
Which of the sequences below is the best synthesis of (E)-3-hexene?
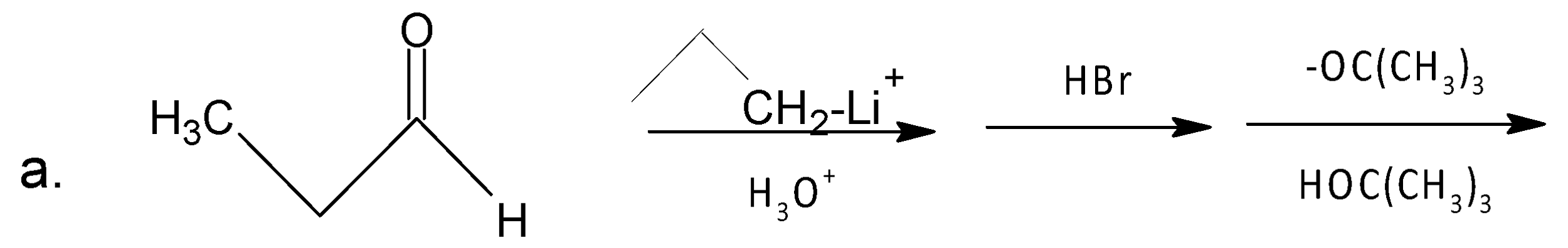
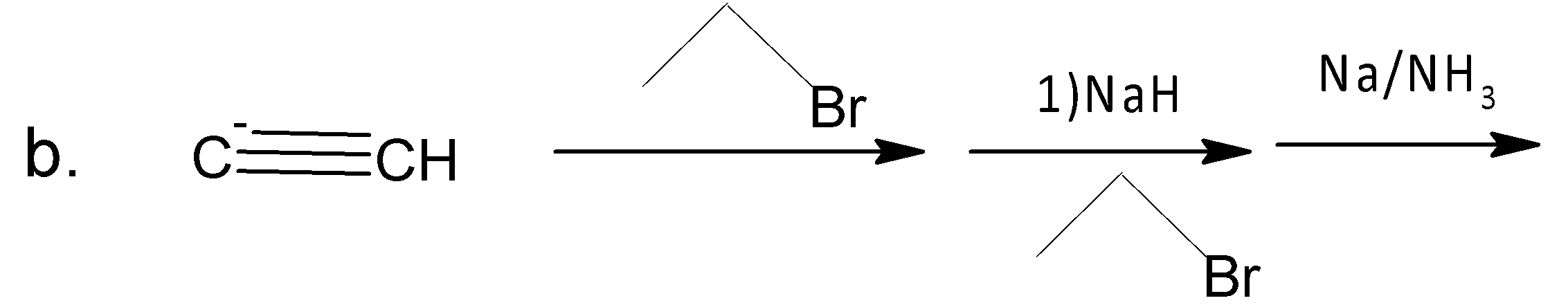
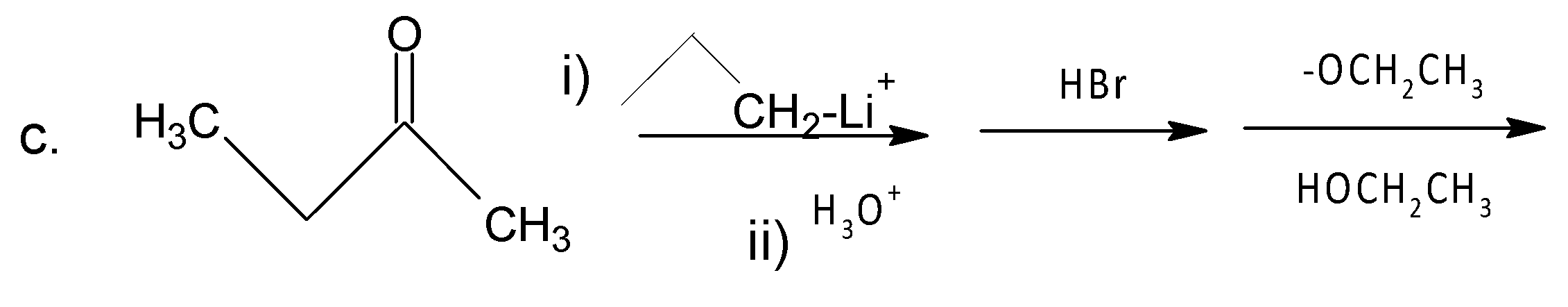
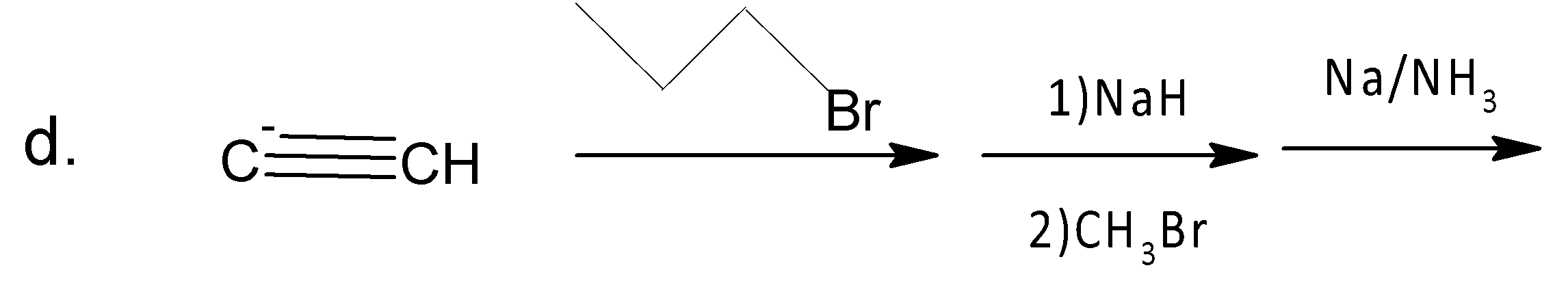
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Like alkene compounds, catalytic hydrogenation occurs in the case of alkyne compounds to cis-alkenes and trans-alkenes depending upon reaction conditions. In alkynes, anti-addition of hydrogen occurs in the presence of lithium or sodium metal dissolved in $N{{H}_{3}}$, resulting in a trans (E)-alkene.
