
Which one of the following molecules will form a linear polymeric structure due to hydrogen bonding?
(A) $N{H_3}$
(B) ${H_2}O$
(C) $HCl$
(D) $HF$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules. A hydrogen bond is formed when the positive end of one molecule is attracted to the negative end of another. It results from the attractive forces between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as N, O, and F.
Complete step by step solution:
HF forms ${(HF)_n}$ linear polymeric structure due to hydrogen bonding. Its structure is as shown:
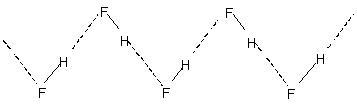
The fairly positive hydrogen on one HF molecule will be attracted to one of these lone pairs on a nearby HF molecule. This is known as a hydrogen bond.
Hydrogen bonds are attractions between a $\delta + $ hydrogen on one molecule and a lone pair on a very electronegative atom on another molecule.
Whereas, no hydrogen bonding exists between HCl, and ${H_2}O$ also has a cage-like structure.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: Hydrogen fluoride is a strong acid. It is gas at room temperature and is supplied as a liquefied gas in the cylinders, and is also widely used in water solutions. Because of its high reactivity towards glass and moderate reactivity towards many metals, it is usually stored in plastic containers.
Complete step by step solution:
HF forms ${(HF)_n}$ linear polymeric structure due to hydrogen bonding. Its structure is as shown:

The fairly positive hydrogen on one HF molecule will be attracted to one of these lone pairs on a nearby HF molecule. This is known as a hydrogen bond.
Hydrogen bonds are attractions between a $\delta + $ hydrogen on one molecule and a lone pair on a very electronegative atom on another molecule.
Whereas, no hydrogen bonding exists between HCl, and ${H_2}O$ also has a cage-like structure.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: Hydrogen fluoride is a strong acid. It is gas at room temperature and is supplied as a liquefied gas in the cylinders, and is also widely used in water solutions. Because of its high reactivity towards glass and moderate reactivity towards many metals, it is usually stored in plastic containers.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




