that belong to other atoms and used in bonds with the central atom must be counted irrespective of the lone pairs available on the other atoms.
At last, these two values must be added in order to obtain the valence shell electron pair number or the VSEP number.


In \[C{O_2}\] , carbon is contributing four electrons for bond formation, and each oxygen atom is donating a pair of electrons i.e. VSEP number is 2. Both the electron groups around the central carbon atom forms bond pairs with carbon as it is the least electronegative atom here. If we focus only on central atom as per VSEPR, the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atoms do not play a role in determining the molecular geometry. To reduce repulsion, the molecular geometry comes out to be linear.
In \[AlC{l_3}\] , aluminium being the least electronegative atom contributes three electrons and each chlorine atom donates one electron to it i.e. its VSEP number is 3. So, its molecular geometry will be trigonal planar.
In \[BeB{r_2}\], Be is the least electronegative atom contributes two electrons and each bromine atom donates one electron to it i.e. its VSEP number is 2. But it has a lone pair on beryllium which leads to repulsion between bond pair-lone pair. So, its molecular geometry will be V-shape or linear if symmetric.
In \[NC{l_3}\] , N is the least electronegative atom contributes three electrons and each chlorine atom donates one electron to it i.e. its VSEP number is 3. But it has a lone pair on nitrogen which leads to repulsion between bond pair-lone pair. So, its molecular geometry will be trigonal pyramidal.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: There comes a steric number i.e. the sum of number of lone pairs and number of atoms attached to the central atom. It is similar to VSPER number. In 3D arrangement of bonds, the solid line represents a bond in the plane of the paper and a dotted line represents a bond going away from you into the paper, and a wedge shows a bond coming towards you as you can see in \[NC{l_3}\] .
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