Complete step by step solution:
For the synthesis of (E) alkene, metals like sodium, and lithium metal in liquid ammonia solution are used. In this case, an anti-addition of alkyne takes place and is reduced to trans alkene.
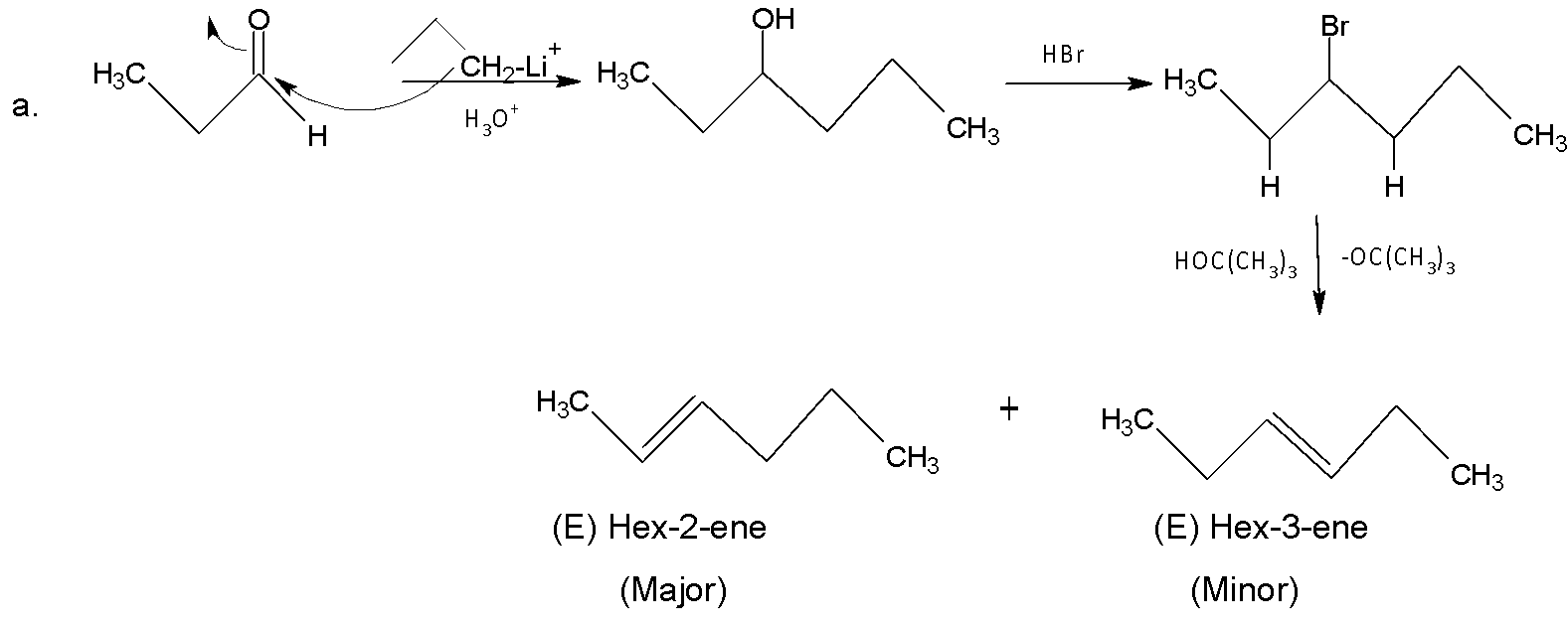
In the case of (a), alkyl lithium acts as a nucleophile, attacks carbonyl carbon, and gives an alcohol compound. Then after bromination, a bulky base${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C{{O}^{-}}$ abstracts ortho H with respect to leaving group, and two products are formed. Here (E)-2-Hexene is the major product (Hofmann product) due to the presence of
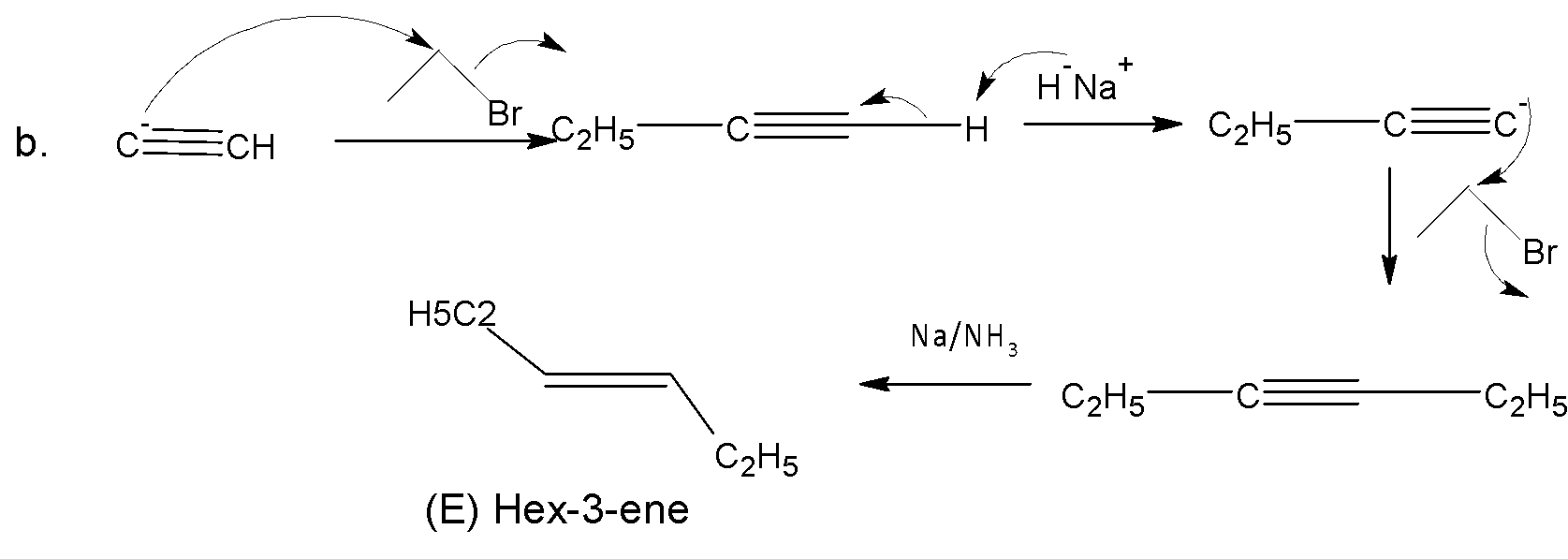
For b, ethyne anion attacks ethyl bromide by the ${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$reaction. Again a ${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$ reaction follows in the next step and finally (E) 3-Hexene is formed in presence of sodium in liquid ammonia.
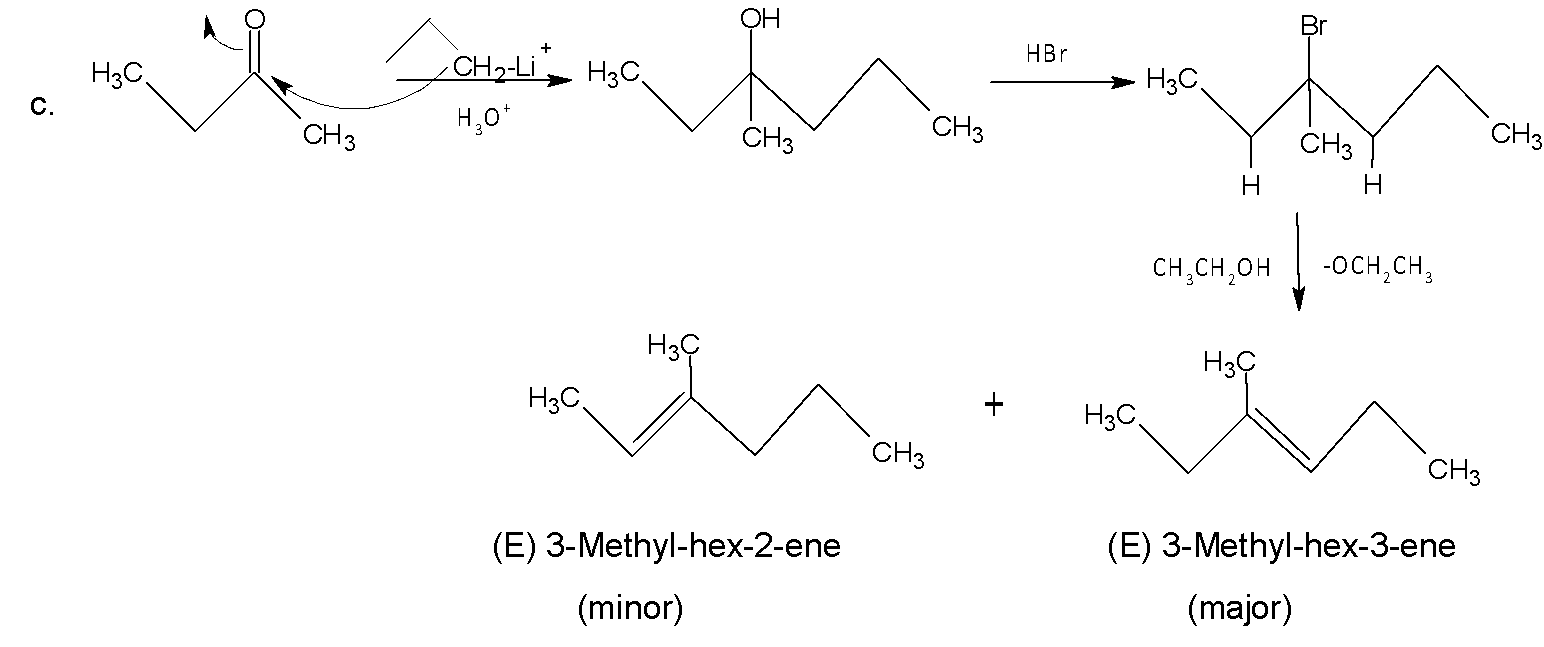
Like a, the same procedure follows for c and here (E) 3-Methyl-hex-3-ene is formed as a major product (Saytzeff’s product).
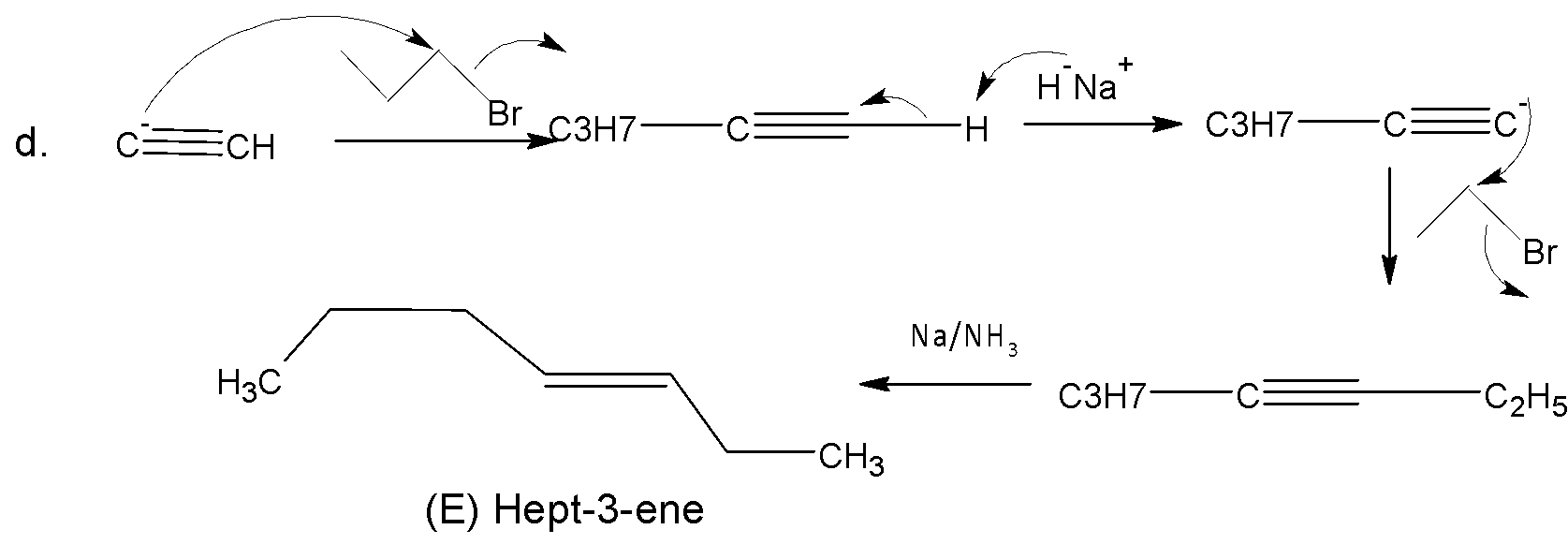
Like b, in (d) the same procedure follows in every step of the mechanism. Here the major product is (E) Hept-3-ene.
Thus, Option (B) is correct.
Note: Reduction of alkyne occurs also in presence of metal catalysts like Pt or Pd, but it gives alkane as the final product. It is impossible to stop the reduction of alkyne at equivalent addition and differentiate the required alkene. But by adding Pd/$CaC{{O}_{3}}$ mixture with $Pb{{(OAc)}_{2}}$ , quinoline, the further reduction of an alkene can be stopped for the desired product (Z)-alkene.
Complete step by step solution:
For the synthesis of (E) alkene, metals like sodium, and lithium metal in liquid ammonia solution are used. In this case, an anti-addition of alkyne takes place and is reduced to trans alkene.
In the case of (a), alkyl lithium acts as a nucleophile, attacks carbonyl carbon, and gives an alcohol compound. Then after bromination, a bulky base${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C{{O}^{-}}$ abstracts ortho H with respect to leaving group, and two products are formed. Here (E)-2-Hexene is the major product (Hofmann product) due to the presence of

For b, ethyne anion attacks ethyl bromide by the ${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$reaction. Again a ${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$ reaction follows in the next step and finally (E) 3-Hexene is formed in presence of sodium in liquid ammonia.

Like a, the same procedure follows for c and here (E) 3-Methyl-hex-3-ene is formed as a major product (Saytzeff’s product).

Like b, in (d) the same procedure follows in every step of the mechanism. Here the major product is (E) Hept-3-ene.

Thus, Option (B) is correct.
Note: Reduction of alkyne occurs also in presence of metal catalysts like Pt or Pd, but it gives alkane as the final product. It is impossible to stop the reduction of alkyne at equivalent addition and differentiate the required alkene. But by adding Pd/$CaC{{O}_{3}}$ mixture with $Pb{{(OAc)}_{2}}$ , quinoline, the further reduction of an alkene can be stopped for the desired product (Z)-alkene.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




